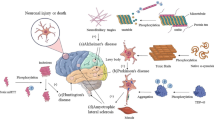
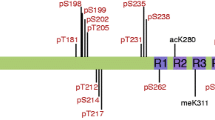
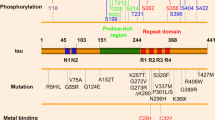
Abstract
Involving addition of chemical groups or protein units to specific residues of the target protein, post-translational modifications (PTMs) alter the charge, hydrophobicity, and conformation of a protein, which in tune influences protein function, protein − protein interaction, and protein aggregation. While the occurrence of PTMs is dynamic and subject to regulations, conformational disorder of the target protein facilitates PTMs. The microtubule-associated protein tau is a typical intrinsically disordered protein that undergoes a variety of PTMs including phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, methylation, and oxidation. Accumulated evidence shows that these PTMs play a critical role in regulating tau-microtubule interaction, tau localization, tau degradation and aggregation, and reinforces the correlation between tau PTMs and pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disease. Here, we review tau PTMs with an emphasis on their influence on tau structure. With available biophysical characterization results, we describe how PTMs induce conformational changes in tau monomer and regulate tau aggregation. Compared to functional analysis of tau PTMs, biophysical characterization of tau PTMs is lagging. While it is challenging, characterizing the specific effects of PTMs on tau conformation and interaction is indispensable to unravel the tau PTM code.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
All data analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abi Habib J, De Plaen E, Stroobant V, Zivkovic D, Bousquet MP, Guillaume B, Wahni K, Messens J, Busse A, Vigneron N et al (2020) Efficiency of the four proteasome subtypes to degrade ubiquitinated or oxidized proteins. Sci Rep 10:15765. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71550-5
Abreha MH, Dammer EB, Ping L, Zhang T, Duong DM, Gearing M, Lah JJ, Levey AI, Seyfried NT (2018) Quantitative analysis of the brain ubiquitylome in Alzheimer’s disease. Proteomics 18:e1800108. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201800108
Abreha MH, Ojelade S, Dammer EB, McEachin ZT, Duong DM, Gearing M, Bassell GJ, Lah JJ, Levey AI, Shulman JM et al (2021) TBK1 interacts with tau and enhances neurodegeneration in tauopathy. J Biol Chem 296:100760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100760
Ajit D, Trzeciakiewicz H, Tseng JH, Wander CM, Chen Y, Ajit A, King DP, Cohen TJ (2019) A unique tau conformation generated by an acetylation-mimic substitution modulates P301S-dependent tau pathology and hyperphosphorylation. J Biol Chem 294:16698–16711. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.009674
Akoury E, Pickhardt M, Gajda M, Biernat J, Mandelkow E, Zweckstetter M (2013) Mechanistic basis of phenothiazine-driven inhibition of tau aggregation. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 52:3511–3515. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201208290
Almansoub H, Tang H, Wu Y, Wang DQ, Mahaman YAR, Wei N, Almansob YAM, He W, Liu D (2019) Tau abnormalities and the potential therapy in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 67:13–33. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-180868
Alonso A, Zaidi T, Novak M, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (2001) Hyperphosphorylation induces self-assembly of tau into tangles of paired helical filaments/straight filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6923–6928. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.121119298
Alonso AD, Di Clerico J, Li B, Corbo CP, Alaniz ME, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (2010) Phosphorylation of tau at Thr212, Thr231, and Ser262 combined causes neurodegeneration. J Biol Chem 285:30851–30860. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.110957
Alquezar C, Arya S, Kao AW (2020) Tau post-translational modifications: dynamic transformers of tau function, degradation, and aggregation. Front Neurol 11:595532. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.595532
Amaral AC, Perez-Nievas BG, Siao Tick Chong M, Gonzalez-Martinez A, Argente-Escrig H, Rubio-Guerra S, Commins C, Muftu S, Eftekharzadeh B, Hudry E et al (2021) Isoform-selective decrease of glycogen synthase kinase-3-beta (GSK-3beta) reduces synaptic tau phosphorylation, transcellular spreading, and aggregation. iScience 24:102058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2021.102058
Ambadipudi S, Biernat J, Riedel D, Mandelkow E, Zweckstetter M (2017) Liquid-liquid phase separation of the microtubule-binding repeats of the Alzheimer-related protein tau. Nat Commun 8:275. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00480-0
Ambadipudi S, Reddy JG, Biernat J, Mandelkow E, Zweckstetter M (2019) Residue-specific identification of phase separation hot spots of Alzheimer’s-related protein tau. Chem Sci 10:6503–6507. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9sc00531e
Arakhamia T, Lee CE, Carlomagno Y, Duong DM, Kundinger SR, Wang K, Williams D, DeTure M, Dickson DW, Cook CN et al (2020) Posttranslational modifications mediate the structural diversity of tauopathy strains. Cell 180:633–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.01.027
Areche C, Zapata F, Gonzalez M, Diaz E, Montecinos R, Hernandez M, Melo F, Cornejo A (2019) Anthraquinone derivative reduces tau oligomer progression by inhibiting cysteine-cysteine interaction. ChemistryOpen 8:554–559. https://doi.org/10.1002/open.201800222
Arnold CS, Johnson GV, Cole RN, Dong DL, Lee M, Hart GW (1996) The microtubule-associated protein tau is extensively modified with O-linked N-acetylglucosamine. J Biol Chem 271:28741–28744. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.271.46.28741
Ash PEA, Lei S, Shattuck J, Boudeau S, Carlomagno Y, Medalla M, Mashimo BL, Socorro G, Al-Mohanna LFA, Jiang L et al (2021) TIA1 potentiates tau phase separation and promotes generation of toxic oligomeric tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 118:e2014188118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2014188118
Augustinack JC, Schneider A, Mandelkow EM, Hyman BT (2002) Specific tau phosphorylation sites correlate with severity of neuronal cytopathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 103:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010100423
Babinchak WM, Dumm BK, Venus S, Boyko S, Putnam AA, Jankowsky E, Surewicz WK (2020) Small molecules as potent biphasic modulators of protein liquid-liquid phase separation. Nat Commun 11:5574. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-19211-z
Babu JR, Geetha T, Wooten MW (2005) Sequestosome 1/p62 shuttles polyubiquitinated tau for proteasomal degradation. J Neurochem 94:192–203. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03181.x
Bailey RM, Covy JP, Melrose HL, Rousseau L, Watkinson R, Knight J, Miles S, Farrer MJ, Dickson DW, Giasson BI et al (2013) LRRK2 phosphorylates novel tau epitopes and promotes tauopathy. Acta Neuropathol 126:809–827. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1188-4
Bancher C, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Fried VA, Smith HT, Wisniewski HM (1991) Abnormal phosphorylation of tau precedes ubiquitination in neurofibrillary pathology of Alzheimer disease. Brain Res 539:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(91)90681-k
Barbier P, Zejneli O, Martinho M, Lasorsa A, Belle V, Smet-Nocca C, Tsvetkov PO, Devred F, Landrieu I (2019) Role of tau as a microtubule-associated protein: structural and functional aspects. Front Aging Neurosci 11:204. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2019.00204
Barghorn S, Davies P, Mandelkow E (2004) Tau paired helical filaments from Alzheimer’s disease brain and assembled in vitro are based on beta-structure in the core domain. Biochemistry 43:1694–1703. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0357006
