Abstract
Purpose
To compare the efficacy and the safety of radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation for treatment of benign thyroid nodules using a propensity score matching study design.
Methods
Two hundred and sixty patients with benign thyroid nodules were studied retrospectively, including 102 patients treated with radiofrequency ablation and 158 treated with microwave ablation. To reduce confounding bias due to retrospective assignment, propensity score matching was performed to balance the preablation data of the two groups. After matching, a total of 102 patient pairs (1:1) were created. The volume reduction ratio, therapeutic success rate, symptom and cosmetic score, and major complication were compared between the two groups at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months after treatment.
Results
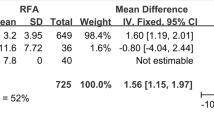
Between the well-matched groups, no significant differences were found in all nodule volume-related end points at 6 months (volume reduction ratio: 79.4 vs. 77.2 %, P = 0.108; symptom score: 2.1 vs. 1.9, P = 0.456; cosmetic score: 2.1 vs. 2.3, P = 0.119; therapeutic success rate: 99 vs. 97 %, P = 0.621) and 12 months (volume reduction ratio: 83.6 vs. 81.6 %, P = 0.144; symptom score: 1.5 vs. 1.5, P = 0.869; cosmetic score: 1.6 vs. 1.7, P = 0.409; therapeutic success rate: 100 vs. 100 %, P > 0.99) after treatment. No major complications occurred in either group (P > 0.99).
Conclusions
With well-matched groups and consistent procedure design, our results demonstrated that the volume reduction ratio, therapeutic success rate, symptom and cosmetic score, and complications related to treatment for the two techniques are equivalent. Radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation are both effective and safe methods in treating benign thyroid nodules.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.K. Klooker, A. Huibers, K. In’t Hof, E.J. Nieveen van Dijkum, S.S. Phoa, S. van Eeden, P.H. Bisschop, Screw needle cytology of thyroid nodules is associated with a lower non-diagnostic rate compared to fine needle aspiration. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 173, 677–681 (2015)
J. Klubo-Gwiezdzinska, L. Wartofsky, Thyroid emergencies. Med. Clin. North Am. 96, 385–403 (2012)
B. Haugen, E.K. R.Alexander, K.C. Bible, G.M. Doherty, S.J. Mandel, Y.E. Nikiforov, F. Pacini, G.W. Randolph, A.M. Sawka, M. Schlumberger, K.G. Schuff, S.I. Sherman, J.A. Sosa, D.L. Steward, R.M. Tuttle, L. Wartofsky, 2015 American thyroid association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 26, 1–133 (2016)
H. Gharib, E. Papini, R. Paschke, D.S. Duick, R. Valcavi, L. Hegedüs, P. Vitti; AACE/AME/ETA Task Force on Thyroid Nodules, American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, Associazione Medici Endocrinologi, and European Thyroid Association Medical Guidelines for clinical practice for the diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 33, 1–50 (2010)
A. Bergenfelz, S. Jansson, A. Kristoffersson, H. Mårtensson, E. Reihnér, G. Wallin, I. Lausen, Complications to thyroid surgery: results as reported in a database from a multicenter audit comprising 3660 patients. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 393, 667–673 (2008)
K.D. Kohlhase, Y. Korkusuz, D. Gröner, C. Erbelding, C. Happel, W. Luboldt, F. Grünwald, Bipolar radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules using a multiple overlapping shot technique in a 3-month follow-up. Int. J. Hyperthermia 28, 1–6 (2016)
K. Heck, C. Happel, F. Grünwald, H. Korkusuz, Percutaneous microwave ablation of thyroid nodules: effects on thyroid function and antibodies. Int. J. Hyperthermia 31, 560–567 (2015)
C.M. Pacella, G. Mauri, G. Achille, D. Barbaro, G. Bizzarri, P. De Feo, E. Di Stasio, R. Esposito, G. Gambelunghe, I. Misischi, B. Raggiunti, T. Rago, G.L. Patelli, S. D'Este, P. Vitti, E. Papini, Outcomes and risk factors for complications of laser ablation for thyroid nodules: a multicenter study on 1531 patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 100, 3903–3910 (2015)
W. Yue, S. Wang, B. Wang, Q. Xu, S. Yu, Z. Yonglin, X. Wang, Ultrasound guided percutaneous microwave ablation of benign thyroid nodules: safety and imaging follow-up in 222 patients. Eur. J. Radiol. 82, e11–16 (2013)
J.Y. Sung, J.H. Baek, K.S. Kim, D. Lee, H. Yoo, J.K. Kim, S.H. Park, Single-session treatment of benign cystic thyroid nodules with ethanol versus radiofrequency ablation: a prospective randomized study. Radiology 269, 293–300 (2013)
N. Kalra, C.K. Ahuja, P. Dutta, A. Rajwanshi, B.R. Mittal, A. Bhansali, N. Khandelwal, Comparison of sonographically guided percutaneous sodium tetradecyl sulfate injection with ethanol injection in the treatment of benign nonfunctioning thyroid nodules. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 25, 1218–1224 (2014)
C.M. Pacella, G. Bizzarri, S. Spiezia, A. Bianchini, R. Guglielmi, A. Crescenzi, S. Pacella, V. Toscano, E. Papini, Thyroid tissue: US-guied percutaneous laser thermal ablation. Radiology 232, 272–280 (2004)
H. Gharib, L. Hegedüs, C.M. Pacella, J.H. Baek, E. Papini, Clinical review: nonsurgical, image-guided, minimally invasive therapy for thyroid nodules. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 98, 3949–3957 (2013)
