Abstract
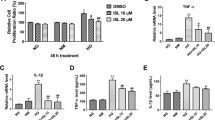
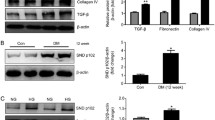
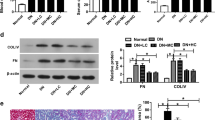
RhoA/ROCK can cause renal inflammation and fibrosis in the context of diabetes by activating nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). TGR5 is known for its role in maintaining metabolic homeostasis and anti-inflammation, which is closely related to NF-κB inhibition. Given that TGR5 is highly enriched in kidney, we aim to investigate the regulatory role of TGR5 on fibronectin (FN) and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) in high glucose (HG)-treated rat glomerular mesangial cells (GMCs). Both the factors are closely related to renal inflammations and mediated by NF-κB. Moreover, our study determines whether such regulation is achieved by the inhibition of RhoA/ROCK and the subsequent NF-κB suppression. Polymerase chain reaction was taken to test the mRNA level of TGR5. Western blot was used to measure the protein expressions of TGR5, FN, TGF-β1, p65, IκBα, phospho-MYPT1 (Thr853), and MYPT1. Glutathione S-transferase-pull down and immunofluorescence were conducted to test the activation of RhoA, the distribution of TGR5, and p65, respectively. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay was adopted to measure the DNA binding activity of NF-κB. In GMCs, TGR5 activation or overexpression significantly suppressed FN and TGF-β1 protein expressions, NF-κB, and RhoA/ROCK activation induced by HG or transfection of constitutively active RhoA. By contrast, TGR5 RNA interference caused enhancement of FN, TGF-β1 protein expressions, increase of RhoA/ROCK activation. However, TGR5 cannot suppress RhoA/ROCK activation when a selective Protein kinase A (PKA) inhibitor was used. This study suggests that in HG-treated GMCs, TGR5 significantly suppresses the NF-κB-mediated upregulation of FN and TGF-β1, which are hallmarks of diabetic nephropathy. These functions are closely related to the suppression of RhoA/ROCK via PKA.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.S. Kanwar, L. Sun, P. Xie, F.Y. Liu, S. Chen, A glimpse of various pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 6, 395–423 (2011)
C. Ponchiardi, M. Mauer, B. Najafian, Temporal profile of diabetic nephropathy pathologic changes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 13(4), 592–599 (2013)
A. Cove-Smith, H. BM, The regulation of mesangial cell proliferation. Nephron. Exp. Nephrol. 108(4), e74–e79 (2008)
H.E. Abboud, Mesangial cell biology. Exp. Cell Res. 318(9), 979–985 (2012)
J.F. Navarro-Gonzalez, C. Mora-Fernandez, M. Muros de Fuentes, J. Garcia-Perez, Inflammatory molecules and pathways in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 7(6), 327–340 (2011)
K.I. Woroniecka, A.S. Park, D. Mohtat, D.B. Thomas, J.M. Pullman, K. Susztak, Transcriptome analysis of human diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes 60(9), 2354–2369 (2011)
I.A. Bondar’, V.V. Klimontov, A.P. Nadeev, Urinary excretion of proinflammatory cytokines and transforming growth factor beta at early stages of diabetic nephropathy. Ter. Arkh. 80(1), 52–56 (2008)
A.P. Sanchez, K. Sharma, Transcription factors in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 11, e13 (2009)
H. Schmid, A. Boucherot, Y. Yasuda, A. Henger, B. Brunner, F. Eichinger, A. Nitsche, E. Kiss, M. Bleich, H.J. Grone, P.J. Nelson, D. Schlondorff, C.D. Cohen, M. Kretzler; European Renal c, D.N.A.B.C., Modular activation of nuclear factor-kappaB transcriptional programs in human diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 55(11), 2993–3003 (2006)