Barghorn S, Mandelkow E (2002) Toward a unified scheme for the aggregation of tau into Alzheimer paired helical filaments. Biochemistry 41:14885–14896. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi026469j
Barthelemy NR, Li Y, Joseph-Mathurin N, Gordon BA, Hassenstab J, Benzinger TLS, Buckles V, Fagan AM, Perrin RJ, Goate AM et al (2020) A soluble phosphorylated tau signature links tau, amyloid and the evolution of stages of dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med 26:398–407. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0781-z
Beharry C, Cohen LS, Di J, Ibrahim K, Briffa-Mirabella S, Alonso Adel C (2014) Tau-induced neurodegeneration: mechanisms and targets. Neurosci Bull 30:346–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-013-1414-z
Berger Z, Roder H, Hanna A, Carlson A, Rangachari V, Yue M, Wszolek Z, Ashe K, Knight J, Dickson D et al (2007) Accumulation of pathological tau species and memory loss in a conditional model of tauopathy. J Neurosci 27:3650–3662. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0587-07.2007
Berriman J, Serpell LC, Oberg KA, Fink AL, Goedert M, Crowther RA (2003) Tau filaments from human brain and from in vitro assembly of recombinant protein show cross-β structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:9034–9038. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1530287100
Berry RW, Abraha A, Lagalwar S, LaPointe N, Gamblin TC, Cryns VL, Binder LI (2003) Inhibition of tau polymerization by its carboxy-terminal caspase cleavage fragment. Biochemistry 42:8325–8331. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi027348m
Bibow S, Mukrasch MD, Chinnathambi S, Biernat J, Griesinger C, Mandelkow E, Zweckstetter M (2011a) The dynamic structure of filamentous tau. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 50:11520–11524. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201105493
Bibow S, Ozenne V, Biernat J, Blackledge M, Mandelkow E, Zweckstetter M (2011b) Structural impact of proline-directed pseudophosphorylation at AT8, AT100, and PHF1 epitopes on 441-residue tau. J Am Chem Soc 133:15842–15845. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja205836j
Bichmann M, Prat Oriol N, Ercan-Herbst E, Schondorf DC, Gomez Ramos B, Schwarzler V, Neu M, Schluter A, Wang X, Jin L et al (2021) SETD7-mediated monomethylation is enriched on soluble tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 16:46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-021-00468-x
Boyko S, Qi X, Chen TH, Surewicz K, Surewicz WK (2019) Liquid-liquid phase separation of tau protein: the crucial role of electrostatic interactions. J Biol Chem 294:11054–11059. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.AC119.009198
Boyko S, Surewicz K, Surewicz WK (2020) Regulatory mechanisms of tau protein fibrillation under the conditions of liquid-liquid phase separation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117:31882–31890. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2012460117
Bruch J, Xu H, De Andrade A, Hoglinger G (2014) Mitochondrial complex 1 inhibition increases 4-repeat isoform tau by SRSF2 upregulation. PLoS One 9:e113070. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0113070
Caballero B, Bourdenx M, Luengo E, Diaz A, Sohn PD, Chen X, Wang C, Juste YR, Wegmann S, Patel B et al (2021) Acetylated tau inhibits chaperone-mediated autophagy and promotes tau pathology propagation in mice. Nat Commun 12:2238. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-22501-9
Cantrelle FX, Loyens A, Trivelli X, Reimann O, Despres C, Gandhi NS, Hackenberger CPR, Landrieu I, Smet-Nocca C (2021) Phosphorylation and O-GlcNAcylation of the PHF-1 epitope of tau protein induce local conformational changes of the C-terminus and modulate tau self-assembly into fibrillar aggregates. Front Mol Neurosci 14:661368. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2021.661368
Cardenas-Aguayo Mdel C, Gomez-Virgilio L, DeRosa S, Meraz-Rios MA (2014) The role of tau oligomers in the onset of Alzheimer’s disease neuropathology. ACS Chem Neurosci 5:1178–1191. https://doi.org/10.1021/cn500148z
Carlomagno Y, Chung DC, Yue M, Castanedes-Casey M, Madden BJ, Dunmore J, Tong J, DeTure M, Dickson DW, Petrucelli L et al (2017) An acetylation-phosphorylation switch that regulates tau aggregation propensity and function. J Biol Chem 292:15277–15286. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.794602
Carroll T, Guha S, Nehrke K, Johnson GVW (2021) Tau post-translational modifications: potentiators of selective vulnerability in sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. Biology (basel) 10:1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10101047
Castillo-Carranza DL, Sengupta U, Guerrero-Munoz MJ, Lasagna-Reeves CA, Gerson JE, Singh G, Estes DM, Barrett AD, Dineley KT, Jackson GR et al (2014) Passive immunization with tau oligomer monoclonal antibody reverses tauopathy phenotypes without affecting hyperphosphorylated neurofibrillary tangles. J Neurosci 34:4260–4272. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3192-13.2014
Chang E, Kim S, Schafer KN, Kuret J (2011) Pseudophosphorylation of tau protein directly modulates its aggregation kinetics. Biochim Biophys Acta 1814:388–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.10.005
Chen D, Drombosky KW, Hou Z, Sari L, Kashmer OM, Ryder BD, Perez VA, Woodard DR, Lin MM, Diamond MI et al (2019) Tau local structure shields an amyloid-forming motif and controls aggregation propensity. Nat Commun 10:2493. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10355-1
Chen H, Liu S, Li S, Chen J, Ni J, Liu Q (2018) Blocking the thiol at cysteine-322 destabilizes tau protein and prevents its oligomer formation. ACS Chem Neurosci 9:1560–1565. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00003
Chidambaram H, Chinnathambi S (2021) Role of cysteines in accelerating tau filament formation. J Biomol Struct Dyn:In press. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2020.1856720
Chu D, Liu F (2019) Pathological changes of tau related to Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Chem Neurosci 10:931–944. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00457
Chu TT, Gao N, Li QQ, Chen PG, Yang XF, Chen YX, Zhao YF, Li YM (2016) Specific knockdown of endogenous tau protein by peptide-directed ubiquitin-proteasome degradation. Cell Chem Biol 23:453–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2016.02.016
Cohen TJ, Friedmann D, Hwang AW, Marmorstein R, Lee VM (2013) The microtubule-associated tau protein has intrinsic acetyltransferase activity. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20:756–762. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2555
Cohen TJ, Guo JL, Hurtado DE, Kwong LK, Mills IP, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2011) The acetylation of tau inhibits its function and promotes pathological tau aggregation. Nat Commun 2:252. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1255
Cook C, Carlomagno Y, Gendron TF, Dunmore J, Scheffel K, Stetler C, Davis M, Dickson D, Jarpe M, DeTure M et al (2014a) Acetylation of the KXGS motifs in tau is a critical determinant in modulation of tau aggregation and clearance. Hum Mol Genet 23:104–116. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddt402
Cook C, Stankowski JN, Carlomagno Y, Stetler C, Petrucelli L (2014b) Acetylation: a new key to unlock tau’s role in neurodegeneration. Alzheimers Res Ther 6:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/alzrt259
Couchie D, Mavilia C, Georgieff IS, Liem RK, Shelanski ML, Nunez J (1992) Primary structure of high molecular weight tau present in the peripheral nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:4378–4381. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.89.10.4378
Cowan CM, Mudher A (2013) Are tau aggregates toxic or protective in tauopathies? Front Neurol 4:114. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2013.00114
