Abstract
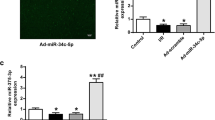
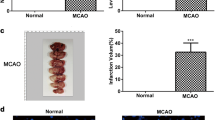
microRNA-134 (miR-134) has been reported to be a brain-specific miRNA and is differently expressed in brain tissues subjected to ischemic injury. However, the underlying mechanism of miR-134 in regulating cerebral ischemic injury remains poorly understood. The current study was designed to delineate the molecular basis of miR-134 in regulating cerebral ischemic injury. Using the oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) model of hippocampal neuron ischemia in vitro, we found that the overexpression of miR-134 mediated by recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector infection significantly promoted neuron death induced by OGD/reoxygenation, whereas the inhibition of miR-134 provided protective effects against OGD/reoxygenation-induced cell death. Moreover, cyclic AMP (cAMP) response element-binding protein (CREB) as a putative target of miR-134 was downregulated and upregulated by miR-134 overexpression or inhibition, respectively. The direct interaction between miR-134 and the 3′-untranslated region (UTR) of CREB mRNA was further confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter assay. Overexpression of miR-134 also inhibited the expression of the downstream gene of CREB, including brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and the anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2, whereas the inhibition of miR-134 upregulated the expression of BDNF and Bcl-2 in neurons after OGD/reoxygenation. Notably, the knockdown of CREB by CREB siRNA apparently abrogated the protective effect of anti-miR-134 on OGD/reoxygenation-induced cell death. Taken together, our study suggests that downregulation of miR-134 alleviates ischemic injury through enhancing CREB expression and downstream genes, providing a promising and potential therapeutic target for cerebral ischemic injury.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- miR-134:
-
MicroRNA-134
- OGD:
-
Oxygen-glucose deprivation
- AAV:
-
Adeno-associated virus
- CREB:
-
Cyclic AMP (cAMP) response element-binding protein
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
References
Almeida RD, Manadas BJ, Melo CV, Gomes JR, Mendes CS, Graos MM, Carvalho RF, Carvalho AP, Duarte CB (2005) Neuroprotection by BDNF against glutamate-induced apoptotic cell death is mediated by ERK and PI3-kinase pathways. Cell Death Differ 12:1329–1343
Arber S, Barbayannis FA, Hanser H, Schneider C, Stanyon CA, Bernard O, Caroni P (1998) Regulation of actin dynamics through phosphorylation of cofilin by LIM-kinase. Nature 393:805–809
Barca-Mayo O, De Pietri Tonelli D (2014) Convergent microRNA actions coordinate neocortical development. Cell Mol Life Sci 71:2975–2995
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Chi W, Meng F, Li Y, Wang Q, Wang G, Han S, Wang P, Li J (2014) Downregulation of miRNA-134 protects neural cells against ischemic injury in N2A cells and mouse brain with ischemic stroke by targeting HSPA12B. Neuroscience 277C:111–122
Di Y, Lei Y, Yu F, Changfeng F, Song W, Xuming M (2014) MicroRNAs expression and function in cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. J Mol Neurosci 53:242–250
Dirnagl U, Iadecola C, Moskowitz MA (1999) Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends Neurosci 22:391–397
Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M, Davis SM (2008) Stroke. Lancet 371:1612–1623
Du K, Montminy M (1998) CREB is a regulatory target for the protein kinase Akt/PKB. J Biol Chem 273:32377–32379
Finkbeiner S (2000) CREB couples neurotrophin signals to survival messages. Neuron 25:11–14
Foust KD, Nurre E, Montgomery CL, Hernandez A, Chan CM, Kaspar BK (2009) Intravascular AAV9 preferentially targets neonatal neurons and adult astrocytes. Nat Biotechnol 27:59–65
Gao J, Wang WY, Mao YW, Graff J, Guan JS, Pan L, Mak G, Kim D, Su SC, Tsai LH (2010) A novel pathway regulates memory and plasticity via SIRT1 and miR-134. Nature 466:1105–1109
Han BH, D’Costa A, Back SA, Parsadanian M, Patel S, Shah AR, Gidday JM, Srinivasan A, Deshmukh M, Holtzman DM (2000) BDNF blocks caspase-3 activation in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Neurobiol Dis 7:38–53
Hu BR, Fux CM, Martone ME, Zivin JA, Ellisman MH (1999) Persistent phosphorylation of cyclic AMP responsive element-binding protein and activating transcription factor-2 transcription factors following transient cerebral ischemia in rat brain. Neuroscience 89:437–452
Jimenez-Mateos EM, Engel T, Merino-Serrais P, McKiernan RC, Tanaka K, Mouri G, Sano T, O’Tuathaigh C, Waddington JL, Prenter S et al (2012) Silencing microRNA-134 produces neuroprotective and prolonged seizure-suppressive effects. Nat Med 18:1087–1094
Jin K, Mao XO, Simon RP, Greenberg DA (2001) Cyclic AMP response element binding protein (CREB) and CREB binding protein (CBP) in global cerebral ischemia. J Mol Neurosci 16:49–56
