Abstract
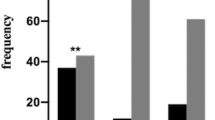
Heritability of major depressive disorder (MDD) is between 36 and 44%, suggesting that up to nearly half of the phenotypic variability is attributable to genes. A number of genetic polymorphisms have been shown to predispose certain individuals to depression. Of particular interest are the polymorphisms of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene. Although the VDR gene has been well characterized and a vast number of polymorphisms have been identified, the association between BsmI (rs1544410), ApaI (rs7975232) and TaqI (rs731236) single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), together with their haplotypes, and MDD risk have yet to be established. We conducted a matched case–control study with a total of 600 participants comprising 300 major depressive disorder (MDD) cases and 300 controls matched by age, gender and ethnicity in a 1:1 ratio, in four public hospitals in Kuala Lumpur and Selangor. Three adjacent SNPs of the VDR gene—BsmI (rs1544410), ApaI (rs7975232) and TaqI (rs731236)—were genotyped using polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP). Odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were obtained from conditional logistic regression using Stata 16. Linkage disequilibrium and haplotype association with MDD were analyzed using the online SNPStats program. None of the genotypes of the three SNPs was significantly associated with risk of developing MDD after adjusting for confounding factors. However, the TAC (BAt) haplotype was associated with increased odds of MDD (adjusted OR = 2.17, 95% CI = 1.30–3.61, p = 0.003) using CCT (baT) as reference haplotype. The findings suggest that the BsmI-ApaI-TaqI TAC (BAt) haplotype of the VDR gene increases susceptibility to MDD.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5, 5th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington
Avenevoli S, Swendsen J, He J-P, Burstein M, Merikangas KR (2015) Major Depression in the National Comorbidity Survey - Adolescent Supplement: Prevalence, Correlates, and Treatment. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 54:37–44.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2014.10.010
Ayman Al-hazmi AA, Mohab Samarkandi, Aseel Alsaadi, Mazen Almehmadi, Sarah Al-Bogami, Ashjan Shami et al. (2019) Vitamin D deficiency and its Receptor Gene Polymorphisms as a risk factor of depression in Saudi Men. Bioscience Researc 16: 1003–8. doi: https://doi.org/10.19082/5427. eCollection 2017 Oct
Baker AR, McDonnell DP, Hughes M, Crisp TM, Mangelsdorf DJ, Haussler MR et al (1988) Cloning and expression of full-length cDNA encoding human vitamin D receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 85:3294–3298. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.85.10.3294
Beelman CA, Parker R (1995) Degradation of mRNA in eukaryotes. Cell 81:179–183
Bierut LJ, Heath AC, Bucholz KK, Dinwiddie SH, Madden PA, Statham DJ et al (1999) Major depressive disorder in a community-based twin sample: are there different genetic and environmental contributions for men and women? Arc Gen Psychiatry 56:557–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(95)90326-7
Border R, Johnson EC, Evans LM, Smolen A, Berley N, Sullivan PF et al (2019) No support for historical candidate gene or candidate gene-by-interaction hypotheses for major depression across multiple large samples. Am J Psychiatry 176:376–387. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2018.18070881.
