Abstract
Purpose
The deiodinases activate or inactivate the thyroid hormones (TH) in virtually all tissues in both physiological and pathological conditions. The three deiodinases, DIO1, DIO2, and DIO3, have different catalytic functions and regulate TH tissue distribution. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the modulation of gene expression of the deiodinases and TH transporters and protein levels of DIO1 in parietal and frontal areas of cerebral cortex of spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs), after two successive mandibular extensions (ME).
Methods
ME was performed on anesthetized rats by a dilatator appropriately designed and real-time PCR and western blotting techniques were employed for gene expression and protein level study.
Results
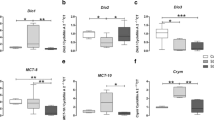
Mean blood pressure (MBP) significantly decreased in 2ME-treated rats when compared to sham-operated rats (p < 0.001) and this decrease lasted for the entire observation period. In gene expression analysis, in 2ME-treated rats we did not observe any significant variation of DIO1 and DIO3 with respect to the sham-operated rats. Differently, DIO2 gene expression significantly increased in frontal area of 2ME-treated rats, with respect to sham-operated rats (p < 0.01). Furthermore, in parietal area, protein levels of DIO1 in 2ME-treated rats were significantly higher than in sham-operated rats (p < 0.01). Moreover MCT8 and OATP1C1 both resulted significantly higher (p < 0.05 and p < 0.001) in sham frontal cortex.
Conclusion
In summary, our data on SHRs, while confirming the hypotensive effect of two MEs, show that the treatment also solicits the three deiodinases production in the cerebral cortex.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Mendoza, A.N. Hollenberg, New insights into thyroid hormone action. Pharmacol. Ther. 173, 135–145 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.02.012
G. Brent, Mechanisms of thyroid hormone action. J. Clin. Investig. 122, 3035–3043 (2012)
J.P. Chanoine, L.E. Braverman, A.P. Farwell, The thyroid gland is a major source of circulating T3 in the rat. J. Clin. Investig. 91, 2709–2713 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI116510
J.J. Distefano III, M. Jang, T.K. Malone, M. Broutman, Comprehensive kinetics of triiodothyronine production, distribution, and metabolism in blood and tissue pools of the rat using optimized blood-sampling protocols. Endocrinology 110, 198–213 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1210/endo-110-1-198
P.R. Larsen, J.E. Silva, M.M. Kaplan, Relationships between circulating and intracellular thyroid hormones: physiological and clinical implications. Endocr. Rev. 2, 87–102 (1981)
B. Gereben, A.M. Zavacki, S. Ribich, B.W. Kim, S.A. Huang, W.S. Simonides, A. Zeold, A.C. Bianco, Cellular and molecular basis of deiodinase-regulated thyroid hormone signaling. Endocr. Rev. 29, 898–938 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2008-0019
C. Luongo, M. Dentice, D. Salvatore, Deiodinases and their intricate role in thyroid hormone homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 15, 479–488 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-019-0218-2
N. Toyoda, E. Kaptein, M.J. Berry, J.W. Harney, P.R. Larsen, T.J. Visser, Structure-activity Relationships for Thyroid Hormone Deiodination by Mammalian Type I Iodothyronine Deiodinases. Endocrinology 138, 213–219 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.138.1.4900
G. Wittmann, J. Szabon, P. Mohácsik, S.S. Nouriel, B. Gereben, C. Fekete, R.M. Lechan, Parallel regulation of thyroid hormone transporters OATP1c1 and MCT8 during and after endotoxemia at the blood-brain barrier of male rodents. Endocrinology 156, 1552–1564 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2014-1830
J. Bernal, A. Guadaño-Ferraz, B. Morte, Thyroid hormone transporters—functions and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 11, 406–417 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2015.66
S. Mayerl, J. Müller, R. Bauer, S. Richert, C.M. Kassmann, V.M. Darras, K. Buder, A. Boelen, T.J. Visser, H. Heuer, Transporters MCT8 and OATP1C1 maintain murine brain thyroid hormone homeostasis. J. Clin. Investig. 124, 1987–1999 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI70324
J. Dernellis, M. Panaretou, Effects of thyroid replacement therapy on arterial blood pressure in patients with hypertension and hypothyroidism. Am. Heart J. 143, 718–724 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1067/mhj.2002.120766
G. Grassi, D.D. Heistad, Remodelling of small cerebral arteries in human hypertension: structural and functional alterations. J. Hypertens. 27, 709–711 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0b013e3283295dd4
C. Cheng, C. Daskalakis, B. Falkner, Alterations in capillary morphology are found in mild blood pressure elevation. J. Hypertens. 28, 2258–2266 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0b013e32833e113b
E. Berta, I. Lengyel, S. Halmi, M. Zrinyl, A. Erdei, M. Harangi, D. Pall, E.V. Nagy, M. Bodor, Hypertension in thyroid disorders. Front. Endocrinol.10, 482 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00482