S. Mezzano, C. Aros, A. Droguett, M.E. Burgos, L. Ardiles, C. Flores, H. Schneider, M. Ruiz-Ortega, J. Egido, NF-kappaB activation and overexpression of regulated genes in human diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 19(10), 2505–2512 (2004)
Y. Kawamata, R. Fujii, M. Hosoya, M. Harada, H. Yoshida, M. Miwa, S. Fukusumi, Y. Habata, T. Itoh, Y. Shintani, S. Hinuma, Y. Fujisawa, M. Fujino, A G protein-coupled receptor responsive to bile acids. J. Biol. Chem. 278(11), 9435–9440 (2003)
T. Maruyama, Y. Miyamoto, T. Nakamura, Y. Tamai, H. Okada, E. Sugiyama, T. Nakamura, H. Itadani, K. Tanaka, Identification of membrane-type receptor for bile acids (M-BAR). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 298(5), 714–719 (2002)
T.W. Pols, L.G. Noriega, M. Nomura, J. Auwerx, K. Schoonjans, The bile acid membrane receptor TGR5 as an emerging target in metabolism and inflammation. J. Hepatol. 54(6), 1263–1272 (2011)
K.L. Pierce, R.T. Premont, R.J. Lefkowitz, Seven-transmembrane receptors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3(9), 639–650 (2002)
C. Thomas, A. Gioiello, L. Noriega, A. Strehle, J. Oury, G. Rizzo, A. Macchiarulo, H. Yamamoto, C. Mataki, M. Pruzanski, R. Pellicciari, J. Auwerx, K. Schoonjans, TGR5-mediated bile acid sensing controls glucose homeostasis. Cell Metab. 10(3), 167–177 (2009)
M. Watanabe, S.M. Houten, C. Mataki, M.A. Christoffolete, B.W. Kim, H. Sato, N. Messaddeq, J.W. Harney, O. Ezaki, T. Kodama, K. Schoonjans, A.C. Bianco, J. Auwerx, Bile acids induce energy expenditure by promoting intracellular thyroid hormone activation. Nature 439(7075), 484–489 (2006)
T.W. Pols, M. Nomura, T. Harach, G. Lo Sasso, M.H. Oosterveer, C. Thomas, G. Rizzo, A. Gioiello, L. Adorini, R. Pellicciari, J. Auwerx, K. Schoonjans, TGR5 activation inhibits atherosclerosis by reducing macrophage inflammation and lipid loading. Cell Metab. 14(6), 747–757 (2011)
Y.D. Wang, W.D. Chen, D. Yu, B.M. Forman, W. Huang, The G-protein-coupled bile acid receptor, Gpbar1 (TGR5), negatively regulates hepatic inflammatory response through antagonizing nuclear factor kappa light-chain enhancer of activated B cells (NF-kappaB) in mice. Hepatology 54(4), 1421–1432 (2011)
C. Guo, H. Qi, Y. Yu, Q. Zhang, J. Su, D. Yu, W. Huang, W.D. Chen, Y.D. Wang, The G-protein-coupled bile acid receptor Gpbar1 (TGR5) inhibits gastric inflammation through antagonizing NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 6, 287 (2015)
D. Bar-Sagi, A. Hall, Ras and Rho GTPases: a family reunion. Cell 103(2), 227–238 (2000)
T. Matsui, M. Amano, T. Yamamoto, K. Chihara, M. Nakafuku, M. Ito, T. Nakano, K. Okawa, A. Iwamatsu, K. Kaibuchi, Rho-associated kinase, a novel serine/threonine kinase, as a putative target for small GTP binding protein Rho. EMBO J. 15(9), 2208–2216 (1996)
H. Zhou, Y. Li, Long-term diabetic complications may be ameliorated by targeting Rho kinase. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 27(4), 318–330 (2011)
E. Amin, B.N. Dubey, S.C. Zhang, L. Gremer, R. Dvorsky, J.M. Moll, M.S. Taha, L. Nagel-Steger, R.P. Piekorz, A.V. Somlyo, M.R. Ahmadian, Rho-kinase: regulation, (dys)function, and inhibition. Biol. Chem. 394(11), 1399–1410 (2013)
F. Peng, D. Wu, B. Gao, A.J. Ingram, B. Zhang, K. Chorneyko, R. McKenzie, J.C. Krepinsky, RhoA/Rho-kinase contribute to the pathogenesis of diabetic renal disease. Diabetes 57(6), 1683–1692 (2008)
V. Kolavennu, L. Zeng, H. Peng, Y. Wang, F.R. Danesh, Targeting of RhoA/ROCK signaling ameliorates progression of diabetic nephropathy independent of glucose control. Diabetes 57(3), 714–723 (2008)
