Abstract
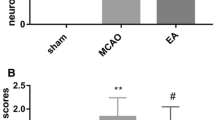
Baihui-penetrating-Qubin acupuncture is frequently used to treat intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) in China. Acupuncture affects multiple microRNAs in diseases. MicroRNA-23a-3p (miR-23a-3p) has been demonstrated to be up-regulated in ICH patients. Herein, the effect of Baihui-penetrating-Qubin acupuncture on miR-23a-3p expression after ICH and the role of miR-23a-3p in ICH were discussed. A rat model of ICH was induced by infusing autologous blood into caudate nucleus. Acupuncture was performed after ICH once a day for 30 min. After 3 consecutive days of acupuncture, the neurobehavioral function, brain edema, neuronal cell death, inflammation, ferroptosis, nuclear factor E2-like 2 (NFE2L2) signaling and miR-23a-3p levels in brain tissues were analyzed. Additionally, antagomiR-23a-3p was injected into rats 3 days prior to ICH modeling to analyze the function of miR-23a-3p in neuronal cell death, inflammation, ferroptosis, and NFE2L2 signaling. Acupuncture relieved the ICH-induced neurological function deficits, increases in brain water content and Fluoro-Jade B (FJB)-positive cells and release of proinflammatory cytokines. Acupuncture also alleviated ferroptosis and decreased miR-23a-3p expression, as evidenced by the increased NFE2L2 nuclear translocation and expressions of heme oxygenase-1 and glutathione peroxidase 4 and the decreased iron and malondialdehyde contents and reactive oxygen species accumulation. Additionally, antagomiR-23a-3p inhibited the ICH-induced increases in FJB-positive cells, release of proinflammatory cytokines, ferroptosis, and promoted NFE2L2 activation. Notably, the binding site of miR-23a-3p existed in NFE2L2. Taken together, acupuncture may alleviate the neuronal cell death, inflammation, and ferroptosis after ICH by down-regulating miR-23a-3p. This study provides a potential mechanism underlying the Baihui-penetrating-Qubin acupuncture improving the early injury after ICH.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
GraphPad Prism 8 software was employed to carry out statistical analyses.
References
Abdalkader M, Lampinen R, Kanninen KM, Malm TM, Liddell JR (2018) Targeting Nrf2 to suppress ferroptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegeneration. Front Neurosci 12:466. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00466
Bai YY, Niu JZ (2020) miR222 regulates brain injury and inflammation following intracerebral hemorrhage by targeting ITGB8. Mol med rep 21:1145–1153. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10903
Behn C, Araneda OF, Llanos AJ, Celedon G, Gonzalez G (2007) Hypoxia-related lipid peroxidation: evidences, implications and approaches. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 158:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resp.2007.06.001
Cai M, Lee JH, Yang EJ (2019) Electroacupuncture attenuates cognition impairment via anti-neuroinflammation in an Alzheimer’s disease animal model. J Neuroinflammation 16:264. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1665-3
Cheong YC, Dix S, Hung Yu Ng E, Ledger WL, Farquhar C (2013) Acupuncture and assisted reproductive technology. Cochrane Database Syst Rev https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD006920.pub3
Cordonnier C, Demchuk A, Ziai W, Anderson CS (2018) Intracerebral haemorrhage: current approaches to acute management. Lancet 392:1257–1268. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31878-6
Deng JJ, Lai MY, Tan X, Yuan Q (2019) Acupuncture protects the interstitial cells of Cajal by regulating miR-222 in a rat model of post-operative ileus. Acupunct Med 37:125–132. https://doi.org/10.1177/0964528419829755
Dixon SJ et al (2012) Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149:1060–1072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Dodson M, Castro-Portuguez R, Zhang DD (2019) NRF2 plays a critical role in mitigating lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Redox biol 23:101107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2019.101107
Garrett MC et al (2009) Synergistic neuroprotective effects of C3a and C5a receptor blockade following intracerebral hemorrhage. Brain Res 1298:171–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.04.047
Hambright WS, Fonseca RS, Chen L, Na R, Ran Q (2017) Ablation of ferroptosis regulator glutathione peroxidase 4 in forebrain neurons promotes cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration. Redox biol 12:8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.01.021
Hu YL, Wang H, Huang Q, Wang G, Zhang HB (2018) MicroRNA-23a-3p promotes the perihematomal edema formation after intracerebral hemorrhage via ZO-1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:2809–2816. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201805_14980
Kang JM, Park HJ, Choi YG, Choe IH, Park JH, Kim YS, Lim S (2007) Acupuncture inhibits microglial activation and inflammatory events in the MPTP-induced mouse model. Brain Res 1131:211–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2006.10.089
Kim ST et al (2012) Acupuncture suppresses kainic acid-induced neuronal death and inflammatory events in mouse hippocampus. J Physiol Sci 62:377–383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12576-012-0216-9
Koivunen RJ et al (2015) Incidence, risk factors, etiology, severity and short-term outcome of non-traumatic intracerebral hemorrhage in young adults. Eur J Neurol 22:123–132. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.12543
Krafft PR et al (2014) Correlation between subacute sensorimotor deficits and brain edema in two mouse models of intracerebral hemorrhage. Behav Brain Res 264:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2014.01.052
Lan L et al (2013) Electroacupuncture exerts anti-inflammatory effects in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats via suppression of the TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. Int J Mol Med 31:75–80. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2012.1184