Cripps D, Thomas SN, Jeng Y, Yang F, Davies P, Yang AJ (2006) Alzheimer disease-specific conformation of hyperphosphorylated paired helical filament-tau is polyubiquitinated through Lys-48, Lys-11, and Lys-6 ubiquitin conjugation. J Biol Chem 281:10825–10838. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M512786200
Crowe A, James MJ, Lee VM, Smith AB 3rd, Trojanowski JQ, Ballatore C, Brunden KR (2013) Aminothienopyridazines and methylene blue affect tau fibrillization via cysteine oxidation. J Biol Chem 288:11024–11037. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.436006
Dai B, Zhong T, Chen ZX, Chen W, Zhang N, Liu XL, Wang LQ, Chen J, Liang Y (2021) Myricetin slows liquid-liquid phase separation of tau and activates ATG5-dependent autophagy to suppress Tau toxicity. J Biol Chem 297:101222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101222
Das RK, Pappu RV (2013) Conformations of intrinsically disordered proteins are influenced by linear sequence distributions of oppositely charged residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:13392–13397. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1304749110
David DC, Layfield R, Serpell L, Narain Y, Goedert M, Spillantini MG (2002) Proteasomal degradation of tau protein. J Neurochem 83:176–185. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2002.01137.x
Despres C, Byrne C, Qi H, Cantrelle FX, Huvent I, Chambraud B, Baulieu EE, Jacquot Y, Landrieu I, Lippens G et al (2017) Identification of the tau phosphorylation pattern that drives its aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:9080–9085. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1708448114
Devitt G, Crisford A, Rice W, Weismiller HA, Fan Z, Commins C, Hyman BT, Margittai M, Mahajan S, Mudher A (2021) Conformational fingerprinting of tau variants and strains by Raman spectroscopy. RSC Adv 11:8899–8915. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra00870f
Dickey CA, Yue M, Lin WL, Dickson DW, Dunmore JH, Lee WC, Zehr C, West G, Cao S, Clark AM et al (2006) Deletion of the ubiquitin ligase CHIP leads to the accumulation, but not the aggregation, of both endogenous phospho- and caspase-3-cleaved tau species. J Neurosci 26:6985–6996. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0746-06.2006
Didonna A, Canto E, Shams H, Isobe N, Zhao C, Caillier SJ, Condello C, Yamate-Morgan H, Tiwari-Woodruff SK, Mofrad MRK et al (2019) Sex-specific tau methylation patterns and synaptic transcriptional alterations are associated with neural vulnerability during chronic neuroinflammation. J Autoimmun 101:56–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2019.04.003
Dorval V, Fraser PE (2006) Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) modification of natively unfolded proteins tau and alpha-synuclein. J Biol Chem 281:9919–9924. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M510127200
Drepper F, Biernat J, Kaniyappan S, Meyer HE, Mandelkow EM, Warscheid B, Mandelkow E (2020) A combinatorial native MS and LC-MS/MS approach reveals high intrinsic phosphorylation of human tau but minimal levels of other key modifications. J Biol Chem 295:18213–18225. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.015882
Duka V, Lee JH, Credle J, Wills J, Oaks A, Smolinsky C, Shah K, Mash DC, Masliah E, Sidhu A (2013) Identification of the sites of tau hyperphosphorylation and activation of tau kinases in synucleinopathies and Alzheimer’s diseases. PLoS One 8:e75025. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075025
Ercan-Herbst E, Ehrig J, Schondorf DC, Behrendt A, Klaus B, Gomez Ramos B, Prat Oriol N, Weber C, Ehrnhoefer DE (2019) A post-translational modification signature defines changes in soluble tau correlating with oligomerization in early stage Alzheimer’s disease brain. Acta Neuropathol Commun 7:192. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-019-0823-2
Falcon B, Zhang W, Murzin AG, Murshudov G, Garringer HJ, Vidal R, Crowther RA, Ghetti B, Scheres SHW, Goedert M (2018a) Structures of filaments from Pick’s disease reveal a novel tau protein fold. Nature 561:137–140. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0454-y
Falcon B, Zhang W, Schweighauser M, Murzin AG, Vidal R, Garringer HJ, Ghetti B, Scheres SHW, Goedert M (2018b) Tau filaments from multiple cases of sporadic and inherited Alzheimer’s disease adopt a common fold. Acta Neuropathol 136:699–708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-018-1914-z
Falcon B, Zivanov J, Zhang W, Murzin AG, Garringer HJ, Vidal R, Crowther RA, Newell KL, Ghetti B, Goedert M et al (2019) Novel tau filament fold in chronic traumatic encephalopathy encloses hydrophobic molecules. Nature 568:420–423. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1026-5
Feinstein HE, Benbow SJ, LaPointe NE, Patel N, Ramachandran S, Do TD, Gaylord MR, Huskey NE, Dressler N, Korff M et al (2016) Oligomerization of the microtubule-associated protein tau is mediated by its N-terminal sequences: implications for normal and pathological tau action. J Neurochem 137:939–954. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13604
Ferreon JC, Jain A, Choi KJ, Tsoi PS, MacKenzie KR, Jung SY, Ferreon AC (2018) Acetylation disfavors tau phase separation. Int J Mol Sci 19:1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051360
Fichou Y, Oberholtzer ZR, Ngo H, Cheng CY, Keller TJ, Eschmann NA, Han S (2019) Tau-cofactor complexes as building blocks of tau fibrils. Front Neurosci 13:1339. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.01339
Fitzpatrick AWP, Falcon B, He S, Murzin AG, Murshudov G, Garringer HJ, Crowther RA, Ghetti B, Goedert M, Scheres SHW (2017) Cryo-EM structures of tau filaments from Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 547:185–190. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23002
Flach K, Ramminger E, Hilbrich I, Arsalan-Werner A, Albrecht F, Herrmann L, Goedert M, Arendt T, Holzer M (2014) Axotrophin/MARCH7 acts as an E3 ubiquitin ligase and ubiquitinates tau protein in vitro impairing microtubule binding. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842:1527–1538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.05.029
Foote AK, Manger LH, Holden MR, Margittai M, Goldsmith RH (2019) Time-resolved multirotational dynamics of single solution-phase tau proteins reveals details of conformational variation. Phys Chem Chem Phys 21:1863–1871. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cp06971a
Friedhoff P, von Bergen M, Mandelkow EM, Davies P, Mandelkow E (1998) A nucleated assembly mechanism of Alzheimer paired helical filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15712–15717. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.26.15712
Funk KE, Thomas SN, Schafer KN, Cooper GL, Liao Z, Clark DJ, Yang AJ, Kuret J (2014) Lysine methylation is an endogenous post-translational modification of tau protein in human brain and a modulator of aggregation propensity. Biochem J 462:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20140372
Furukawa Y, Kaneko K, Nukina N (2011) Tau protein assembles into isoform- and disulfide-dependent polymorphic fibrils with distinct structural properties. J Biol Chem 286:27236–27246. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.248963
Ghetti B, Oblak AL, Boeve BF, Johnson KA, Dickerson BC, Goedert M (2015) Invited review: Frontotemporal dementia caused by microtubule-associated protein tau gene (MAPT) mutations: a chameleon for neuropathology and neuroimaging. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 41:24–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12213
Gibb GM, Pearce J, Betts JC, Lovestone S, Hoffmann MM, Maerz W, Blackstock WP, Anderton BH (2000) Differential effects of apolipoprotein E isoforms on phosphorylation at specific sites on tau by glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta identified by nano-electrospray mass spectrometry. FEBS Lett 485:99–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(00)02196-7