X. Xie, J. Peng, X. Chang, K. Huang, J. Huang, S. Wang, X. Shen, P. Liu, H. Huang, Activation of RhoA/ROCK regulates NF-kappaB signaling pathway in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 369(1–2), 86–97 (2013)
A. Gojo, K. Utsunomiya, K. Taniguchi, T. Yokota, S. Ishizawa, Y. Kanazawa, H. Kurata, N. Tajima, The Rho-kinase inhibitor, fasudil, attenuates diabetic nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 568(1–3), 242–247 (2007)
R. Komers, T.T. Oyama, D.R. Beard, C. Tikellis, B. Xu, D.F. Lotspeich, S. Anderson, Rho kinase inhibition protects kidneys from diabetic nephropathy without reducing blood pressure. Kidney Int. 79(4), 432–442 (2011)
R. Samarakoon, S.P. Higgins, C.E. Higgins, P.J. Higgins, TGF-beta1-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells requires pp60(c-src)/EGFR(Y845) and Rho/ROCK signaling. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 44(3), 527–538 (2008)
H. Shimada, L.E. Rajagopalan, Rho kinase-2 activation in human endothelial cells drives lysophosphatidic acid-mediated expression of cell adhesion molecules via NF-kappaB p65. J. Biol. Chem. 285(17), 12536–12542 (2010)
H. Iwasaki, R. Okamoto, S. Kato, K. Konishi, H. Mizutani, N. Yamada, N. Isaka, T. Nakano, M. Ito, High glucose induces plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression through Rho/Rho-kinase-mediated NF-kappaB activation in bovine aortic endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 196(1), 22–28 (2008)
K. Geoffroy, N.M. Wiernsperger, B.S. El, Bimodal effect of advanced glycation end products on mesangial cell proliferation is mediated by neutral ceramidase regulation and endogenous sphingolipids. J. Biol. Chem. 279(33), 34343–34352 (2004)
M.C. Subauste, M. Von Herrath, V. Benard, C.E. Chamberlain, T.H. Chuang, K. Chu, G.M. Bokoch, K.M. Hahn, Rho family proteins modulate rapid apoptosis induced by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and Fas. J. Biol. Chem. 275(13), 9725–9733 (2000)
Q. Jiang, P. Liu, X. Wu, W. Liu, X. Shen, T. Lan, S. Xu, J. Peng, X. Xie, H. Huang, Berberine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced extracelluar matrix accumulation and inflammation in rat mesangial cells: involvement of NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 331(1), 34–40 (2011)
Y. Rikitake, J.K. Liao, Rho-kinase mediates hyperglycemia-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in vascular endothelial cells. Circulation 111(24), 3261–3268 (2005)
T. Lan, X. Shen, P. Liu, W. Liu, S. Xu, X. Xie, Q. Jiang, W. Li, H. Huang, Berberine ameliorates renal injury in diabetic C57BL/6 mice: Involvement of suppression of SphK-S1P signaling pathway. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 502(2), 112–120 (2010)
Y.X. Tao, Constitutive activation of G protein-coupled receptors and diseases: insights into mechanisms of activation and therapeutics. Pharmacol. Ther. 120(2), 129–148 (2008)
R. Seifert, K. Wenzel-Seifert, Constitutive activity of G-protein-coupled receptors: cause of disease and common property of wild-type receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 366(5), 381–416 (2002)
A.B. Sanz, M.D. Sanchez-Nino, A.M. Ramos, J.A. Moreno, B. Santamaria, M. Ruiz-Ortega, J. Egido, A. Ortiz, NF-kappaB in renal inflammation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 21(8), 1254–1262 (2010)
T. Ishizaki, M. Uehata, I. Tamechika, J. Keel, K. Nonomura, M. Maekawa, S. Narumiya, Pharmacological properties of Y-27632, a specific inhibitor of rho-associated kinases. Mol. Pharmacol. 57(5), 976–983 (2000)
