Abstract
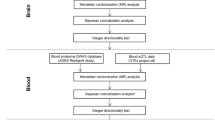
N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) methylation is the most abundant post-transcription modification in eukaryotes and plays a vital role in many pathological conditions including cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and vascular inflammation. Moreover, recent studies have reported that single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can affect the m6A modification. Therefore, we investigated the relationship between m6A-SNPs and ischemic stroke (IS) risk through integrative analysis of an IS genome-wide association study and m6A-SNP list from the m6AVar database. Next, we performed eQTL and differential expression analysis to support these IS-associated m6A-SNPs. Finally, using the identified polymorphisms, a PPI network was constructed using the STRING database, and GO and pathway enrichment analyses were performed using the DAVID online tool. Accordingly, we identified 305 IS-associated SNPs that could affect m6A methylation. Next, 158 of these SNPs were determined to have eQTL signals on local genes. We further identified 84 local genes (containing a total of 87 SNPs) that were differentially expressed in IS patients. Finally, we identified several biological processes and pathways related to IS pathogenesis, such as “leukocyte migration” and “focal adhesion.” In summary, our study detected dozens of m6A-SNPs as critical functional polymorphisms and novel genetic biomarkers for IS susceptibility and provided a new means of elucidating the biological mechanism underlying IS development.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
The summary statistics of IS GWAS meta-analysis were publicly available from https://www.megastroke.org/download.html. The m6A‐SNPs dataset can be downloaded from the m6AVar database (http://m6avar.renlab.org/). Three public gene expression microarray datasets (GSE16561, GSE22255, and GSE58294) can be downloaded from GEO database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/).
References
Abbassi R, Johns TG, Kassiou M, Munoz L (2015) DYRK1A in neurodegeneration and cancer: molecular basis and clinical implications. Pharmacol Ther 151:87–98 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.03.004
Barr TL, Conley Y, Ding J, Dillman A, Warach S, Singleton A, Matarin M (2010) Genomic biomarkers and cellular pathways of ischemic stroke by RNA gene expression profiling. Neurology 75:1009–1014. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f2b37f
Carrera C et al (2016) Whole exome sequencing analysis reveals TRPV3 as a risk factor for cardioembolic stroke. Thromb Haemost 116:1165–1171
Desrosiers R, Friderici K, Rottman F (1974) Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger RNA from Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71:3971–3975
Di Raimondo D et al (2013) Metabolic and anti-inflammatory effects of a home-based programme of aerobic physical exercise. Int J Clin Pract 67:1247–1253. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcp.12269
Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M, Davis SM (2008) Stroke Lancet 371:1612–1623. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60694-7
Elkind MSV, Sciacca RR, Boden-Albala B, Rundek T, Paik MC, Sacco RL (2005) Relative elevation in baseline leukocyte count predicts first cerebral infarction. Neurology 64:2121–2125
eGTEx Project (2017) Enhancing GTEx by bridging the gaps between genotype gene expression, and disease. Nat Genet 49:1664–1670. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3969
Feigin VL et al (2016) Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Neurol 15:913–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(16)30073-4
Galkina E, Ley K (2009) Immune and inflammatory mechanisms of atherosclerosis (*) Annu Rev Immunol 27:165–197 https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.021908.132620
Gautam J, Miner JH, Yao Y (2019) Loss of endothelial laminin α5 exacerbates hemorrhagic brain injury. Transl Stroke Res 10:705–718 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-019-0688-5
Hankey GJ (2017) Stroke Lancet 389:641–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(16)30962-x
GTEx Consortium (2015) Human genomics. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) pilot analysis: multitissue gene regulation in humans. Science 348:648–660 https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1262110
Hyysalo A, Ristola M, Mäkinen MEL, Häyrynen S, Nykter M, Narkilahti S (2017) Laminin α5 substrates promote survival, network formation and functional development of human pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons in vitro. Stem Cell Res 24:118–127 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scr.2017.09.002
Ilinca A et al (2020) Whole-exome sequencing in 22 young ischemic stroke patients with familial clustering of stroke. Stroke 51:1056–1063 https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.027474
Kilarski LL et al (2014) Meta-analysis in more than 17,900 cases of ischemic stroke reveals a novel association at 12q24.12. Neurology 83:678–685 https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000000707
Kim J, Chae YK (2009) Genomewide association studies of stroke. N Engl J Med 361:722; author reply 722 https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc091089
Krug T et al (2012) TTC7B emerges as a novel risk factor for ischemic stroke through the convergence of several genome-wide approaches. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:1061–1072 https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2012.24
Liao D et al (1997) Familial history of stroke and stroke risk. The Family Heart Study Stroke 28:1908–1912
Malik R et al (2018) Multiancestry genome-wide association study of 520,000 subjects identifies 32 loci associated with stroke and stroke subtypes. Nat Genet 50:524–537 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0058-3
Meschia JF, Worrall BB, Rich SS (2011) Genetic susceptibility to ischemic stroke Nature reviews. Neurology 7:369–378. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2011.80
Meyer KD, Jaffrey SR (2014) The dynamic epitranscriptome: N6-methyladenosine and gene expression control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:313–326 https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3785