Goedert M (2005) Tau gene mutations and their effects. Mov Disord 20(Suppl 12):S45-52. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20539
Goedert M, Eisenberg DS, Crowther RA (2017) Propagation of tau aggregates and neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Neurosci 40:189–210. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-072116-031153
Goedert M, Jakes R (1990) Expression of separate isoforms of human tau protein: correlation with the tau pattern in brain and effects on tubulin polymerization. EMBO J 9:4225–4230
Goedert M, Spillantini MG (2019) Ordered assembly of tau protein and neurodegeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol 1184:3–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-32-9358-8_1
Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Crowther RA (1992) Cloning of a big tau microtubule-associated protein characteristic of the peripheral nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:1983–1987. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.89.5.1983
Gong CX, Liu F, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (2005) Post-translational modifications of tau protein in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm (vienna) 112:813–838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-004-0221-0
Gong CX, Liu F, Iqbal K (2016) O-GlcNAcylation: a regulator of tau pathology and neurodegeneration. Alzheimers Dement 12:1078–1089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2016.02.011
Gorsky MK, Burnouf S, Dols J, Mandelkow E, Partridge L (2016) Acetylation mimic of lysine 280 exacerbates human tau neurotoxicity in vivo. Sci Rep 6:22685. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22685
Gorsky MK, Burnouf S, Sofola-Adesakin O, Dols J, Augustin H, Weigelt CM, Gronke S, Partridge L (2017) Pseudo-acetylation of multiple sites on human tau proteins alters tau phosphorylation and microtubule binding, and ameliorates amyloid beta toxicity. Sci Rep 7:9984. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10225-0
Grune T, Botzen D, Engels M, Voss P, Kaiser B, Jung T, Grimm S, Ermak G, Davies KJ (2010) Tau protein degradation is catalyzed by the ATP/ubiquitin-independent 20S proteasome under normal cell conditions. Arch Biochem Biophys 500:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2010.05.008
Gu J, Xu W, Jin N, Li L, Zhou Y, Chu D, Gong CX, Iqbal K, Liu F (2020) Truncation of tau selectively facilitates its pathological activities. J Biol Chem 295:13812–13828. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.012587
Haj-Yahya M, Gopinath P, Rajasekhar K, Mirbaha H, Diamond MI, Lashuel HA (2020) Site-specific hyperphosphorylation inhibits, rather than promotes, tau fibrillization, seeding capacity, and its microtubule binding. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 59:4059–4067. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201913001
Haj-Yahya M, Lashuel HA (2018) Protein semisynthesis provides access to tau disease-associated post-translational modifications (PTMs) and paves the way to deciphering the tau PTM code in health and diseased states. J Am Chem Soc 140:6611–6621. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b02668
Hanger DP, Anderton BH, Noble W (2009) Tau phosphorylation: the therapeutic challenge for neurodegenerative disease. Trends Mol Med 15:112–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2009.01.003
Hasegawa M, Smith MJ, Goedert M (1998) Tau proteins with FTDP-17 mutations have a reduced ability to promote microtubule assembly. FEBS Lett 437:207–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(98)01217-4
Haukedal H, Freude KK (2020) Implications of glycosylation in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurosci 14:625348. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.625348
Hernandez-Vega A, Braun M, Scharrel L, Jahnel M, Wegmann S, Hyman BT, Alberti S, Diez S, Hyman AA (2017) Local nucleation of microtubule bundles through tubulin concentration into a condensed tau phase. Cell Rep 20:2304–2312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.08.042
Hernandez F, Merchan-Rubira J, Valles-Saiz L, Rodriguez-Matellan A, Avila J (2020) Differences between human and murine tau at the N-terminal end. Front Aging Neurosci 12:11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2020.00011
Hong M, Zhukareva V, Vogelsberg-Ragaglia V, Wszolek Z, Reed L, Miller BI, Geschwind DH, Bird TD, McKeel D, Goate A et al (1998) Mutation-specific functional impairments in distinct tau isoforms of hereditary FTDP-17. Science 282:1914–1917. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.282.5395.1914
Horowitz PM, LaPointe N, Guillozet-Bongaarts AL, Berry RW, Binder LI (2006) N-terminal fragments of tau inhibit full-length tau polymerization in vitro. Biochemistry 45:12859–12866. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi061325g
Huseby CJ, Hoffman CN, Cooper GL, Cocuron JC, Alonso AP, Thomas SN, Yang AJ, Kuret J (2019) Quantification of tau protein lysine methylation in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 71:979–991. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-190604
Iqbal K, Liu F, Gong CX (2016) Tau and neurodegenerative disease: the story so far. Nat Rev Neurol 12:15–27. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2015.225
Irwin DJ, Cohen TJ, Grossman M, Arnold SE, McCarty-Wood E, Van Deerlin VM, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2013) Acetylated tau neuropathology in sporadic and hereditary tauopathies. Am J Pathol 183:344–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.04.025
Irwin DJ, Cohen TJ, Grossman M, Arnold SE, Xie SX, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2012) Acetylated tau, a novel pathological signature in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies. Brain 135:807–818. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws013
Jakes R, Novak M, Davison M, Wischik CM (1991) Identification of 3- and 4-repeat tau isoforms within the PHF in Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO J 10:2725–2729
Jeganathan S, Hascher A, Chinnathambi S, Biernat J, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (2008) Proline-directed pseudo-phosphorylation at AT8 and PHF1 epitopes induces a compaction of the paperclip folding of tau and generates a pathological (MC-1) conformation. J Biol Chem 283:32066–32076. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M805300200
Jeganathan S, von Bergen M, Brutlach H, Steinhoff HJ, Mandelkow E (2006) Global hairpin folding of tau in solution. Biochemistry 45:2283–2293. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0521543
Kadavath H, Cabrales Fontela Y, Jaremko M, Jaremko L, Overkamp K, Biernat J, Mandelkow E, Zweckstetter M (2018) The binding mode of a tau peptide with tubulin. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 57:3246–3250. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201712089
Kamah A, Huvent I, Cantrelle FX, Qi H, Lippens G, Landrieu I, Smet-Nocca C (2014) Nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of the acetylation pattern of the neuronal tau protein. Biochemistry 53:3020–3032. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi500006v
Kametani F, Yoshida M, Matsubara T, Murayama S, Saito Y, Kawakami I, Onaya M, Tanaka H, Kakita A, Robinson AC et al (2020) Comparison of common and disease-specific post-translational modifications of pathological tau associated with a wide range of tauopathies. Front Neurosci 14:581936. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.581936
Kanaan NM, Hamel C, Grabinski T, Combs B (2020) Liquid-liquid phase separation induces pathogenic tau conformations in vitro. Nat Commun 11:2809. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16580-3
Kang SG, Han ZZ, Daude N, McNamara E, Wohlgemuth S, Molina-Porcel L, Safar JG, Mok SA, Westaway D (2021) Pathologic tau conformer ensembles induce dynamic, liquid-liquid phase separation events at the nuclear envelope. BMC Biol 19:199. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-021-01132-y
