Abstract
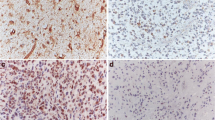
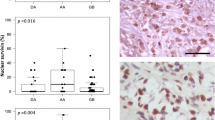
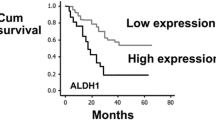
Malignant astrocytomas presenting in humans of any age group are a challenge to diagnose and treat. Hence, there is a quest for new markers to ascertain their grades and predict disease outcomes. Proline, glutamic acid, and leucine-rich protein 1 (PELP1), a nuclear receptor co-regulator, is an oncogene found in various cancers. We postulate that by screening for PELP1, its correlation with survival outcomes of patients across various grades can indicate a plausible novel diagnostic marker and a potential therapeutic target in gliomas. Immunostaining of 100 cases of astrocytomas for PELP1 was performed on paraffin-embedded sections. Results showed that PELP1 expression increases with higher grades; the mean H-score of PELP1 in grade-I astrocytomas was determined to be 112.3, whereas in grade-IV it was 235.1 (P value = 0.0001). Survival analysis of patients with H-score of 200–300 was only 8.8% and 68.8% in patients with scores of 0–100. PELP1 expression in high-grade astrocytomas is an important factor in determining the outcomes.

Evaluation of molecular expression of PELP1 along with Ki-67 LI signifies a linear increase in its expression pattern among different grades of astrocytomas from low- to high-grade tumors, which can serve as a potential prognostic molecular marker in differentiating various types of astrocytomas in humans.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- FFPE:
-
Formalin fixed paraffin embedded
- IHC:
-
Immuno histo chemistry
- PELP1:
-
Proline, glutamic acid, leucine rich protein 1
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Altieri R, Agnoletti A, Quattrucci F, Garbossa D, Calamo Specchia FM, Bozzaro M et al (2014) Molecular biology of gliomas: present and future challenges. Transl Med UniSa 10:29–37
Ambroise MM, Khosla C, Ghosh M, Mallikarjuna VS, Annapurneswari S (2011) Practical value of MIB-1 index in predicting behavior of astrocytomas. Ind J Pathol Microbiol 54(3):520–525. https://doi.org/10.4103/0377-4929.85085
Aziz S, Wik E, Knutsvik G, Klingen TA, Chen Y, Davidsen B et al (2016) Evaluation of tumor cell proliferation by Ki-67 expression and mitotic count in lymph node metastases from breast Cancer. PLoS One 11(3):e0150979. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0150979
Bostrom J, Meyer-Puttlitz B, Wolter M, Blaschke B, Weber RG, Lichter P et al (2001) Alterations of the tumor suppressor genes CDKN2A (p16(INK4a)), p14(ARF), CDKN2B (p15(INK4b)), and CDKN2C (p18(INK4c)) in atypical and anaplastic meningiomas. Am J Pathol 159(2):661–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61737-3
Burger PC, Green SB (1987) Patient age, histologic features, and length of survival in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer 59(9):1617–1625
Cairncross JG, Ueki K, Zlatescu MC, Lisle DK, Finkelstein DM, Hammond RR et al (1998) Specific genetic predictors of chemotherapeutic response and survival in patients with anaplastic oligodendrogliomas. J Natl Cancer Inst 90(19):1473–1479
Chirieac LR (2016) Tumor cell proliferation, proliferative index and mitotic count in lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res 5(5):554–556. https://doi.org/10.21037/tlcr.2016.10.10
Coons SW, Johnson PC, Pearl DK (1997) The prognostic significance of Ki-67 labeling indices for oligodendrogliomas. Neurosurgery 41(4):878–884, discussion 884–875
Daumas-Duport C, Scheithauer B, O'Fallon J, Kelly P (1988) Grading of astrocytomas. A simple and reproducible method. Cancer 62(10):2152–2165
Davis ME (2016) Glioblastoma: overview of disease and treatment. Clin J Oncol Nurs 20(5 Suppl):S2–S8. https://doi.org/10.1188/16.CJON.S1.2-8
De Luca A, Avena P, Sirianni R, Chimento A, Fallo F, Pilon C et al (2017) Role of scaffold protein proline-, glutamic acid-, and leucine-rich protein 1 (PELP1) in the modulation of adrenocortical Cancer cell growth. Cells 6(4):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells6040042
Detre S, Saclani Jotti G, Dowsett M (1995) A "quickscore" method for immunohistochemical semiquantitation: validation for oestrogen receptor in breast carcinomas. J Clin Pathol 48(9):876–878. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.48.9.876
Fernandez C, Figarella-Branger D, Girard N, Bouvier-Labit C, Gouvernet J, Paz Paredes A, Lena G (2003) Pilocytic astrocytomas in children: prognostic factors--a retrospective study of 80 cases. Neurosurgery 53(3):544–553, discussion 554–545
Grivas PD, Tzelepi V, Sotiropoulou-Bonikou G, Kefalopoulou Z, Papavassiliou AG, Kalofonos H (2009) Expression of ERalpha, ERbeta and co-regulator PELP1/MNAR in colorectal cancer: prognostic significance and clinicopathologic correlations. Cell Oncol 31(3):235–247. https://doi.org/10.3233/CLO-2009-0467
Habashy HO, Powe DG, Rakha EA, Ball G, Macmillan RD, Green AR, Ellis IO (2010) The prognostic significance of PELP1 expression in invasive breast cancer with emphasis on the ER-positive luminal-like subtype. Breast Cancer Res Treat 120(3):603–612. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0419-9