Li HQ, Li JH, Liu AJ, Ye MY, Zheng GQ (2014) GV20-based acupuncture for animal models of acute intracerebral haemorrhage: a preclinical systematic review and meta-analysis. Acupuncture in medicine : journal of the British Medical Acupuncture Society 32:495–502. https://doi.org/10.1136/acupmed-2014-010546
Li LX, Yin LH, Gao M, Xu LN, Qi Y, Peng JY (2020) MiR-23a-5p exacerbates intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury by promoting oxidative stress via targeting PPAR alpha. Biochem Pharmacol 180:114194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114194
Li Q et al (2017) Inhibition of neuronal ferroptosis protects hemorrhagic brain JCI. Insight 2:e90777. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.90777
Li Y, Yan H, Xu X, Liu H, Wu C, Zhao L (2020) Erastin/sorafenib induces cisplatin-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cell ferroptosis through inhibition of the Nrf2/xCT pathway. Oncol Lett 19:323–333. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.11066
Liu XY et al (2018) Acupuncture through Baihui (DU20) to Qubin (GB7) mitigates neurological impairment after intracerebral hemorrhage. Neural Regen Res 13:1425–1432. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.235298
Liu Z, Guan L, Wang Y, Xie CL, Lin XM, Zheng GQ (2012) History and mechanism for treatment of intracerebral hemorrhage with scalp acupuncture. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012:895032. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/895032
Lyngsie G, Krumina L, Tunlid A, Persson P (2018) Generation of hydroxyl radicals from reactions between a dimethoxyhydroquinone and iron oxide nanoparticles. Sci Rep 8:10834. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-29075-5
Mao H, Zhao Y, Li H, Lei L (2020) Ferroptosis as an emerging target in inflammatory diseases. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 155:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2020.04.001
Mracsko E, Veltkamp R (2014) Neuroinflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage. Front Cell Neurosci 8:388. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2014.00388
Mu Y et al (2020) Integrated miRNA-seq analysis reveals the molecular mechanism underlying the effect of acupuncture on endometrial receptivity in patients undergoing fertilization: embryo transplantation. 3 Biotech 10:6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1990-3
Ouyang Y et al (2019) MiR-21–5p/dual-specificity phosphatase 8 signalling mediates the anti-inflammatory effect of haem oxygenase-1 in aged intracerebral haemorrhage rats. Aging Cell 18:e13022. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13022
Qu X, Wang N, Chen W, Qi M, Xue Y, Cheng W (2019) RNF34 overexpression exacerbates neurological deficits and brain injury in a mouse model of intracerebral hemorrhage by potentiating mitochondrial dysfunction-mediated oxidative stress. Sci Rep 9:16296. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52494-x
Ramires CC, Balbinot DT, Cidral-Filho FJ, Dias DV, Dos Santos AR, da Silva MD (2020) Acupuncture reduces peripheral and brainstem cytokines in rats subjected to lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation. Acupunct Med https://doi.org/10.1177/0964528420938379
Sacco S, Ornello R, Degan D, Tiseo C, Pistoia F, Carolei A (2016) Declining incidence of intracerebral hemorrhage over two decades in a population-based study. European J Neurol 23:1627–1634. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13099
Sha R, Zhang B, Han X, Peng J, Zheng C, Zhang F, Huang X (2019) Electroacupuncture Alleviates Ischemic Brain Injury by Inhibiting the miR-223/NLRP3 Pathway. Medical science monitor: international medical journal of experimental and clinical research 25:4723–4733. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.917213
Shang Y, Dai S, Chen X, Wen W, Liu X (2019) MicroRNA-93 regulates the neurological function, cerebral edema and neuronal apoptosis of rats with intracerebral hemorrhage through TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Cell Cycle 18:3160–3176. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2019.1670509
Shen EY, Chen FJ, Chen YY, Lin MF (2011) Locating the Acupoint Baihui (GV20) Beneath the Cerebral Cortex with MRI Reconstructed 3D Neuroimages. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2011:362494. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecam/neq047
Shen H, Liu C, Zhang D, Yao X, Zhang K, Li H, Chen G (2017) Role for RIP1 in mediating necroptosis in experimental intracerebral hemorrhage model both in vivo and in vitro. Cell Death Dis 8:e2641. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.58
Shinbara H, Okubo M, Kimura K, Mizunuma K, Sumiya E (2015) Contributions of nitric oxide and prostaglandins to the local increase in muscle blood flow following manual acupuncture in rats. Acupunct Med 33:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1136/acupmed-2014-010634
Sugiyama T, Imai T, Nakamura S, Yamauchi K, Sawada S, Shimazawa M, Hara H (2018) A novel Nrf2 activator, RS9, attenuates secondary brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage in sub-acute phase. Brain Res 1701:137–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2018.08.021
Sun X, Ou Z, Chen R, Niu X, Chen D, Kang R, Tang D (2016) Activation of the p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway protects against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 63:173–184. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.28251
Tian H, Zhang H, Zhu J, Zhang J, Cai H, Zhang Y, Chen C (2012) Acupuncture activates signal transduction pathways related to brain-tissue restoration after ischemic injury. Neural Regen Res 7:1866–1872. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.24.004
Ursini F, Maiorino M (2020) Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: The role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic Biol Med 152:175–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.027
