Abstract
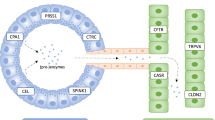
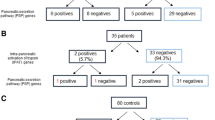
It is thought that many of the idiopathic pancreatitis could have a genetic base. Approximately 50% of them correspond to CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene) and SPINK-1 (serine protease inhibitor Kazal type 1) mutations. A recent study compares patients with acute pancreatitis and SPINK-1 mutation with patients with idiopathic acute pancreatitis. The study highlights a 12-fold increased risk of developing pancreatic cancer with SPINK-1 mutation versus the control group. Nonetheless, authors conclude that only specific pN34s mutation is related to pancreatic cancer. This relation is controversial, and international consensus guidelines for the follow-up in chronic pancreatitis with pancreatic cancer still do not recommend follow-up in SPINK-1 p. N34S mutation. We believe that developing prospective studies in which subgroups of patients with SPINK-1 mutation benefit from closer follow-ups would be necessary.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh VK, et al. Diagnosis and management of chronic pancreatitis: a review. JAMA. 2019;322(24):2422–34. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.19411.
Witt H, et al. Mutations in the gene encoding the serine protease inhibitor, Kazal type 1 are associated with chronic pancreatitis. Nat Genet. 2000;25:213–6.
Hegyi E, et al. Genetic risk in chronic pancreatitis: the trypsin-dependent pathway. Dig Dis Sci. 2017;62(7):1692–701.
Zou WB, et al. Clarifying the clinical relevance of SPINK-1 intronic variants in chronic pancreatitis. Gut. 2016;65(5):884–6.
Muller, et al. Natural History of SPINK-1 germline mutation. EBioMedicine. 2019 Oct;48:581–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.09.032.
Guerra C, et al. Pancreatitis-induced inflammation contributes to pancreatic ancer by inhibiting oncogene-induced senscence. Canc Cell. 2011;19:728–39.
Malka D, et al. F. Risk of pancreatic adenocarcinoma in chronic pancreatitis. Gut. 2002;51(6): 849–52.
Schubert, et al. CFTR, SPINK-1, PRSS1 and CTRC mutations are not associated with pancreatic cancer in German patients. Pancreas. 2014;43:1078–82.
Greenhalf W, et al. International consensus guidelines on surveillance for pancreatic cancer in chronic pancreatitis. Recommendations from the working group for the international consensus guidelines for chronic pancreatitis in collaboration with the International Association of Pancreatology, the American Pancreatic Association, the Japan Pancreas Society, and European Pancreatic Club. Pancreatology. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2020.05.011.
Suzuki M, et al. Is Spink1 gene mutation associated with development of pancreatic cancer? New insight from a large retrospective study. EBioMedicine. 2019;50:5–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom2019.10.065.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Enjuto, D.T., Herrera, N., J. Ceinos, C. et al. Hereditary Pancreatitis Related to SPINK-1 Mutation. Is There an Increased Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer?. J Gastrointest Canc 54, 268–269 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-021-00729-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-021-00729-4