Bromet E, Andrade LH, Hwang I, Sampson NA, Alonso J, de Girolamo G et al (2011) Cross-national epidemiology of DSM-IV major depressive episode. BMC Med 9:90. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-9-90
Can MŞ, Baykan H, Baykan Ö, Erensoy N, Karlıdere T (2017) Vitamin D levels and vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism in major depression. Psychiatria Danubina 29:179–185. https://doi.org/10.24869/psyd.2017.179
Carling T, Ridefelt P, Hellman P, Rastad J, Akerstrom G (1997) Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms correlate to parathyroid cell function in primary hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:1772–1775. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.82.6.4012
Carling T, Rastad J, Gr Å, Westin G (1998) Vitamin D receptor (VDR) and parathyroid hormone messenger ribonucleic acid levels correspond to polymorphic VDR alleles in human parathyroid Tumors1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:2255–2259. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.83.7.4862
Côté F, Thévenot E, Fligny C, Fromes Y, Darmon M, Ripoche MA (2003) Disruption of the nonneuronal tph1 gene demonstrates the importance of peripheral serotonin in cardiac function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:13525–13530. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2233056100
Court M (2008) Court Lab Calculator http://www.tufts.edu/. Accessed 03 March 2019
Crofts L, Morrison N, Eisman J (1996) Differential expression of VDR gene alleles. J Bone Miner Res 11:S208 (Abstract)
Demay MB, Kiernan MS, DeLuca HF, Kronenberg HM (1992) Characterization of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor interactions with target sequences in the rat osteocalcin gene. Mol Endocrinol 6:557–562. https://doi.org/10.1210/mend.6.4.1316548
Durrin LK, Haile RW, Ingles SA, Coetzee GA (1999) Vitamin D receptor 3′-untranslated region polymorphisms: lack of effect on mRNA stability. Biochim Biophys Acta 1453:311–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4439(99)00007-1
Fang Y, van Meurs JBJ, d'Alesio A, Jhamai M, Zhao H, Rivadeneira F et al (2005) Promoter and 3'-untranslated-region haplotypes in the vitamin D receptor gene predispose to osteoporotic fracture: the Rotterdam study. Am J Hum Genet 77:807–823. https://doi.org/10.1086/497438.
Faraco JH, Morrison NA, Baker A, Shine J, Frossard PM (1989) ApaI dimorphism at the human vitamin D receptor gene locus. Nucleic Acids Res 17:2150. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/17.5.2150
Fernandez-Pujals AM, Adams MJ, Thomson P, McKechanie AG, Blackwood DHR, Smith BH et al (2015) Epidemiology and heritability of major depressive disorder, stratified by age of onset, sex, and illness course in generation Scotland: Scottish family health study (GS:SFHS). PLoS One 10:e0142197. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0142197. eCollection. 2015
Ferrari AJ, Charlson FJ, Norman RE, Patten SB, Freedman G, Murray CJ et al (2010) Burden of depressive disorders by country, sex, age, and year: findings from the global burden of disease study. PLoS Med 10:e1001547. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001547
Gelehrter TD, Collins FS, Ginsburg D (1998) Principles of medical genetics, 2nd edn. Williams & Wilkins, Maryland
Greenland S, Rothman K (2012) Introduction to stratified analysis: selecting confounders for control. In: Rothman K, Greenland S, Lash T (eds) Modern Epidemiology, 3rd edn. Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott & Wilkins, New York, pp 261–262
Gutknecht L, Araragi N, Merker S, Waider J, Sommerlandt FM, Mlinar B et al (2012) Impacts of brain serotonin deficiency following Tph2 inactivation on development and raphe neuron serotonergic specification. PLoS One 7:e43157. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0043157
Guy M, Lowe LC, Bretherton-Watt D, Mansi JL, Peckitt C, Bliss J et al (2004) Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and breast Cancer risk. Clin Cancer Res 10:5472–5481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3332-3
Haeffel GJ, Getchell M, Koposov RA, Yrigollen CM, Deyoung CG, Kliteberg BA et al (2008) Association between polymorphisms in the dopamine transporter gene and depression:evidence for a gene–environment interaction in a sample of juvenile detainees. Psychol Sci 19:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02047.x.
Hasegawa H, Nakamura K (2010) Tryptophan hydroxylase and serotonin synthesis regulation. In: Müller CP, Jacobs BL (eds) Handbook of behavioral neuroscience, 1st edn. Academic Press, pp 183–202
Hustmyer FG, DeLuca HF, Peacock M (1993) Apal, Bsml, EcoRV and Taql polymorphisms at the human vitamin D receptor gene locus in Caucasians, blacks and Asians. Hum Mol Genet 2:487. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/2.4.487
Ibrahim N, Sherina MS, Phang CK, Mukhtar F, Awang H, Ang JK et al (2017) Prevalence and predictors of depression and suicidal ideation among adolescents attending government secondary schools in Malaysia. Med J Malaysia 72:221–227
Jurutka PW, Whitfield GK, Hsieh J-C, Thompson PD, Haussler CA, Haussler MR (2001) Molecular nature of the vitamin D receptor and its role in regulation of gene expression. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2:203–216. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1010062929140.