Kaniyappan S, Chandupatla RR, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (2017) Extracellular low-n oligomers of tau cause selective synaptotoxicity without affecting cell viability. Alzheimers Dement 13:1270–1291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2017.04.002
Kellogg EH, Hejab NMA, Poepsel S, Downing KH, DiMaio F, Nogales E (2018) Near-atomic model of microtubule-tau interactions. Science 360:1242–1246. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aat1780
Keramidis I, Vourkou E, Papanikolopoulou K, Skoulakis EMC (2020) Functional interactions of tau phosphorylation sites that mediate toxicity and deficient learning in Drosophila melanogaster. Front Mol Neurosci 13:569520. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2020.569520
Kim D, Lim S, Haque MM, Ryoo N, Hong HS, Rhim H, Lee DE, Chang YT, Lee JS, Cheong E et al (2015) Identification of disulfide cross-linked tau dimer responsible for tau propagation. Sci Rep 5:15231. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15231
Kim GW, Yang XJ (2011) Comprehensive lysine acetylomes emerging from bacteria to humans. Trends Biochem Sci 36:211–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2010.10.001
Kim JH, Lee J, Choi WH, Park S, Park SH, Lee JH, Lim SM, Mun JY, Cho HS, Han D et al (2021) CHIP-mediated hyperubiquitylation of tau promotes its self-assembly into the insoluble tau filaments. Chem Sci 12:5599–5610. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1sc00586c
Kontaxi C, Piccardo P, Gill AC (2017) Lysine-directed post-translational modifications of tau protein in Alzheimer’s disease and related tauopathies. Front Mol Biosci 4:56. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2017.00056
Kovacs GG (2015) Invited review: neuropathology of tauopathies: principles and practice. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 41:3–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12208
Kumar H, Udgaonkar JB (2021) The Lys 280 –> Gln mutation mimicking disease-linked acetylation of Lys 280 in tau extends the structural core of fibrils and modulates their catalytic properties. Protein Sci 30:785–803. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.4030
Kumar S, Tepper K, Kaniyappan S, Biernat J, Wegmann S, Mandelkow EM, Muller DJ, Mandelkow E (2014) Stages and conformations of the tau repeat domain during aggregation and its effect on neuronal toxicity. J Biol Chem 289:20318–20332. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.554725
Lasagna-Reeves CA, Castillo-Carranza DL, Guerrero-Muoz MJ, Jackson GR, Kayed R (2010) Preparation and characterization of neurotoxic tau oligomers. Biochemistry 49:10039–10041. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi1016233
Lasagna-Reeves CA, Castillo-Carranza DL, Sengupta U, Clos AL, Jackson GR, Kayed R (2011) Tau oligomers impair memory and induce synaptic and mitochondrial dysfunction in wild-type mice. Mol Neurodegener 6:39. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-6-39
Lasagna-Reeves CA, Castillo-Carranza DL, Sengupta U, Sarmiento J, Troncoso J, Jackson GR, Kayed R (2012) Identification of oligomers at early stages of tau aggregation in Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J 26:1946–1959. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.11-199851
Lee G, Newman ST, Gard DL, Band H, Panchamoorthy G (1998) Tau interacts with src-family non-receptor tyrosine kinases. J Cell Sci 111(Pt 21):3167–3177
Lee VM, Goedert M, Trojanowski JQ (2001) Neurodegenerative tauopathies. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:1121–1159. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.1121
Lin Y, Fichou Y, Longhini AP, Llanes LC, Yin P, Bazan GC, Kosik KS, Han S (2021) Liquid-liquid phase separation of tau driven by hydrophobic interaction facilitates fibrillization of tau. J Mol Biol 433:166731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2020.166731
Lin Y, Fichou Y, Zeng Z, Hu NY, Han S (2020) Electrostatically driven complex coacervation and amyloid aggregation of tau are independent processes with overlapping conditions. ACS Chem Neurosci 11:615–627. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00627
Lin Y, McCarty J, Rauch JN, Delaney KT, Kosik KS, Fredrickson GH, Shea JE, Han S (2019) Narrow equilibrium window for complex coacervation of tau and RNA under cellular conditions. Elife 8:e42571. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42571
Liu C, Song X, Nisbet R, Gotz J (2016) Co-immunoprecipitation with tau isoform-specific antibodies reveals distinct protein interactions and highlights a putative role for 2N tau in disease. J Biol Chem 291:8173–8188. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.641902
Liu F, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Hart GW, Gong CX (2004) O-GlcNAcylation regulates phosphorylation of tau: a mechanism involved in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:10804–10809. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0400348101
Liu F, Li B, Tung EJ, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Gong CX (2007) Site-specific effects of tau phosphorylation on its microtubule assembly activity and self-aggregation. Eur J Neurosci 26:3429–3436. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05955.x
Liu F, Zaidi T, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Merkle RK, Gong CX (2002) Role of glycosylation in hyperphosphorylation of tau in Alzheimer’s disease. FEBS Lett 512:101–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(02)02228-7
Liu M, Sui D, Dexheimer T, Hovde S, Deng X, Wang KW, Lin HL, Chien HT, Kweon HK, Kuo NS et al (2020) Hyperphosphorylation renders tau prone to aggregate and to cause cell death. Mol Neurobiol 57:4704–4719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-02034-w
Losev Y, Frenkel-Pinter M, Abu-Hussien M, Viswanathan GK, Elyashiv-Revivo D, Geries R, Khalaila I, Gazit E, Segal D (2021) Differential effects of putative N-glycosylation sites in human tau on Alzheimer’s disease-related neurodegeneration. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences : CMLS 78:2231–2245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03643-3
Losev Y, Paul A, Frenkel-Pinter M, Abu-Hussein M, Khalaila I, Gazit E, Segal D (2019) Novel model of secreted human tau protein reveals the impact of the abnormal N-glycosylation of tau on its aggregation propensity. Sci Rep 9:2254. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-39218-x
Luo HB, Xia YY, Shu XJ, Liu ZC, Feng Y, Liu XH, Yu G, Yin G, Xiong YS, Zeng K et al (2014a) SUMOylation at K340 inhibits tau degradation through deregulating its phosphorylation and ubiquitination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:16586–16591. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1417548111
Luo Y, Ma BY, Nussinov R, Wei GH (2014b) Structural insight into tau protein’s paradox of intrinsically disordered behavior, self-acetylation activity, and aggregation. J Phys Chem Lett 5:3026–3031. https://doi.org/10.1021/jz501457f
Lyu C, Da Vela S, Al-Hilaly Y, Marshall KE, Thorogate R, Svergun D, Serpell LC, Pastore A, Hanger DP (2021) The disease associated tau35 fragment has an increased propensity to aggregate compared to full-length tau. Front Mol Biosci 8:779240. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2021.779240
Maeda S, Sahara N, Saito Y, Murayama M, Yoshiike Y, Kim H, Miyasaka T, Murayama S, Ikai A, Takashima A (2007) Granular tau oligomers as intermediates of tau filaments. Biochemistry 46:3856–3861. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi061359o
Majumdar A, Dogra P, Maity S, Mukhopadhyay S (2019) Liquid-liquid phase separation is driven by large-scale conformational unwinding and fluctuations of intrinsically disordered protein molecules. J Phys Chem Lett 10:3929–3936. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b01731