Mo XB, Lei SF, Qian QY, Guo YF, Zhang YH, Zhang H (2019) Integrative analysis revealed potential causal genetic and epigenetic factors for multiple sclerosis. J Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09476-w
Mo XB, Lei SF, Zhang YH, Zhang H (2018) Detection of m(6)A-associated SNPs as potential functional variants for coronary artery disease. Epigenomics 10:1279–1287 https://doi.org/10.2217/epi-2018-0007
Network NSG, International Stroke Genetics C (2016) Loci associated with ischaemic stroke and its subtypes (SiGN): a genome-wide association study. Lancet Neurol 15:174–184 https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00338-5
O’Connell GC, Petrone AB, Treadway MB, Tennant CS, Lucke-Wold N, Chantler PD, Barr TL (2016) Machine-learning approach identifies a pattern of gene expression in peripheral blood that can accurately detect ischaemic stroke. NPJ Genom Med 1:16038. https://doi.org/10.1038/npjgenmed.2016.38
Omar MH et al (2017) CNS neurons deposit laminin α5 to stabilize synapses Cell Rep 21:1281–1292 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.028
Ovbiagele B et al (2013) Forecasting the future of stroke in the United States: a policy statement from the American Heart Association and American Stroke Association. Stroke 44:2361–2375. https://doi.org/10.1161/str.0b013e31829734f2
Pinto A, Tuttolomondo A, Di Raimondo D, Fernandez P, Licata G (2006) Risk factors profile and clinical outcome of ischemic stroke patients admitted in a Department of Internal Medicine and classified by TOAST classification. Int Angiol 25:261–267
Qi X et al (2020) Integrating genome-wide association study and methylation functional annotation data identified candidate genes and pathways for schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 96:109736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109736
Roignant J-Y, Soller M (2017) mA in mRNA: an ancient mechanism for fine-tuning gene expression. Trends Genet 33:380–390 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2017.04.003
Rozen EJ et al (2018) DYRK1A kinase positively regulates angiogenic responses in endothelial cells. Cell Rep 23:1867–1878 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.04.008
Sampaolo S et al (2017) Identification of the first dominant mutation of LAMA5 gene causing a complex multisystem syndrome due to dysfunction of the extracellular matrix. J Med Genet 54:710–720 https://doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2017-104555
Sham PC, Purcell SM (2014) Statistical power and significance testing in large-scale genetic studies. Nat Rev Genet 15:335–346. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3706
Sobey CG, Judkins CP, Sundararajan V, Phan TG, Drummond GR, Srikanth VK (2015) Risk of Major Cardiovascular Events in People with Down Syndrome. PloS One 10:e0137093. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0137093
Stamova B et al (2014) Gene expression in peripheral immune cells following cardioembolic stroke is sexually dimorphic. PLoS One 9:e102550. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0102550
Traylor M et al (2012) Genetic risk factors for ischaemic stroke and its subtypes (the METASTROKE collaboration): a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet Neurol 11:951–962 https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70234-X
Tuttolomondo A, Maida C, Pinto A (2015) Diabetic foot syndrome as a possible cardiovascular marker in diabetic patients. J Diabetes Res 2015:268390. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/268390
Tuttolomondo A, Maida C, Pinto A (2015b) Diabetic foot syndrome: Immune-inflammatory features as possible cardiovascular markers in diabetes. World J Orthop 6:62–76. https://doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v6.i1.62
Wang T, Kong S, Tao M, Ju S (2020) The potential role of RNA N6-methyladenosine in cancer progression. Mol Cancer 19:88 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01204-7
Ward LD, Kellis M (2012) HaploReg: a resource for exploring chromatin states, conservation, and regulatory motif alterations within sets of genetically linked variants. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D930–934 https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr917
Wu L, Pei Y, Zhu Y, Jiang M, Wang C, Cui W, Zhang D (2019) Association of N6-methyladenine DNA with plaque progression in atherosclerosis via myocardial infarction-associated transcripts. Cell Death Dis 10 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-2152-6
Wu TH, Chien KL, Lin HJ, Hsu HC, Su TC, Chen MF, Lee YT (2013) Total white blood cell count or neutrophil count predict ischemic stroke events among adult Taiwanese: report from a community-based cohort study. BMC Neurol 13:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-13-7
Xu K et al (2020) N-Methyladenosine demethylases Alkbh5/Fto regulate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Ther Adv Chronic Dis 11:2040622320916024 https://doi.org/10.1177/2040622320916024
Zheng Y et al (2018) m6AVar: a database of functional variants involved in m6A modification. Nucleic Acids Res 46:D139-D145 https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx895
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the MEGASTROKE consortium for providing summarized data of IS GWAS meta-analysis. All MEGASTROKE authors appearing in the main author byline are listed in the supplementary material.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81400950, 81501006), Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (Grant Nos. 2019-MS-365, 2019-MS-364). The MEGASTROKE project received funding from sources specified at https://www.megastroke.org/acknowledgments.html.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ruixia Zhu, Dandan Tian, Yating Zhao, and Chenguang Zhang acquired, analyzed, and interpreted the data. Ruixia Zhu wrote the manuscript. Xu Liu designed the study and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The data sources were approved by relevant institutional review boards in the original studies from the MEGASTROKE consortium. All participants provided informed consent in the original studies from the MEGASTROKE consortium.
Consent for Publication
Allowed for publication.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, R., Tian, D., Zhao, Y. et al. Genome-Wide Detection of m6A-Associated Genetic Polymorphisms Associated with Ischemic Stroke. J Mol Neurosci 71, 2107–2115 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01805-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01805-x