Kader Maideen SF, Mohd Sidik S, Rampal L, Mukhtar F (2014) Prevalence, Associated Factors and Predictors of Depression among Adults in the Community of Selangor, Malaysia. PLoS One 9:e95395. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095395
Kambale PR, Haldar D, Kabi BC, Kambale KP (2017) Study of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism (FokI, TaqI and ApaI) among prostate Cancer patients in North India. J Clin Diagn Res 11:BC05–BBC8. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2017/24290.9976
Kuningas M, Mooijaart SP, Jolles J, Slagboom PE, Westendorp RGJ, van Heemst D (2009) VDR gene variants associate with cognitive function and depressive symptoms in old age. Neurobiol Aging 30:466–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.07.001
Lemeshow S, Hosmer D, Klar J, Lwanga S, World Health Organization (1990) Adequacy of sample size in health studies. Wiley, Chichester
Little J, Higgins JP, Ioannidis JP, Moher D, Gagnon F, von Elm E et al (2009) STrengthening the REporting of genetic association studies (STREGA): an extension of the STROBE statement. Genet Epidemiol 3:581–598. https://doi.org/10.1002/gepi.20410.
McDonald JH (2012) Handbook of Biological Statistics http://www.biostathandbook.com/multiplecomparisons.html. Accessed 12 March 2019
Morrison NA, Yeoman R, Kelly PJ, Eisman JA (1992) Contribution of trans-acting factor alleles to normal physiological variability: vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism and circulating osteocalcin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:6665–6669. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.89.15.6665
Morrison NA, Qi JC, Tokita A, Kelly PJ, Crofts L, Nguyen TV et al (1994) Prediction of bone density from vitamin D receptor alleles. Nature 367:284–287. https://doi.org/10.1038/367284a0
Ohtera K, Ishii S, Matsuyama T (2001) Influence of the vitamin D receptor alleles on human osteoblast-like cells. J Bone Jt Surg Br 83:134–138. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.83b1.10050
Patrick RP, Ames BN (2014) Vitamin D hormone regulates serotonin synthesis. Part 1: relevance for autism. FASEB J 28:2398–2413. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.13-246546
Pattarachotanant N, Sritharathikhun T, Suttirat S, Tencomnao T (2010) Association of C/T polymorphism in intron 14 of the dopamine transporter gene (rs40184) with major depression in a northeastern Thai population. Genet Mol Res 9:565–572. https://doi.org/10.4238/vol9-1gmr757
Patten SB, Williams JVA, Lavorato DH, Wang JL, McDonald K, Bulloch AGM (2015) Descriptive epidemiology of major depressive disorder in Canada in 2012. Can J Psychiatr 60:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1177/070674371506000106
Remus L, Whitfield G, Jurutka P, et al. (1998) Functional evaluation of endogenous VDR alleles in human fibroblast cell lines: Relative contribution of F/f and L/S genotypes to 1,25(OH)2D3-elicited VDR transactivation ability. Bone 23(Suppl. 5):S198 (abstract 1205).