Manger LH, Foote AK, Wood SL, Holden MR, Heylman KD, Margittai M, Goldsmith RH (2017) Revealing conformational variants of solution-phase intrinsically disordered tau protein at the single-molecule level. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56:15584–15588. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201708242
McKibben KM, Rhoades E (2019) Independent tubulin binding and polymerization by the proline-rich region of tau is regulated by tau’s N-terminal domain. J Biol Chem 294:19381–19394. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.010172
Min SW, Chen X, Tracy TE, Li Y, Zhou Y, Wang C, Shirakawa K, Minami SS, Defensor E, Mok SA et al (2015) Critical role of acetylation in tau-mediated neurodegeneration and cognitive deficits. Nat Med 21:1154–1162. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3951
Min SW, Cho SH, Zhou Y, Schroeder S, Haroutunian V, Seeley WW, Huang EJ, Shen Y, Masliah E, Mukherjee C et al (2010) Acetylation of tau inhibits its degradation and contributes to tauopathy. Neuron 67:953–966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2010.08.044
Mirbaha H, Chen D, Morazova OA, Ruff KM, Sharma AM, Liu X, Goodarzi M, Pappu RV, Colby DW, Mirzaei H et al (2018) Inert and seed-competent tau monomers suggest structural origins of aggregation. Elife 7:e36584. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.36584
Morishima-Kawashima M, Hasegawa M, Takio K, Suzuki M, Titani K, Ihara Y (1993) Ubiquitin is conjugated with amino-terminally processed tau in paired helical filaments. Neuron 10:1151–1160. https://doi.org/10.1016/0896-6273(93)90063-w
Morris M, Knudsen GM, Maeda S, Trinidad JC, Ioanoviciu A, Burlingame AL, Mucke L (2015) Tau post-translational modifications in wild-type and human amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. Nat Neurosci 18:1183–1189. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4067
Moschner K, Sundermann F, Meyer H, da Graca AP, Appel N, Paululat A, Bakota L, Brandt R (2014) RNA protein granules modulate tau isoform expression and induce neuronal sprouting. J Biol Chem 289:16814–16825. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.541425
Mukrasch MD, Bibow S, Korukottu J, Jeganathan S, Biernat J, Griesinger C, Mandelkow E, Zweckstetter M (2009) Structural polymorphism of 441-residue tau at single residue resolution. PLoS Biol 7:e34. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1000034
Mukrasch MD, Markwick P, Biernat J, Bergen M, Bernado P, Griesinger C, Mandelkow E, Zweckstetter M, Blackledge M (2007) Highly populated turn conformations in natively unfolded tau protein identified from residual dipolar couplings and molecular simulation. J Am Chem Soc 129:5235–5243. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0690159
Munari F, Barracchia CG, Franchin C, Parolini F, Capaldi S, Romeo A, Bubacco L, Assfalg M, Arrigoni G, D’Onofrio M (2020a) Semisynthetic and enzyme-mediated conjugate preparations illuminate the ubiquitination-dependent aggregation of tau protein. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 59:6607–6611. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201916756
Munari F, Barracchia CG, Parolini F, Tira R, Bubacco L, Assfalg M, D’Onofrio M (2020b) Semisynthetic modification of tau protein with di-ubiquitin chains for aggregation studies. Int J Mol Sci 21:4400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124400
Myeku N, Clelland CL, Emrani S, Kukushkin NV, Yu WH, Goldberg AL, Duff KE (2016) Tau-driven 26S proteasome impairment and cognitive dysfunction can be prevented early in disease by activating cAMP-PKA signaling. Nat Med 22:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4011
Mylonas E, Hascher A, Bernado P, Blackledge M, Mandelkow E, Svergun DI (2008) Domain conformation of tau protein studied by solution small-angle X-ray scattering. Biochemistry 47:10345–10353. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi800900d
Nath A, Sammalkorpi M, DeWitt DC, Trexler AJ, Elbaum-Garfinkle S, O’Hern CS, Rhoades E (2012) The conformational ensembles of α-synuclein and tau: combining single-molecule FRET and simulations. Biophys J 103:1940–1949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2012.09.032
Necula M, Kuret J (2004) Pseudophosphorylation and glycation of tau protein enhance but do not trigger fibrillization in vitro. J Biol Chem 279:49694–49703. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M405527200
Nelson PT, Stefansson K, Gulcher J, Saper CB (1996) Molecular evolution of tau protein: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 67:1622–1632. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1996.67041622.x
Niewiadomska G, Niewiadomski W, Steczkowska M, Gasiorowska A (2021) Tau Oligomers Neurotoxicity Life (basel) 11:28. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11010028
Orozco D, Tahirovic S, Rentzsch K, Schwenk BM, Haass C, Edbauer D (2012) Loss of fused in sarcoma (FUS) promotes pathological tau splicing. EMBO Rep 13:759–764. https://doi.org/10.1038/embor.2012.90
Park S, Lee JH, Jeon JH, Lee MJ (2018) Degradation or aggregation: the ramifications of post-translational modifications on tau. BMB Rep 51:265–273. https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2018.51.6.077
Parolini F, Tira R, Barracchia CG, Munari F, Capaldi S, D’Onofrio M, Assfalg M (2022) Ubiquitination of Alzheimer’s-related tau protein affects liquid-liquid phase separation in a site- and cofactor-dependent manner. Int J Biol Macromol 201:173–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.12.191
Patterson KR, Remmers C, Fu Y, Brooker S, Kanaan NM, Vana L, Ward S, Reyes JF, Philibert K, Glucksman MJ et al (2011) Characterization of prefibrillar tau oligomers in vitro and in Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem 286:23063–23076. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.237974
Petrucelli L, Dickson D, Kehoe K, Taylor J, Snyder H, Grover A, De Lucia M, McGowan E, Lewis J, Prihar G et al (2004) CHIP and Hsp70 regulate tau ubiquitination, degradation and aggregation. Hum Mol Genet 13:703–714. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddh083
Preuss U, Biernat J, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (1997) The ‘jaws’ model of tau-microtubule interaction examined in CHO cells. J Cell Sci 110(Pt 6):789–800
Prifti E, Tsakiri EN, Vourkou E, Stamatakis G, Samiotaki M, Papanikolopoulou K (2021) The two cysteines of tau protein are functionally distinct and contribute differentially to its pathogenicity in vivo. J Neurosci 41:797–810. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1920-20.2020
Ramachandran G, Udgaonkar JB (2011) Understanding the kinetic roles of the inducer heparin and of rod-like protofibrils during amyloid fibril formation by tau protein. J Biol Chem 286:38948–38959. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.271874
Rani L, Mallajosyula SS (2021) Phosphorylation-induced structural reorganization in tau-paired helical filaments. ACS Chem Neurosci 12:1621–1631. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00084
Rani L, Mittal J, Mallajosyula SS (2020) Effect of phosphorylation and O-GlcNAcylation on proline-rich domains of tau. J Phys Chem B 124:1909–1918. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.9b11720
Robertson LA, Moya KL, Breen KC (2004) The potential role of tau protein O-glycosylation in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 6:489–495. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-2004-6505
Rosenberg KJ, Ross JL, Feinstein HE, Feinstein SC, Israelachvili J (2008) Complementary dimerization of microtubule-associated tau protein: implications for microtubule bundling and tau-mediated pathogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:7445–7450. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0802036105
Sadowski M, Suryadinata R, Tan AR, Roesley SN, Sarcevic B (2012) Protein monoubiquitination and polyubiquitination generate structural diversity to control distinct biological processes. IUBMB Life 64:136–142. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.589