T. Chijiwa, A. Mishima, M. Hagiwara, M. Sano, K. Hayashi, T. Inoue, K. Naito, T. Toshioka, H. Hidaka, Inhibition of forskolin-induced neurite outgrowth and protein phosphorylation by a newly synthesized selective inhibitor of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, N-[2-(p-bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H-89), of PC12D pheochromocytoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 265(9), 5267–5272 (1990)
C. Eboh, T.A. Chowdhury, Management of diabetic renal disease. Ann. Transl. Med 3(11), 154 (2015)
K. Reidy, H.M. Kang, T. Hostetter, K. Susztak, Molecular mechanisms of diabetic kidney disease. J. Clin. Invest. 124(6), 2333–2340 (2014)
F.G. Schaap, M. Trauner, P.L. Jansen, Bile acid receptors as targets for drug development. Nat. Rev. Gastrol. Hepatol. 11(1), 55–67 (2014)
V. Stepanov, K. Stankov, M. Mikov, The bile acid membrane receptor TGR5: a novel pharmacological target in metabolic, inflammatory and neoplastic disorders. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 33(4), 213–223 (2013)
R. Pellicciari, A. Gioiello, A. Macchiarulo, C. Thomas, E. Rosatelli, B. Natalini, R. Sardella, M. Pruzanski, A. Roda, E. Pastorini, K. Schoonjans, J. Auwerx, Discovery of 6alpha-ethyl-23(S)-methylcholic acid (S-EMCA, INT-777) as a potent and selective agonist for the TGR5 receptor, a novel target for diabesity. J. Med. Chem. 52(24), 7958–7961 (2009)
X. Chen, G. Lou, Z. Meng, W. Huang, TGR5: a novel target for weight maintenance and glucose metabolism. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2011, 853501 (2011)
X.X. Wang, M.H. Edelstein, U. Gafter, L. Qiu, Y. Luo, E. Dobrinskikh, S. Lucia, L. Adorini, V.D. D'Agati, J. Levi, A. Rosenberg, J.B. Kopp, D.R. Gius, M.A. Saleem, M. Levi, protein-coupled bile acid receptor TGR5 activation inhibits kidney disease in obesity and diabetes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. (2015).
P. Lang, F. Gesbert, M. Delespine-Carmagnat, R. Stancou, M. Pouchelet, J. Bertoglio, Protein kinase A phosphorylation of RhoA mediates the morphological and functional effects of cyclic AMP in cytotoxic lymphocytes. EMBO J. 15(3), 510–519 (1996)
S. Rajagopal, D.P. Kumar, S. Mahavadi, S. Bhattacharya, R. Zhou, C.U. Corvera, N.W. Bunnett, J.R. Grider, K.S. Murthy, Activation of G protein-coupled bile acid receptor, TGR5, induces smooth muscle relaxation via both Epac- and PKA-mediated inhibition of RhoA/Rho kinase pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 304(5), G527–G535 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by research grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81373457, No. 81573477), the National Science and Technology Major Project (No. 2014ZX09301307-008), Doctoral Fund Project of the Ministry of Education of China (No. 20130171110097), the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong province, PR China (No. 2012B050300017, No. 2014A020210007), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. S2013010015765).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All animal experiments were conformed to the China Animal Welfare Legislation and were reviewed and approved by the Sun Yat-sen University Committee on Ethics in the Care and Use of Laboratory Animal.
Additional information
Fengxiao Xiong and Xuejuan Li contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, F., Li, X., Yang, Z. et al. TGR5 suppresses high glucose-induced upregulation of fibronectin and transforming growth factor-β1 in rat glomerular mesangial cells by inhibiting RhoA/ROCK signaling. Endocrine 54, 657–670 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-1032-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-1032-4