Abstract
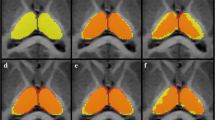
This study aims to determine the most reliable method for infant hippocampal segmentation by comparing magnetic resonance (MR) imaging post-acquisition processing techniques: contrast to noise ratio (CNR) enhancement, or reformatting to standard orientation. MR scans were performed with a 1.5 T GE scanner to obtain dual echo T2 and proton density (PD) images at term equivalent (38–42 weeks’ gestational age). 15 hippocampi were manually traced four times on ten infant images by 2 independent raters on the original T2 image, as well as images processed by: a) combining T2 and PD images (T2-PD) to enhance CNR; then b) reformatting T2-PD images perpendicular to the long axis of the left hippocampus. CNRs and intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) were calculated. T2-PD images had 17% higher CNR (15.2) than T2 images (12.6). Original T2 volumes’ ICC was 0.87 for rater 1 and 0.84 for rater 2, whereas T2-PD images’ ICC was 0.95 for rater 1 and 0.87 for rater 2. Reliability of hippocampal segmentation on T2-PD images was not improved by reformatting images (rater 1 ICC = 0.88, rater 2 ICC = 0.66). Post-acquisition processing can improve CNR and hence reliability of hippocampal segmentation in neonate MR scans when tissue contrast is poor. These findings may be applied to enhance boundary definition in infant segmentation for various brain structures or in any volumetric study where image contrast is sub-optimal, enabling hippocampal structure-function relationships to be explored.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abernethy, L. J., Palaniappan, M., & Cooke, R. W. (2002). Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in survivors of very low birth weight. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 87(4), 279–283.
Abernethy, L. J., Cooke, R. W. I., & Foulder-Hughes, L. (2004). Caudate and hippocampal volumes, intelligence, and motor impairment in 7-year-old children who were born preterm. Pediatric Research, 55(5), 884–893.
Bartzokis, G., Altshuler, L. L., Greider, T., Curran, J., Keen, B., & Dixon, W. J. (1998). Reliability of medial temporal lobe volume measurements using reformatted 3D images. Psychiatry Research, 82(1), 11–24.
Bergouignan, L., Chupin, M., Czechowska, Y., Kinkingnehun, S., Lemogne, C., Le Bastard, G., et al. (2009). Can voxel based morphometry, manual segmentation and automated segmentation equally detect hippocampal volume differences in acute depression? NeuroImage, 45(1), 29–37.
Bridle, N., Pantelis, C., Wood, S. J., Coppola, R., Velakoulis, D., McStephen, M., et al. (2002). Thalamic and caudate volumes in monozygotic twins discordant for schizophrenia. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 36(3), 347–354.
Conklin, J., Winter, J. D., Thompson, R. T., & Gelman, N. (2008). High-contrast 3D neonatal brain imaging with combined T1- and T2-weighted MP-RAGE. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 59(5), 1190–1196.
Duvernoy, H. M. (1988). The human Hippocampus. An atlas of applied anatomy. Munchen: J. F. Bergmann Verlag.
Geuze, E., Vermetten, E., & Bremner, J. D. (2005a). MR-based in vivo hippocampal volumetrics: 1. Review of methodologies currently employed. Molecular Psychiatry, 10(2), 147–159.
Geuze, E., Vermetten, E., & Bremner, J. D. (2005b). MR-based in vivo hippocampal volumetrics: 2. Findings in neuropsychiatric disorders. Molecular Psychiatry, 10(2), 160–184.
Hasboun, D., Chantome, M., Zouaoui, A., Sahel, M., Deladoeuille, M., Sourour, N., et al. (1996). MR determination of hippocampal volume: Comparison of three methods. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 17(6), 1091–1098.
Jack, C., Jr., Bentley, M., Twomey, C., & Zinsmeister, A. (1990). MR imaging-based volume measurements of the hippocampal formation and anterior temporal lobe: validation studies. Radiology, 176(1), 205–209.
Jack, C. R., Jr., Theodore, W. H., Cook, M., & McCarthy, G. (1995). MRI-based hippocampal volumetrics: data acquisition, normal ranges, and optimal protocol. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 13(8), 1057–1064.
Jeukens, C. R., Vlooswijk, M. C., Majoie, H. J., de Krom, M. C., Aldenkamp, A. P., Hofman, P. A., et al. (2009). Hippocampal MRI volumetry at 3 Tesla: reliability and practical guidance. Investigative Radiology, 44(9), 509–517.
Klauschen, F., Goldman, A., Barra, V., Meyer-Lindenberg, A., & Lundervold, A. (2009). Evaluation of automated brain MR image segmentation and volumetry methods. Human Brain Mapping, 30(4), 1310–1327.
Konrad, C., Ukas, T., Nebel, C., Arolt, V., Toga, A. W., & Narr, K. L. (2009). Defining the human hippocampus in cerebral magnetic resonance images–an overview of current segmentation protocols. NeuroImage, 47(4), 1185–1195.
Kretschmann, H. J., Kammradt, G., Krauthausen, I., Sauer, B., & Wingert, F. (1986). Growth of the hippocampal formation in man. Bibliotheca Anatomica, 28, 27–52.
Lim, K. O., & Pfefferbaum, A. (1989). Segmentation of MR brain images into cerebrospinal fluid spaces, white and grey matter. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography, 13, 588–593.
Lodygensky, G. A., Rademaker, K., Zimine, S., Gex-Fabry, M., Lieftink, A. F., Lazeyras, F., et al. (2005). Structural and functional brain development after hydrocortisone treatment for neonatal chronic lung disease. Pediatrics, 116(1), 1–7.