Kitagawa K (2007) CREB and cAMP response element-mediated gene expression in the ischemic brain. FEBS J 274:3210–3217
Krohn AJ, Preis E, Prehn JH (1998) Staurosporine-induced apoptosis of cultured rat hippocampal neurons involves caspase-1-like proteases as upstream initiators and increased production of superoxide as a main downstream effector. J Neurosci 18:8186–8197
Liu C, Peng Z, Zhang N, Yu L, Han S, Li D, Li J (2012) Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs and their PKC-isoform specific gene network prediction during hypoxic pre-conditioning and focal cerebral ischemia of mice. J Neurochem 120:830–841
Liu X, Li F, Zhao S, Luo Y, Kang J, Zhao H, Yan F, Li S, Ji X (2013) MicroRNA-124-mediated regulation of inhibitory member of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 family in experimental stroke. Stroke 44:1973–1980
Lo EH, Dalkara T, Moskowitz MA (2003) Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:399–415
Mabuchi T, Kitagawa K, Kuwabara K, Takasawa K, Ohtsuki T, Xia Z, Storm D, Yanagihara T, Hori M, Matsumoto M (2001) Phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein in hippocampal neurons as a protective response after exposure to glutamate in vitro and ischemia in vivo. J Neurosci 21:9204–9213
Marsh JD, Keyrouz SG (2010) Stroke prevention and treatment. J Am Coll Cardiol 56:683–691
Martinou JC, Dubois-Dauphin M, Staple JK, Rodriguez I, Frankowski H, Missotten M, Albertini P, Talabot D, Catsicas S, Pietra C et al (1994) Overexpression of BCL-2 in transgenic mice protects neurons from naturally occurring cell death and experimental ischemia. Neuron 13:1017–1030
Mayr BM, Canettieri G, Montminy MR (2001) Distinct effects of cAMP and mitogenic signals on CREB-binding protein recruitment impart specificity to target gene activation via CREB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:10936–10941
Mendell JT, Olson EN (2012) MicroRNAs in stress signaling and human disease. Cell 148:1172–1187
Peng Z, Li J, Li Y, Yang X, Feng S, Han S (2013) Downregulation of miR-181b in mouse brain following ischemic stroke induces neuroprotection against ischemic injury through targeting heat shock protein A5 and ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L1. J Neurosci Res 91:1349–1362
Riccio A, Ahn S, Davenport CM, Blendy JA, Ginty DD (1999) Mediation by a CREB family transcription factor of NGF-dependent survival of sympathetic neurons. Science 286:2358–2361
Santarelli DM, Beveridge NJ, Tooney PA, Cairns MJ (2011) Upregulation of dicer and microRNA expression in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex Brodmann area 46 in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 69:180–187
Schratt GM, Tuebing F, Nigh EA, Kane CG, Sabatini ME, Kiebler M, Greenberg ME (2006) A brain-specific microRNA regulates dendritic spine development. Nature 439:283–289
Shaywitz AJ, Greenberg ME (1999) CREB: a stimulus-induced transcription factor activated by a diverse array of extracellular signals. Annu Rev Biochem 68:821–861
Tanaka K (2001) Alteration of second messengers during acute cerebral ischemia—adenylate cyclase, cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, and cyclic AMP response element binding protein. Prog Neurobiol 65:173–207
Tao X, Finkbeiner S, Arnold DB, Shaywitz AJ, Greenberg ME (1998) Ca2+ influx regulates BDNF transcription by a CREB family transcription factor-dependent mechanism. Neuron 20:709–726
Walton M, Connor B, Lawlor P, Young D, Sirimanne E, Gluckman P, Cole G, Dragunow M (1999) Neuronal death and survival in two models of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 29:137–168
Wang P, Liang J, Li Y, Li J, Yang X, Zhang X, Han S, Li S (2014) Down-regulation of miRNA-30a alleviates cerebral ischemic injury through enhancing beclin 1-mediated autophagy. Neurochem Res 39:1279–1291
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI, Diederichs S (2009) Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol 11:228–234
Yang N, Higuchi O, Ohashi K, Nagata K, Wada A, Kangawa K, Nishida E, Mizuno K (1998) Cofilin phosphorylation by LIM-kinase 1 and its role in Rac-mediated actin reorganization. Nature 393:809–812
Yellon DM, Hausenloy DJ (2007) Myocardial reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med 357:1121–1135
Zhu F, Liu JL, Li JP, Xiao F, Zhang ZX, Zhang L (2014) MicroRNA-124 (miR-124) regulates Ku70 expression and is correlated with neuronal death induced by ischemia/reperfusion. J Mol Neurosci 52:148–155
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Weidong Huang and Xiaobin Liu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, W., Liu, X., Cao, J. et al. miR-134 Regulates Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury-Induced Neuronal Cell Death by Regulating CREB Signaling. J Mol Neurosci 55, 821–829 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0434-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0434-0