Sahara N, Maeda S, Murayama M, Suzuki T, Dohmae N, Yen SH, Takashima A (2007) Assembly of two distinct dimers and higher-order oligomers from full-length tau. Eur J Neurosci 25:3020–3029. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05555.x
Saito T, Chiku T, Oka M, Wada-Kakuda S, Nobuhara M, Oba T, Shinno K, Abe S, Asada A, Sumioka A et al (2021) Disulfide bond formation in microtubule-associated tau protein promotes tau accumulation and toxicity in vivo. Hum Mol Genet 30:1955–1967. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddab162
Sato Y, Naito Y, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Endo T (2001) Analysis of N-glycans of pathological tau: possible occurrence of aberrant processing of tau in Alzheimer’s disease. FEBS Lett 496:152–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(01)02421-8
Savastano A, Flores D, Kadavath H, Biernat J, Mandelkow E, Zweckstetter M (2021) Disease-associated tau phosphorylation hinders tubulin assembly within tau condensates. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 60:726–730. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202011157
Schedin-Weiss S, Winblad B, Tjernberg LO (2014) The role of protein glycosylation in Alzheimer disease. FEBS J 281:46–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.12590
Schneider A, Biernat J, von Bergen M, Mandelkow E, Mandelkow EM (1999) Phosphorylation that detaches tau protein from microtubules (Ser262, Ser214) also protects it against aggregation into Alzheimer paired helical filaments. Biochemistry 38:3549–3558. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi981874p
Schwalbe M, Ozenne V, Bibow S, Jaremko M, Jaremko L, Gajda M, Jensen MR, Biernat J, Becker S, Mandelkow E et al (2014) Predictive atomic resolution descriptions of intrinsically disordered hTau40 and α-synuclein in solution from NMR and small angle scattering. Structure 22:238–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2013.10.020
Schweers O, Mandelkow EM, Biernat J, Mandelkow E (1995) Oxidation of cysteine-322 in the repeat domain of microtubule-associated protein tau controls the in vitro assembly of paired helical filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:8463–8467. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.18.8463
Schweers O, Schönbrunn-Hanebeck E, Marx A, Mandelkow E (1994) Structural studies of tau protein and Alzheimer paired helical filaments show no evidence for β-structure. J Biol Chem 269:24290–24297
Shi Y, Murzin AG, Falcon B, Epstein A, Machin J, Tempest P, Newell KL, Vidal R, Garringer HJ, Sahara N et al (2021a) Cryo-EM structures of tau filaments from Alzheimer’s disease with PET ligand APN-1607. Acta Neuropathol 141:697–708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-021-02294-3
Shi Y, Zhang W, Yang Y, Murzin AG, Falcon B, Kotecha A, van Beers M, Tarutani A, Kametani F, Garringer HJ et al (2021b) Structure-based classification of tauopathies. Nature 598:359–363. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03911-7
Shimura H, Schwartz D, Gygi SP, Kosik KS (2004) CHIP-Hsc70 complex ubiquitinates phosphorylated tau and enhances cell survival. J Biol Chem 279:4869–4876. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M305838200
Shin MK, Vazquez-Rosa E, Koh Y, Dhar M, Chaubey K, Cintron-Perez CJ, Barker S, Miller E, Franke K, Noterman MF et al (2021) Reducing acetylated tau is neuroprotective in brain injury. Cell 184(2715–2732):e2723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.032
Sillen A, Barbier P, Landrieu I, Lefebvre S, Wieruszeski JM, Leroy A, Peyrot V, Lippens G (2007) NMR investigation of the interaction between the neuronal protein tau and the microtubules. Biochemistry 46:3055–3064. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi061920i
Sillen A, Wieruszeski JM, Leroy A, Younes AB, Landrieu I, Lippens G (2005) High-resolution magic angle spinning NMR of the neuronal tau protein integrated in Alzheimer’s-like paired helical fragments. J Am Chem Soc 127:10138–10139. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0516211
Simic G, Babic Leko M, Wray S, Harrington C, Delalle I, Jovanov-Milosevic N, Bazadona D, Buee L, de Silva R, Di Giovanni G et al (2016) Tau protein hyperphosphorylation and aggregation in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies, and possible neuroprotective strategies. Biomolecules 6:6. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom6010006
Singh V, Xu L, Boyko S, Surewicz K, Surewicz WK (2020) Zinc promotes liquid-liquid phase separation of tau protein. J Biol Chem 295:5850–5856. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.AC120.013166
Smet-Nocca C, Broncel M, Wieruszeski JM, Tokarski C, Hanoulle X, Leroy A, Landrieu I, Rolando C, Lippens G, Hackenberger CP (2011) Identification of O-GlcNAc sites within peptides of the Tau protein and their impact on phosphorylation. Mol Biosyst 7:1420–1429. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0mb00337a
Smith PY, Delay C, Girard J, Papon MA, Planel E, Sergeant N, Buee L, Hebert SS (2011) MicroRNA-132 loss is associated with tau exon 10 inclusion in progressive supranuclear palsy. Hum Mol Genet 20:4016–4024. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr330
Soeda Y, Yoshikawa M, Almeida OF, Sumioka A, Maeda S, Osada H, Kondoh Y, Saito A, Miyasaka T, Kimura T et al (2015) Toxic tau oligomer formation blocked by capping of cysteine residues with 1,2-dihydroxybenzene groups. Nat Commun 6:10216. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10216
Sohn PD, Tracy TE, Son HI, Zhou Y, Leite RE, Miller BL, Seeley WW, Grinberg LT, Gan L (2016) Acetylated tau destabilizes the cytoskeleton in the axon initial segment and is mislocalized to the somatodendritic compartment. Mol Neurodegener 11:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-016-0109-0
Sperber BR, Leight S, Goedert M, Lee VM (1995) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta phosphorylates tau protein at multiple sites in intact cells. Neurosci Lett 197:149–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3940(95)11902-9
Spillantini MG, Goedert M (2013) Tau pathology and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol 12:609–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70090-5
Spittaels K, Van den Haute C, Van Dorpe J, Geerts H, Mercken M, Bruynseels K, Lasrado R, Vandezande K, Laenen I, Boon T et al (2000) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta phosphorylates protein tau and rescues the axonopathy in the central nervous system of human four-repeat tau transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 275:41340–41349. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M006219200
Stefanoska K, Volkerling A, Bertz J, Poljak A, Ke YD, Ittner LM, Ittner A (2018) An N-terminal motif unique to primate tau enables differential protein-protein interactions. J Biol Chem 293:3710–3719. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.001784
Strang KH, Sorrentino ZA, Riffe CJ, Gorion KM, Vijayaraghavan N, Golde TE, Giasson BI (2019) Phosphorylation of serine 305 in tau inhibits aggregation. Neurosci Lett 692:187–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2018.11.011
Tan JM, Wong ES, Kirkpatrick DS, Pletnikova O, Ko HS, Tay SP, Ho MW, Troncoso J, Gygi SP, Lee MK et al (2008) Lysine 63-linked ubiquitination promotes the formation and autophagic clearance of protein inclusions associated with neurodegenerative diseases. Hum Mol Genet 17:431–439. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddm320
Tan R, Lam AJ, Tan T, Han J, Nowakowski DW, Vershinin M, Simo S, Ori-McKenney KM, McKenney RJ (2019) Microtubules gate tau condensation to spatially regulate microtubule functions. Nat Cell Biol 21:1078–1085. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-019-0375-5
Thomas SN, Funk KE, Wan Y, Liao Z, Davies P, Kuret J, Yang AJ (2012) Dual modification of Alzheimer’s disease PHF-tau protein by lysine methylation and ubiquitylation: a mass spectrometry approach. Acta Neuropathol 123:105–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-011-0893-0