Huang HS, Nagane M, Klingbeil CK, Lin H, Nishikawa R, Ji XD et al (1997) The enhanced tumorigenic activity of a mutant epidermal growth factor receptor common in human cancers is mediated by threshold levels of constitutive tyrosine phosphorylation and unattenuated signaling. J Biol Chem 272(5):2927–2935
James CD, Carlbom E, Dumanski JP, Hansen M, Nordenskjold M, Collins VP, Cavenee WK (1988) Clonal genomic alterations in glioma malignancy stages. Cancer Res 48(19):5546–5551
Kefalopoulou Z, Tzelepi V, Zolota V, Grivas PD, Christopoulos C, Kalofonos H et al (2012) Prognostic value of novel biomarkers in astrocytic brain tumors: nuclear receptor co-regulators AIB1, TIF2, and PELP1 are associated with high tumor grade and worse patient prognosis. J Neuro-Oncol 106(1):23–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0637-y
Ladstein RG, Bachmann IM, Straume O, Akslen LA (2010) Ki-67 expression is superior to mitotic count and novel proliferation markers PHH3, MCM4 and mitosin as a prognostic factor in thick cutaneous melanoma. BMC Cancer 10:140. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-10-140
Libermann TA, Nusbaum HR, Razon N, Kris R, Lax I, Soreq H et al (1985) Amplification and overexpression of the EGF receptor gene in primary human glioblastomas. J Cell Sci Suppl 3:161–172
Louis DN (1994) The p53 gene and protein in human brain tumors. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 53(1):11–21
Marquez-Garban DC, Chen HW, Fishbein MC, Goodglick L, Pietras RJ (2007) Estrogen receptor signaling pathways in human non-small cell lung cancer. Steroids 72(2):135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2006.11.019
Montine TJ, Vandersteenhoven JJ, Aguzzi A, Boyko OB, Dodge RK, Kerns BJ, Burger PC (1994) Prognostic significance of Ki-67 proliferation index in supratentorial fibrillary astrocytic neoplasms. Neurosurgery 34(4):674–678, discussion 678–679
Ohgaki H (2009) Epidemiology of brain tumors. Methods Mol Biol 472:323–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-492-0_14
Rajhans R, Nair S, Holden AH, Kumar R, Tekmal RR, Vadlamudi RK (2007) Oncogenic potential of the nuclear receptor coregulator proline-, glutamic acid-, leucine-rich protein 1/modulator of the nongenomic actions of the estrogen receptor. Cancer Res 67(11):5505–5512. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3647
Sareddy GR, Vadlamudi RK (2016) PELP1: structure, biological function and clinical significance. Gene 585(1):128–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2016.03.017
Sukheeja D, Singhvi S, Rai NN, Midya M (2015) A comparative study of histopathology of Astrocytomas with intraoperative cytology with special reference to MIB-1 labelling index. J Clin Diagn Res 9(8):EC01–EC03. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2015/12372.6281
Tihan T, Davis R, Elowitz E, DiCostanzo D, Moll U (2000) Practical value of Ki-67 and p53 labeling indexes in stereotactic biopsies of diffuse and pilocytic astrocytomas. Arch Pathol Lab Med 124(1):108–113. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-9985(2000)124<0108:PVOKAP>2.0.CO;2
Vadlamudi RK, Kumar R (2007) Functional and biological properties of the nuclear receptor coregulator PELP1/MNAR. Nucl Recept Signal 5:e004. https://doi.org/10.1621/nrs.05004
Vadlamudi RK, Wang RA, Mazumdar A, Kim Y, Shin J, Sahin A, Kumar R (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of PELP1, a novel human coregulator of estrogen receptor alpha. J Biol Chem 276(41):38272–38279. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M103783200
Vadlamudi RK, Manavathi B, Balasenthil S, Nair SS, Yang Z, Sahin AA, Kumar R (2005) Functional implications of altered subcellular localization of PELP1 in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 65(17):7724–7732. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0614
Verhaak RG, Hoadley KA, Purdom E, Wang V, Qi Y, Wilkerson MD et al (2010) Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 17(1):98–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2009.12.020
Wen PY, Kesari S (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359(5):492–507. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra0708126
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the management of SRIHER for support & encouragement.
Funding
Indo-Russia grant DST/INT/RUS/RSF/P-26 to SKR is acknowledged. Funding for this project was partly supported by the grant from Department of Biotechnology (GV, DP & KG) vide sanction no. BT/PR5034/BRB/10/1057/2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study concept and design—GV and RSK; scientific guidance—DP and GV; data collection—KP, LDC, AV, HP, DP, KG; data analysis and manuscript preparation—VK, LDC and DP; statistical analysis-RSP; manuscript review—all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the IEC of Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education & Research.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Padmavathy, K.P., Vuttaradhi, V.K., Venu, A. et al. Clinical Evaluation of Proline, Glutamic acid, and Leucine-Rich Protein 1 Expression in Astrocytomas and Correlations with the Proliferation Marker Ki-67. J Mol Neurosci 71, 724–733 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01690-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01690-w