W.K. Jeong, J.H. Baek, H. Rhim, Y.S. Kim, M.S. Kwak, H.J. Jeong, D. Lee, Radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules: safety and imaging follow-up in 236 patients. Eur. Radiol. 18, 1244–1250 (2008)
M. Deandrea, P. Limone, E. Basso, A. Mormile, F. Ragazzoni, E. Gamarra, S. Spiezia, A. Faggiano, A. Colao, F. Molinari, R. Garberoglio, US-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation for the treatment of solid benign hyperfunctioning or compressive thyroid nodules. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 34, 784–791 (2008)
B. Feng, P. Liang, Z. Cheng, X. Yu, J. Yu, Z. Han, F. Liu, Ultrasound guided percutaneous microwave ablation of benign thyroid nodules:experimental and clinical studies. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 166, 1031–1037 (2012)
E.S. Cibas, S.Z. Ali, The bethesda system for reporting thyroid cytopathology. Thyroid 19, 1159–1165 (2009)
W.E. Saad, M.J. Wallace, J.C. Wojak, S. Kundu, J.F. Cardella, Quality improvement guidelines for percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography, biliary drainage, and percutaneous cholecystostomy. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 21, 789–795 (2010)
P.R. Rosenbaum, D.B. Rubin, The central role of the propensity score in observational studies for causal effects. Biometrika 70, 41–55 (1983)
H. Døssing, F.N. Bennedbaek, L. Hegedüs, Effect of ultrasound-guided interstitial laser photocoagulation on benign solitary solid cold thyroid nodules—a randomised study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 152, 341–345 (2005)
G.D. Dodd, N.A. Dodd, A.C. Lanctot, D.A. Glueck, Effect of variation of portal venous blood flow on radiofrequency and microwave ablations in a blood-perfused bovine liver model. Radiology 267, 129–136 (2013)
S. Garrean, J. Hering, A. Saied, P.J. Hoopes, W.S. Helton, T.P. Ryan, N.J. Espat, Ultrasound monitoring of a novel microwave ablation (MWA) device in porcine liver: lessons learned and phenomena observed on ablative effects near major intrahepatic vessels. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 13, 334–340 (2009)
N.C. Yu, S.S. Raman, Y.J. Kim, C. Lassman, X. Chang, D.S. Lu, Microwave liver ablation: influence of hepatic vein size on heat-sink effect in a porcine model. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 19, 1087–1092 (2008)
X.L. Li, H.X. Xu, F. Lu, W.W. Yue, L.P. Sun, X.W. Bo, L.H. Guo, J.M. Xu, B.J. Liu, D.D. Li, S. Qu, Treatment efficacy and safety of ultrasound-guided percutaneous bipolar radiofrequency ablation for benign thyroid nodules. Br. J. Radiol. 89(1059), 20150858 (2016). doi:10.1259/bjr.20150858
M.H. Yu, J.Y. Lee, S.R. Jun, K.W. Kim, S.H. Kim, J.K. Han, B.I. Choi, Radiofrequency ablation with an Internally cooled monopolar directional electrode: ex vivo and in vivo experimental studies in the liver. Radiology 14, 142269 (2015)
K.P. Wong, B.H. Lang, Use of radiofrequency ablation in benign thyroid nodules: a literature review and updates. Int. J. Endocrinol. 428363 (2013). doi: 10.1155
S. Tungjitkusolmun, S.T. Staelin, D. Haemmerich, J.Z. Tsai, J.G. Webster, F.T. Lee Jr, D.M. Mahvi, V.R. Vorperian, Three-dimensional finite-element analyses for radio-frequency hepatic tumor ablation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 49, 3–9 (2002)
P. Liang, B. Dong, X. Yu, D. Yu, Z. Cheng, L. Su, J. Peng, Q. Nan, H. Wang, Computer-aided dynamic simulation of microwave-induced thermal distribution in coagulation of liver cancer. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 48, 821–829 (2001)
A.S. Wright, L.A. Sampson, T.F. Warner, D.M. Mahvi, F.T. Lee Jr., Radiofrequency versus microwave ablation in a hepatic porcine model. Radiology 236, 132–139 (2005)
G.J. Qian, N. Wang, Q. Shen, Y.H. Sheng, J.Q. Zhao, M. Kuang, G.J. Liu, M.C. Wu, Efficacy of microwave versus radiofrequency ablation for treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma: experimental and clinical studies. Eur. Radiol. 22, 1983–1990 (2012)
T. Shibata, Y. Iimuro, Y. Yamamoto, Y. Maetani, F. Ametani, K. Itoh, J. Konishi, Small hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of radio-frequency ablation and percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy. Radiology 223, 331–337 (2002)
T. Liukko, A.A. Mäkitie, A. Markkola, J. Ylikoski, L. Bäck, Radiofrequency induced thermotherapy: an alternative palliative treatment modality in head and neck cancer. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 263, 532–536 (2006)
K. Heck, C. Happel, F. Grünwald, H. Korkusuz, Percutaneous microwave ablation of thyroid nodules: effects on thyroid function and antibodies. Int. J. Hyperthermia 31(5), 560–567 (2015)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Shanghai Hospital Development Center (Grant SHDC 12014229), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Grants 14441900900, 16411971100), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 81601502, 81501475).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, WW., Wang, SR., Lu, F. et al. Radiofrequency ablation vs. microwave ablation for patients with benign thyroid nodules: a propensity score matching study. Endocrine 55, 485–495 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-1173-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-1173-5