Tian H, Davidowitz E, Lopez P, Emadi S, Moe J, Sierks M (2013) Trimeric tau is toxic to human neuronal cells at low nanomolar concentrations. Int J Cell Biol 2013:260787. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/260787
Tracy TE, Sohn PD, Minami SS, Wang C, Min SW, Li Y, Zhou Y, Le D, Lo I, Ponnusamy R et al (2016) Acetylated tau obstructs KIBRA-mediated signaling in synaptic plasticity and promotes tauopathy-related memory loss. Neuron 90:245–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.03.005
Trzeciakiewicz H, Tseng JH, Wander CM, Madden V, Tripathy A, Yuan CX, Cohen TJ (2017) A dual pathogenic mechanism links tau acetylation to sporadic tauopathy. Sci Rep 7:44102. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44102
Tseng JH, Ajit A, Tabassum Z, Patel N, Tian X, Chen Y, Prevatte AW, Ling K, Rigo F, Meeker RB et al (2021) Tau seeds are subject to aberrant modifications resulting in distinct signatures. Cell Rep 35:109037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109037
Wang JZ, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (1996) Glycosylation of microtubule-associated protein tau: an abnormal posttranslational modification in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med 2:871–875. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0896-871
Wang JZ, Wu Q, Smith A, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (1998) Tau is phosphorylated by GSK-3 at several sites found in Alzheimer disease and its biological activity markedly inhibited only after it is prephosphorylated by A-kinase. FEBS Lett 436:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(98)01090-4
Wang Y, Mandelkow E (2012) Degradation of tau protein by autophagy and proteasomal pathways. Biochem Soc Trans 40:644–652. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20120071
Wang Y, Mandelkow E (2016) Tau in physiology and pathology. Nat Rev Neurosci 17:5–21. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2015.1
Ward SM, Himmelstein DS, Lancia JK, Binder LI (2012) Tau oligomers and tau toxicity in neurodegenerative disease. Biochem Soc Trans 40:667–671. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20120134
Watanabe A, Hong WK, Dohmae N, Takio K, Morishima-Kawashima M, Ihara Y (2004) Molecular aging of tau: disulfide-independent aggregation and non-enzymatic degradation in vitro and in vivo. J Neurochem 90:1302–1311. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02611.x
Wegmann S, Eftekharzadeh B, Tepper K, Zoltowska KM, Bennett RE, Dujardin S, Laskowski PR, MacKenzie D, Kamath T, Commins C et al (2018) Tau protein liquid-liquid phase separation can initiate tau aggregation. EMBO J 37:e98049. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201798049
Wegmann S, Medalsy ID, Mandelkow E, Muller DJ (2013) The fuzzy coat of pathological human Tau fibrils is a two-layered polyelectrolyte brush. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:E313-321. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1212100110
Wegmann S, Scholer J, Bippes CA, Mandelkow E, Muller DJ (2011) Competing interactions stabilize pro- and anti-aggregant conformations of human tau. J Biol Chem 286:20512–20524. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.237875
Weingarten MD, Lockwood AH, Hwo SY, Kirschner MW (1975) A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:1858–1862
Wen J, Hong L, Krainer G, Yao QQ, Knowles TPJ, Wu S, Perrett S (2021) Conformational expansion of tau in condensates promotes irreversible aggregation. J Am Chem Soc 143:13056–13064. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c03078
Wischik CM, Novak M, Edwards PC, Klug A, Tichelaar W, Crowther RA (1988a) Structural characterization of the core of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:4884–4888
Wischik CM, Novak M, Thogersen HC, Edwards PC, Runswick MJ, Jakes R, Walker JE, Milstein C, Roth M, Klug A (1988b) Isolation of a fragment of tau derived from the core of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:4506–4510
Wu C, Zhao J, Wu Q, Tan Q, Liu Q, Xiao S (2021) Tau N-terminal inserts regulate tau liquid-liquid phase separation and condensates maturation in a neuronal cell model. Int J Mol Sci 22:9728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189728
Xia Y, Bell BM, Giasson BI (2021) Tau K321/K353 pseudoacetylation within KXGS motifs regulates tau-microtubule interactions and inhibits aggregation. Sci Rep 11:17069. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-96627-7
Yao TP (2010) The role of ubiquitin in autophagy-dependent protein aggregate processing. Genes Cancer 1:779–786. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947601910383277
Yoshitake J, Soeda Y, Ida T, Sumioka A, Yoshikawa M, Matsushita K, Akaike T, Takashima A (2016) Modification of tau by 8-nitroguanosine 3’,5’-cyclic monophosphate (8-Nitro-cGMP): Effects of nitric oxide-linked chemical modification on tau aggregation. J Biol Chem 291:22714–22720. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.734350
Yuzwa SA, Cheung AH, Okon M, McIntosh LP, Vocadlo DJ (2014) O-GlcNAc modification of tau directly inhibits its aggregation without perturbing the conformational properties of tau monomers. J Mol Biol 426:1736–1752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2014.01.004
Yuzwa SA, Shan X, Macauley MS, Clark T, Skorobogatko Y, Vosseller K, Vocadlo DJ (2012) Increasing O-GlcNAc slows neurodegeneration and stabilizes tau against aggregation. Nat Chem Biol 8:393–399. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.797
Yuzwa SA, Yadav AK, Skorobogatko Y, Clark T, Vosseller K, Vocadlo DJ (2011) Mapping O-GlcNAc modification sites on tau and generation of a site-specific O-GlcNAc tau antibody. Amino Acids 40:857–868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0705-1
Zeng Y, Yang J, Zhang B, Gao M, Su Z, Huang Y (2021) The structure and phase of tau: from monomer to amyloid filament. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences : CMLS 78:1873–1886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03681-x
Zhang JY, Liu SJ, Li HL, Wang JZ (2005) Microtubule-associated protein tau is a substrate of ATP/Mg(2+)-dependent proteasome protease system. J Neural Transm (vienna) 112:547–555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-004-0196-x
Zhang W, Tarutani A, Newell KL, Murzin AG, Matsubara T, Falcon B, Vidal R, Garringer HJ, Shi Y, Ikeuchi T et al (2020a) Novel tau filament fold in corticobasal degeneration. Nature 580:283–287. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2043-0
Zhang X, Lin Y, Eschmann NA, Zhou H, Rauch JN, Hernandez I, Guzman E, Kosik KS, Han S (2017) RNA stores tau reversibly in complex coacervates. PLoS Biol 15:e2002183. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2002183
Zhang X, Vigers M, McCarty J, Rauch JN, Fredrickson GH, Wilson MZ, Shea JE, Han S, Kosik KS (2020b) The proline-rich domain promotes tau liquid-liquid phase separation in cells. J Cell Biol 219:e202006054. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.202006054
Zhu S, Shala A, Bezginov A, Sljoka A, Audette G, Wilson DJ (2015) Hyperphosphorylation of intrinsically disordered tau protein induces an amyloidogenic shift in its conformational ensemble. PLoS One 10:e0120416. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120416
Funding
This work was supported by funding from Hubei University of Technology (Y. Huang. and Z. Su).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y. Huang and Z. Su had the idea for the article, H. Ye, Y. Han, and P. Li performed the literature search and data analysis, and H. Ye and Y. Huang drafted and/or critically revised the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, H., Han, Y., Li, P. et al. The Role of Post-Translational Modifications on the Structure and Function of Tau Protein. J Mol Neurosci 72, 1557–1571 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-02002-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-02002-0