van Asch CJ, Luitse MJ, Rinkel GJ, van der Tweel I, Algra A, Klijn CJ (2010) Incidence, case fatality, and functional outcome of intracerebral haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and ethnic origin: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 9:167–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70340-0
Wang J, Zhu Y, Jin F, Tang L, He Z, He Z (2016) Differential expression of circulating microRNAs in blood and haematoma samples from patients with intracerebral haemorrhage. J Int Med Res 44:419–432. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060516630852
Wilkinson DA, Pandey AS, Thompson BG, Keep RF, Hua Y, Xi G (2018) Injury mechanisms in acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Neuropharmacology 134:240–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.09.033
Wu H et al (2010) Time course of upregulation of inflammatory mediators in the hemorrhagic brain in rats: correlation with brain edema. Neurochem Int 57:248–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2010.06.002
Xi G, Keep RF, Hoff JT (2006) Mechanisms of brain injury after intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol 5:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(05)70283-0
Xi T et al (2018) miR-27a-3p protects against blood-brain barrier disruption and brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage by targeting endothelial aquaporin-11. J Biol Chem 293:20041–20050. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.001858
Xiong XY, Wang J, Qian ZM, Yang QW (2014) Iron and intracerebral hemorrhage: from mechanism to translation. Transl Stroke Res 5:429–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-013-0317-7
Xu W, Li F, Liu Z, Xu Z, Sun B, Cao J, Liu Y (2017) MicroRNA-27b inhibition promotes Nrf2/ARE pathway activation and alleviates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced brain injury. Oncotarget 8:70669–70684. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19974
Yu A et al (2017) miRNA-144 induces microglial autophagy and inflammation following intracerebral hemorrhage. Immunol Lett 182:18–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2017.01.002
Zeng J et al (2017) Isoliquiritigenin alleviates early brain injury after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage via suppressing ROS- and/or NF-kappaB-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation by promoting Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. J Neuroinflammation 14:119. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-017-0895-5
Zhang B et al (2018a) Baihui (DU20)-penetrating-Qubin (GB7) acupuncture inhibits apoptosis in the perihemorrhagic penumbra. Neural Regen Res 13:1602–1608. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.237123
Zhang CY et al (2019a) Simvastatin alleviates inflammation and oxidative stress in rats with cerebral hemorrhage through Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:6321–6329. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201907_18455
Zhang P et al (2019b) Exploration of MST1-mediated secondary brain injury induced by intracerebral hemorrhage in rats via Hippo signaling pathway. Transl Stroke Res 10:729–743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-019-00702-1
Zhang S et al (2020) Electro-acupuncture promotes the differentiation of endogenous neural stem cells via exosomal microRNA 146b after ischemic stroke. Front Cell Neurosci 14:223. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.00223
Zhang Z et al (2018b) Glutathione peroxidase 4 participates in secondary brain injury through mediating ferroptosis in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Brain Res 1701:112–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2018.09.012
Zheng H, Chen C, Zhang J, Hu Z (2016) Mechanism and therapy of brain edema after intracerebral hemorrhage. Cerebrovasc Dis 42:155–169. https://doi.org/10.1159/000445170
Zheng HW et al (2012) Circulating MicroRNAs as potential risk biomarkers for hematoma enlargement after intracerebral hemorrhage. CNS Neurosci Ther 18:1003–1011. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12019
Zille M et al (2017) Neuronal death after hemorrhagic stroke in vitro and in vivo shares features of ferroptosis and necroptosis. Stroke 48:1033–1043. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.015609
Zou W, Chen QX, Sun XW, Chi QB, Kuang HY, Yu XP, Dai XH (2015) Acupuncture inhibits Notch1 and Hes1 protein expression in the basal ganglia of rats with cerebral hemorrhage. Neural Regen Res 10:457–462. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.153696
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81904305), the Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine Doctoral Innovation Foundation (No. 2017bs05), the Heilongjiang Provincial Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. LBH-Z12249), the Project of Science and Technology of Education Department of Heilongjiang Province (No. 12531633) and the Foundation of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine (No. 2019PT10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wei Zou designed the study. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Ying Kong, Shulin Li, Miao Zhang, Wenting Xu, Qiuxin Chen, Lihong Zheng, and Peng Liu. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Ying Kong. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical Approval
Animal experiments were performed and approved by the ethics committee of Second Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, Y., Li, S., Zhang, M. et al. Acupuncture Ameliorates Neuronal Cell Death, Inflammation, and Ferroptosis and Downregulated miR-23a-3p After Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rats. J Mol Neurosci 71, 1863–1875 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01770-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01770-x