Abstract
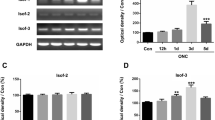
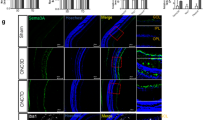
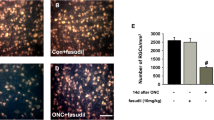
To explore the hypothesis that CD200Fc, a CD200R1 agonist with anti-inflammatory properties, will inhibit retinal glial cells hyperactivation and retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) apoptosis after optic nerve injury. CD200Fc was immediately administered after optic nerve crush (ONC) once by intravitreal injection. Rats were euthanized at 5 days after ONC. The density of RGCs was counted by immunostaining of retina flat mounts for Brn3a. TUNEL assay, immunoblotting analysis of ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1(iba1) (microglia marker) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (astrocytes and Müller cells marker), RT-PCR analysis of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-8 and IL-10, ELISA measure protein levels of inflammatory cytokines and western blot analysis of CD200 and CD200R1 were evaluated. CD200Fc treatment suppressed ONC-induced RGCs loss through inhibition of RGCs apoptosis. Additionally, expression of glial cells activation markers GFAP and iba1 and production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (COX-2, iNOS, MCP-1, TNF-α, IL-8) were decreased in CD200Fc treated animals after ONC. Meanwhile, anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 was increased by CD200Fc treatment in ONC-induced rat retina. Finally, we found that CD200Fc significantly inhibited ONC-induced increased in expression of CD200 and raised the already high basal CD200R1 expression in the rat retina after ONC. Our results demonstrated that the anti-inflammatory effects of CD200Fc in ONC rats model through inhibited the activation of retinal glial cells via the interaction between CD200 and CD200R1, and the neuroprotective effects of CD200Fc on RGCs thought inhibited its apoptosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calkins DJ, Pekny M, Cooper ML, Benowitz L, Lasker IIA, Glaucomatous Neurodegeneration P (2017) The challenge of regenerative therapies for the optic nerve in glaucoma. Exp Eye Res 157:28–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2017.01.007
Chitnis T, Imitola J, Wang Y, Elyaman W, Chawla P, Sharuk M, Raddassi K, Bronson RT, Khoury SJ (2007) Elevated neuronal expression of CD200 protects Wld s mice from inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration. Am J Pathol 170(5):1695–1712. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2007.060677
Cox FF, Carney D, Miller AM, Lynch MA (2012) CD200 fusion protein decreases microglial activation in the hippocampus of aged rats. Brain Behav Immun 26(5):789–796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2011.10.004
Davis BM, Crawley L, Pahlitzsch M, Javaid F, Cordeiro MF (2016) Glaucoma: the retina and beyond. Acta Neuropathol 132(6):807–826. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-016-1609-2
Feng Z et al (2017) Anti-inflammation conferred by stimulation of CD200R1 via Dok1 pathway in rat microglia after germinal matrix hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X17725211
He A, Shao J, Zhang Y, Lu H, Wu Z, Xu Y (2017) CD200Fc reduces LPS-induced IL-1beta activation in human cervical cancer cells by modulating TLR4-NF-kappaB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Oncotarget 8:33214–33224. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16596
Hernangomez M, Carrillo-Salinas F, Mecha M, Correa F, Mestre L, Loria F, Feliu A, Docagne F, Guaza C (2014) Brain innate immunity in the regulation of neuroinflammation: therapeutic strategies by modulating CD200-CD200R interaction involve the cannabinoid system. Curr Pharm Des 20(29):4707–4722. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612820666140130202911
Hernangomez M, Klusakova I, Joukal M, Hradilova-Svizenska I, Guaza C, Dubovy P (2016) CD200R1 agonist attenuates glial activation, inflammatory reactions, and hypersensitivity immediately after its intrathecal application in a rat neuropathic pain model. J Neuroinflammation 13(1):43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0508-8
Hoek RM, Ruuls SR, Murphy CA, Wright GJ, Goddard R, Zurawski SM, Blom B, Homola ME, Streit WJ, Brown MH, Barclay AN, Sedgwick JD (2000) Down-regulation of the macrophage lineage through interaction with OX2 (CD200). Science 290(5497):1768–1771. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.290.5497.1768
Jiang L, Xu F, He W, Chen L, Zhong H, Wu Y, Zeng S, Li L, Li M (2016) CD200Fc reduces TLR4-mediated inflammatory responses in LPS-induced rat primary microglial cells via inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway. Inflamm Res 65(7):521–532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-016-0932-3
Kim SJ, Ko JH, Yun JH, Kim JA, Kim TE, Lee HJ, Kim SH, Park KH, Oh JY (2013) Stanniocalcin-1 protects retinal ganglion cells by inhibiting apoptosis and oxidative damage. PLoS One 8(5):e63749. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063749
Koning N, Swaab DF, Hoek RM, Huitinga I (2009) Distribution of the immune inhibitory molecules CD200 and CD200R in the normal central nervous system and multiple sclerosis lesions suggests neuron-glia and glia-glia interactions. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 68(2):159–167. https://doi.org/10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181964113
Krizaj D, Ryskamp DA, Tian N, Tezel G, Mitchell CH, Slepak VZ, Shestopalov VI (2014) From mechanosensitivity to inflammatory responses: new players in the pathology of glaucoma. Curr Eye Res 39(2):105–119. https://doi.org/10.3109/02713683.2013.836541
Levin LA, Crowe ME, Quigley HA, Lasker IIA, Glaucomatous Neurodegeneration P (2017) Neuroprotection for glaucoma: requirements for clinical translation. Exp Eye Res 157:34–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2016.12.005