Lodygensky, G. A., Seghier, M. L., Warfield, S. K., Tolsa, C. B., Sizonenko, S., Lazeyras, F., et al. (2008). Intrauterine growth restriction affects the preterm infant’s hippocampus. Pediatric Research, 63(4), 438–443.
Mai, J. K., Assheuer, J., & Paxinos, G. (1997). Atlas of the human brain. San Diego: Academic.
Malykhin, N. V., Bouchard, T. P., Ogilvie, C. J., Coupland, N. J., Seres, P., & Camicioli, R. (2007). Three-dimensional volumetric analysis and reconstruction of amygdala and hippocampal head, body and tail. Psychiatry Research, 155(2), 155–165.
Naidich, T. P., Daniels, D. L., Haughton, V. M., Williams, A., Pojunas, K., & Palacios, E. (1987). Hippocampal formation and related structures of the limbic lobe: anatomic-MR correlation. Part I. Surface features and coronal sections. Radiology, 162(3), 747–754.
Obenaus, A., Yong-Hing, C. J., Tong, K. A., & Sarty, G. E. (2001). A reliable method for measurement and normalization of pediatric hippocampal volumes. Pediatric Research, 50(1), 124–132.
Pantel, J., O’Leary, D. S., Cretsinger, K., Bockholt, H. J., Keefe, H., Magnotta, V. A., et al. (2000). A new method for the in vivo volumetric measurement of the human hippocampus with high neuroanatomical accuracy. Hippocampus, 10(6), 752–758.
Patwardhan, A. J., Eliez, S., Warsofsky, I. S., Glover, G. H., White, C. D., Giedd, J. N., et al. (2001). Effects of image orientation on the comparability of pediatric brain volumes using three-dimensional MR data. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography, 25(3), 452–457.
Peterson, B. S., Vohr, B., Staib, L. H., Cannistraci, C. J., Dolberg, A., Schneider, K. C., et al. (2000). Regional brain volume abnormalities and long-term cognitive outcome in preterm infants. Journal of the American Medical Association, 284(15), 1939–1947.
Saitoh, O., Karns, C. M., & Courchesne, E. (2001). Development of the hippocampal formation from 2 to 42 years: MRI evidence of smaller area dentata in autism. Brain, 124(Pt 7), 1317–1324.
Schuff, N., Woerner, N., Boreta, L., Kornfield, T., Shaw, L. M., Trojanowski, J. Q., et al. (2009). MRI of hippocampal volume loss in early Alzheimer’s disease in relation to ApoE genotype and biomarkers. Brain, 132(Pt 4), 1067–1077.
Thompson, D. K., Wood, S. J., Doyle, L. W., Warfield, S. K., Lodygensky, G. A., Anderson, P. J., et al. (2008). Neonate hippocampal volumes: Prematurity, perinatal predictors, and 2-year outcome. Annals of Neurology, 63(5), 642–651.
Thompson, D. K., Wood, S. J., Doyle, L. W., Warfield, S. K., Egan, G. F., & Inder, T. E. (2009). MR-determined hippocampal asymmetry in full-term and preterm neonates. Hippocampus, 19(2), 118–123.
Vannier, M. W., Butterfield, R. L., Jordan, D., Murphy, W. A., Levitt, R. G., & Gado, M. (1985). Multispectral analysis of magnetic resonance images. Radiology, 154(1), 221–224.
Watson, C., Andermann, F., Gloor, P., Jonesgotman, M., Peters, T., Evans, A., et al. (1992). Anatomic Basis of Amygdaloid and Hippocampal Volume Measurement by Magnetic-Resonance-Imaging. Neurology, 42(9), 1743–1750.
Wieshmann, U. C., Free, S. L., Stevens, J. M., & Shorvon, S. D. (1998). Image contrast and hippocampal volumetric measurements. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 16(1), 13–17.
Williams, L. A., Gelman, N., Picot, P. A., Lee, D. S., Ewing, J. R., Han, V. K., et al. (2005). Neonatal brain: regional variability of in vivo MR imaging relaxation rates at 3.0T–initial experience. Radiology, 235(2), 595–603.
Williams, L. A., DeVito, T. J., Winter, J. D., Orr, T. N., Thompson, R. T., & Gelman, N. (2007). Optimization of 3D MP-RAGE for neonatal brain imaging at 3.0T. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 25(8), 1162–1170.
Wu, W. C., Huang, C. C., Chung, H. W., Liou, M., Hsueh, C. J., Lee, C. S., et al. (2005). Hippocampal alterations in children with temporal lobe epilepsy with or without a history of febrile convulsions: evaluations with MR volumetry and proton MR spectroscopy. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 26(5), 1270–1275.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully thank Merilyn Bear, Michael Kean, Katherine Lee, Gregory A. Lodygensky, Hong X. Wang, Michael J.Farrell, Peter J. Anderson, and Rodney W. Hunt, the VIBeS and Developmental Imaging teams at the Murdoch Childrens Research Institute, as well as the families and infants who participated in this study.
Grant sponsors
National Medical and Health Research Council of Australia; Grant number: 237117; Grant sponsor: NIH; Grant number: R01 RR021885, R01 GM074068, R01 EB008015, P30 HD018655; Grant sponsor: NHMRC Research Fellowship; Grant number: 400317; Grant sponsors: United Cerebral Palsy Foundation (USA), Mather Foundation (USA), Brown Foundation (USA), NHMRC Clinical Career Development Award, NARSAD Young Investigator Award, Victorian Government’s Operational Infrastructure Support Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, D.K., Ahmadzai, Z.M., Wood, S.J. et al. Optimizing Hippocampal Segmentation in Infants Utilizing MRI Post-Acquisition Processing. Neuroinform 10, 173–180 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-011-9137-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-011-9137-7