Sidik SM, Arroll B, Goodyear-Smith F, Ahmad R (2012) Prevalence of depression among women attending a primary urban care clinic in Malaysia. Singap Med J 53:468–473
Sund AM, Larsson B, Wichstrøm L (2011) Prevalence and characteristics of depressive disorders in early adolescents in Central Norway. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health 5:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/1753-2000-5-28
Tan KL, Yadav H (2013) Depression among the urban poor in peninsular Malaysia: a community based cross-sectional study. J Health Psychol 18:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359105311433908
Uitterlinden AG, Fang Y, van Meurs JBJ, Pols HAP, van Leeuwen JPTM (2004) Genetics and biology of vitamin D receptor polymorphisms. Gene 338:143–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2004.05.014
Verbeek W, Gombart AF, Shiohara M, Campbell M, Koeffler HP (1997) Vitamin D receptor: no evidence for allele-specific mRNA stability in cells which are heterozygous for the TaqI restriction enzyme polymorphism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 238:77–80. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1997.7239
von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP (2007) The Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE)statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 370:1453–1457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2014.07.013.
Whitfield GK, Remus LS, Jurutka PW, Zitzer H, Oza AK, Dang HT et al (2001) Functionally relevant polymorphisms in the human nuclear vitamin D receptor gene. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol 177:145–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0303-7207(01)00406-3
WHO (2014) Preventing suicide: a global imperative. World Health Organisation. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/131056/9789241564779_eng.pdf?sequence=1 Accessed 01 March 2019
WHO 2017 Depression and other common mental disorders. Global Health estimates. Geneva: World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/mental_health/management/depression/prevalence_global_health_estimates/en/. Accessed 01 March 2019
WHO 2018 Depression: World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression. Accessed 03 March 2020
Wong SY, Lua PL (2011) Anxiety and depressive symptoms among communities in the East Coast of peninsular Malaysia: a rural exploration. Malaysian J Psychiatry 20.
Yalamanchili V, Gallagher JC (2012) Treatment with hormone therapy and calcitriol did not affect depression in older postmenopausal women: no interaction with estrogen and vitamin D receptor genotype polymorphisms. Menopause 19:697–703. https://doi.org/10.1097/gme.0b013e31823bcec5
Yamagata M, Nakajima S, Tokita A, Sakai N, Yanagihara I, Yabuta K et al (1999) Analysis of the stable levels of messenger RNA derived from different polymorphic alleles in the vitamin D receptor gene. J Bone Miner Metab 17:164–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007740050080.
Zmuda JM, Cauley JA, Ferrell RE (2000) Molecular epidemiology of vitamin D receptor gene variants. Epidemiol Rev 22:203–217. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a018033
Acknowledgements
We thank the Director General of Health Malaysia for his permission to publish this study; we also thank the patients and staff of the hospitals involved, the research assistants, as well as Dr. Azizul Awaluddin, Dr. Sharifah Suziah Syed Mokhtar, Dr. Mazni Mat Junus, Dr. Elinda Tunan, Dr. Ibrahim Mohammed Badamasi, Dr. Vaidehi Ulanganathan, Ms. Aldoghachi Asraa Faris Abdulridha, Mr. Khairul Aiman Bin Lokman, Ms. Nurul Asyikin Abdul Razaq, Ms. Siti Zubaidah Redzuan, and all those who have assisted in one way or another.
Funding
The project was funded by the Research Management Centre Universiti Putra Malaysia (GP-IPB/2013/9415700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS, KH, NI, JS, SP and RR conceptualized and designed the study. AS and YS conducted the molecular work (genotyping). YY, MS and YS analyzed the data. MS, YY, YS and AS wrote the manuscript. MS, YY, YS, KH, NI, JS and SP revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding agency played no role in the study design, analysis, interpretation of data or writing of the manuscript.
Ethics Approval
This study was approved by the Medical and Research Ethics Committee (MREC) of the Ministry of Health Malaysia (NMRR No. NMRR-14-688-19696).
Consent to Participate
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent for Publication
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants at the time of obtaining consent to participate.
Availability of Data and Material
Data and material will be provided upon request.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lye, MS., Tor, YS., Tey, YY. et al. BsmI-ApaI-TaqI TAC (BAt) Haplotype of Vitamin D Receptor Gene Is Associated with Increased Risk of Major Depressive Disorder. J Mol Neurosci 71, 981–990 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01719-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01719-0