L.M. Prisant, J.S. Gujral, A.L. Mulloy, Hyperthyroidism: a secondary cause of isolated systolic hypertension. J. Clin. Hypertens. 8, 596–599 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-6175.2006.05180.x
C.Del Seppia, D. Lapi, S. Ghione, G. Federighi, L. Sabatino, E. Fommei, A. Colantuoni, R. Scuri, Evidence in hypertensive rats of hypotensive effect after mandibular extension. Physiol. Rep. 6, e13911 (2018). https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.13911
L. Sabatino, C. Costagli, D. Lapi, C. Del Seppia, G. Federighi, S. Balzan, A. Colantuoni, G. Iervasi, R. Scuri, Renin-angiotensin system responds to prolonged hypotensive effect induced by mandibular extension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Front. Physiol. 9, 1613 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01613
D. Lapi, A. Colantuoni, C. Del Seppia, S. Ghione, D. Tonlorenzi, M. Brunelli, R. Scuri, Persistent effects after trigeminal nerve proprioceptive stimulation by mandibular extension on rat blood pressure, heart rate and pial microcirculation. Arch. Ital. Biol. 151, 11–23 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4449/aib.v151i1.1470
D. Lapi, M. Varanini, A. Colantuoni, C. Del Seppia, S. Ghione, E. Fommei, R. Scuri, Repeated mandibular extension in rat: a procedure to modulate the cerebral arteriolar tone. Front Physiol. 8, 625 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00625
L. Sabatino, V. Lubrano, S. Balzan, C. Kusmic, S. Del Turco, G. Iervasi, Thyroid hormone deiodinases DIO1, DIO2, and DIO3 are expressed in human endothelial dermal microvascular line: effects of thyroid hormones. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 399, 87–94 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2235-8
Y.Y. Liu, G.A. Brent, Thyroid hormone and the brain: mechanisms of action in development and role in protection and promotion of recovery after brain injury. Pharmacol. Ther. 186, 176–185 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.01.007
O.M. Ahmed, A.W. El-Gareib, A.M. El-Bakry, S.M. Abd El-Tawab, R.G. Ahmed, Thyroid hormones states and brain development interactions. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 26, 147–209 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2007.09.011
A.C. Bianco, A. Dumitrescu, B. Gereben, M.O. Ribeiro, T.L. Fonseca, G.W. Fernandes, B.M.L.C. Bocco, Paradigms of dynamic control of thyroid hormone signaling. Endocr. Rev. 40, 1000–1047 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2018-00275
D. Lapi, G. Federighi, M.P. Fantozzi, C. Del Seppia, S. Ghione, A. Colantuoni, R. Scuri, Trigeminocardiac reflex by mandibular extension on rat pial microcirculation: role of nitric oxide. PLoS One 9, e115767 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0115767
M.M. Kaplan, K.A. Yaskoski, Maturational patterns of iodothyronine phenolic and tyrosyl ring deiodinase activities in rat cerebrum, cerebellum, and hypothalamus. J. Clin. Investig. 67, 1208–1214 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1172/jci110136
S. Bárez-López, A. Guadaño-Ferraz, Thyroid hormone availability and action during brain development in rodents. Front. Cell Neurosci. 11, 240 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00240
O. Gumieniak, T.S. Perlstein, J.S. Williams, P.N. Hopkins, N.J. Brown, B.A. Raby, G.H. Willimas, Ala92 type 2 deiodinase allele increases risk for the development of hypertension. Hypertension 49, 461–466 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000256295.72185.fd
F. Brandt, A. Green, L. Hegedüs, T.H. Brix, A critical review and meta-analysis of the association between overt hyperthyroidism and mortality. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 165, 491–497 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-11-0299D.H
A. Marsili, A.M. Zavacki, J.W. Harney, P.R. Larsen, Physiological role and regulation of iodothyronine deiodinases: a 2011 update. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 34, 395–407 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347465
A.R. Drigo, A.C. Bianco, Type 2 deiodinase at the crossroads of thyroid hormone action. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 43, 1432–1441 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2011.05.016
A.L. Maia, I.M. Goemann, E.L. Meyer, S.M. Wajner, Type 1 iodothyronine deiodinase in human physiology and disease. J. Endocrinol. 209, 283–297 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-10-0481
A. Hernandez, J.P. Stohn, The Type 3 Deiodinase: Epigenetic Control of Brain Thyroid Hormone Action and Neurological Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 1804 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061804
M.E. Martinez, M. Charalambous, A. Saferali, S. Fiering, A.K. Naumova, D. St Germain, A.C. Ferguson, A. Hernandez, Genomic imprinting variations in the mouse type 3 deiodinase gene between tissues and brain regions. Mol. Endocrinol. 28, 1875–1886 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2014-1210
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabatino, L., Federighi, G., Del Seppia, C. et al. Thyroid hormone deiodinases response in brain of spontaneausly hypertensive rats after hypotensive effects induced by mandibular extension. Endocrine 74, 100–107 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02684-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02684-3