Levkovitch-Verbin H (2015) Retinal ganglion cell apoptotic pathway in glaucoma: initiating and downstream mechanisms. Prog Brain Res 220:37–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pbr.2015.05.005
Lin SF, Chien JY, Kapupara K, Huang CF, Huang SP (2017) Oroxylin A promotes retinal ganglion cell survival in a rat optic nerve crush model. PLoS One 12(6):e0178584. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0178584
Liu Y, Bando Y, Vargas-Lowy D, Elyaman W, Khoury SJ, Huang T, Reif K, Chitnis T (2010) CD200R1 agonist attenuates mechanisms of chronic disease in a murine model of multiple sclerosis. J Neurosci 30(6):2025–2038. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4272-09.2010
Liu L, Sun Q, Wang R, Chen Z, Wu J, Xia F, Fan XQ (2016) Methane attenuates retinal ischemia/reperfusion injury via anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic pathways. Brain Res 1646:327–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.05.037
Lu YB et al (2013) Biomechanical properties of retinal glial cells: comparative and developmental data. Exp Eye Res 113:60–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2013.05.012
Mac Nair CE, Nickells RW (2015) Neuroinflammation in glaucoma and optic nerve damage. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 134:343–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.06.010
Mac Nair CE, Schlamp CL, Montgomery AD, Shestopalov VI, Nickells RW (2016) Retinal glial responses to optic nerve crush are attenuated in Bax-deficient mice and modulated by purinergic signaling pathways. J Neuroinflammation 13(1):93. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0558-y
Mesentier-Louro LA et al (2017) Time-dependent nerve growth factor signaling changes in the rat retina during optic nerve crush-induced degeneration of retinal ganglion cells. Int J Mol Sci 18(1):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010098
Ramirez AI, de Hoz R, Salobrar-Garcia E, Salazar JJ, Rojas B, Ajoy D, López-Cuenca I, Rojas P, Triviño A, Ramírez JM (2017) The role of microglia in retinal neurodegeneration: Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson, and glaucoma. Front Aging Neurosci 9:214. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00214
Ren Y, Ye M, Chen S, Ding J (2016) CD200 inhibits inflammatory response by promoting KATP Channel opening in microglia cells in Parkinson’s disease. Med Sci Monit 22:1733–1741. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.898400
Ribas VT, Koch JC, Michel U, Bahr M, Lingor P (2017) Attenuation of axonal degeneration by calcium channel inhibitors improves retinal ganglion cell survival and regeneration after optic nerve crush. Mol Neurobiol 54(1):72–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9676-2
Rosen AM, Stevens B (2010) The role of the classical complement cascade in synapse loss during development and glaucoma. Adv Exp Med Biol 703:75–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-5635-4_6
Ryul Ahn H, Kim KA, Kang SW, Lee JY, Kim TJ, Jung SH (2017) Persimmon leaves (Diospyros kaki) extract protects optic nerve crush-induced retinal degeneration. Sci Rep 7:46449. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46449
Schuld NJ, Hussong SA, Kapphahn RJ, Lehmann U, Roehrich H, Rageh AA, Heuss ND, Bratten W, Gregerson DS, Ferrington DA (2015) Immunoproteasome deficiency protects in the retina after optic nerve crush. PLoS One 10(5):e0126768. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126768
Taylor S, Calder CJ, Albon J, Erichsen JT, Boulton ME, Morgan JE (2011) Involvement of the CD200 receptor complex in microglia activation in experimental glaucoma. Exp Eye Res 92(5):338–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2011.01.012
Vecino E, Rodriguez FD, Ruzafa N, Pereiro X, Sharma SC (2016) Glia-neuron interactions in the mammalian retina. Prog Retin Eye Res 51:1–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2015.06.003
Walker DG, Dalsing-Hernandez JE, Campbell NA, Lue LF (2009) Decreased expression of CD200 and CD200 receptor in Alzheimer’s disease: a potential mechanism leading to chronic inflammation. Exp Neurol 215(1):5–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.09.003
Williams PA, Marsh-Armstrong N, Howell GR, Lasker IIA, Glaucomatous Neurodegeneration P (2017) Neuroinflammation in glaucoma: a new opportunity. Exp Eye Res 157:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2017.02.014
Xu J, Lu L, Lu J, Xia J, Lu H, Yang L, Xia W, Shen S (2016) CD200Fc attenuates inflammatory responses and maintains barrier function by suppressing NF-kappaB pathway in cigarette smoke extract induced endothelial cells. Biomed Pharmacother 84:714–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.093
Xu Y, Yang B, Hu Y, Lu L, Lu X, Wang J, Xu F, Yu S, Huang J, Liang X (2016) Wogonin prevents TLR4-NF-kappaB-medicated neuro-inflammation and improves retinal ganglion cells survival in retina after optic nerve crush. Oncotarget 7:72503–72517. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12700
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81660168, 81560166, 81460087, 81760172, 81760178, and 81660161), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (No. 2012GXNSFAA276039 and No. 2011GXNSFA018228), and 139 Guangxi Training Program Foundation for the High-level Talents.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All experimental protocols of this study were enforced in accordance with the procedure outlined in the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) Statement for the Use of Animals in Ophthalmic and Vision Research, and were handled in conformity to the Ethics Committee of the People’s Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, R., Lan, Q., Chen, L. et al. CD200Fc Attenuates Retinal Glial Responses and RGCs Apoptosis After Optic Nerve Crush by Modulating CD200/CD200R1 Interaction. J Mol Neurosci 64, 200–210 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-017-1020-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-017-1020-z