Abstract
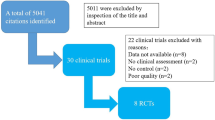
Whether intensive glycemic control can reduce incidence of diabetic retinopathy or other diabetes-associated ocular complications remains undefined. In this meta-analysis, we assessed the effects of intensive versus conventional glycemic control in ocular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes. A systematic literature search of PubMed, Web of Knowledge, and Scopus (until December 12, 2013) was conducted. Randomized controlled trials which compared intensive glycemic control with conventional glycemic control in ocular events in patients with type 2 diabetes were included. Random-effects models were used to measure the pooled odds ratio (OR) with 95 % confidence interval (CI). Seven trials involving 32,523 patients were included. Intensive glycemic control reduced the risks of retinal photocoagulation or vitrectomy (OR 0.86; 95 % CI 0.75–0.98), macular edema (OR 0.65; 95 % CI 0.43–0.99), and progression of retinopathy (OR 0.69; 95 % CI 0.55–0.87). No significant risk reduction was shown in incidence of retinopathy (OR 0.67; 95 % CI 0.26–1.73), cataract surgery (OR 0.88; 95 % CI 0.76–1.03), or severe loss of vision or blindness (OR 0.99; 95 % CI 0.86–1.13). Intensive glycemic control reduces the risk of most retinopathy-related events. But no beneficial effect was shown in ocular endpoint as severe loss of vision or blindness.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.E. Klein, Overview of epidemiologic studies of diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmic. Epidemiol. 14, 179–183 (2007)
D.A. Antonetti, R. Klein, T.W. Gardner, Diabetic retinopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 366, 1227–1239 (2012)
J.W. Yau, S.L. Rogers, R. Kawasaki, E.L. Lamoureux, J.W. Kowalski, T. Bek, S.J. Chen, J.M. Dekker, A. Fletcher, J. Grauslund, S. Haffner, R.F. Hamman, M.K. Ikram, T. Kayama, B.E. Klein, R. Klein, S. Krishnaiah, K. Mayurasakorn, J.P. O’Hare, T.J. Orchard, M. Porta, M. Rema, M.S. Roy, T. Sharma, J. Shaw, H. Taylor, J.M. Tielsch, R. Varma, J.J. Wang, N. Wang, S. West, L. Xu, M. Yasuda, X. Zhang, P. Mitchell, T.Y. Wong, Meta-Analysis for Eye Disease (META-EYE) Study Group, Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 35, 556–564 (2012)
E.L. Lamoureux, T.Y. Wong, Diabetic retinopathy in 2011: further insights from new epidemiological studies and clinical trials. Diabetes Care 34, 1066–1067 (2011)
Y.J. Cheng, E.W. Gregg, L.S. Geiss, G. Imperatore, D.E. Williams, X. Zhang, A.L. Albright, C.C. Cowie, R. Klein, J.B. Saaddine, Association of A1C and fasting plasma glucose levels with diabetic retinopathy prevalence in the U.S. population Implications for diabetes diagnostic thresholds. Diabetes Care 32, 2027–2032 (2009)
H.T. Nguyen, S.D. Luzio, J. Dolben, J. West, L. Beck, P.A. Coates, D.R. Owens, Dominant risk factors for retinopathy at clinical diagnosis in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Complications 10, 211–219 (1996)
R. Klein, B.E. Klein, S.E. Moss, K.J. Cruickshanks, Relationship of hyperglycemia to the long-term incidence and progression of diabetic retinopathy. Arch. Intern. Med. 154, 2169–2178 (1994)
T. Shiraiwa, H. Kaneto, T. Miyatsuka, K. Kato, K. Yamamoto, A. Kawashima, T. Kanda, M. Suzuki, E. Imano, M. Matsuhisa, M. Hori, Y. Yamasaki, Postprandial hyperglycemia is a better predictor of the progression of diabetic retinopathy than HbA1c in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 28, 2806–2807 (2005)
X.W. Xie, L. Xu, Y.X. Wang, J.B. Jonas, Prevalence and associated factors of diabetic retinopathy. The Beijing Eye Study 2006. Graefes. Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 246, 1519–1526 (2008)
M.S. Roy, M. Affouf, Six-year progression of retinopathy and associated risk factors in African American patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: the New Jersey 725. Arch. Ophthalmol. 124, 1297–1306 (2006)
R. Klein, K.E. Lee, R.E. Gangnon, B.E. Klein, The 25-year incidence of visual impairment in type 1 diabetes mellitus: the wisconsin epidemiologic study of diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmology 117, 63–70 (2010)
M. Heniricsson, L. Nyström, G. Blohmé, J. Ostman, C. Kullberg, M. Svensson, A. Schölin, H.J. Arnqvist, E. Björk, J. Bolinder, J.W. Eriksson, G. Sundkvist, The incidence of retinopathy 10 years after diagnosis in young adult people with diabetes: results from the nationwide population-based Diabetes Incidence Study in Sweden (DISS). Diabetes Care 26, 349–354 (2003)
F. Ismail-Beigi, T. Craven, M.A. Banerji, J. Basile, J. Calles, R.M. Cohen, R. Cuddihy, W.C. Cushman, S. Genuth, R.H. Grimm, B.P. Hamilton, B. Hoogwerf, D. Karl, L. Katz, A. Krikorian, P. O’Connor, R. Pop-Busui, U. Schubart, D. Simmons, H. Taylor, A. Thomas, D. Weiss, I. Hramiak, ACCORD trial group, Effect of intensive treatment of hyperglycaemia on microvascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an analysis of the ACCORD randomised trial. Lancet 376, 419–430 (2010)
A. Patel, S. MacMahon, J. Chalmers, B. Neal, L. Billot, M. Woodward, M. Marre, M. Cooper, P. Glasziou, D. Grobbee, P. Hamet, S. Harrap, S. Heller, L. Liu, G. Mancia, C.E. Mogensen, C. Pan, N. Poulter, A. Rodgers, B. Williams, S. Bompoint, B.E. de Galan, R. Joshi, F. Travert, ADVANCE Collaborative Group, Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 358, 2560–2572 (2008)
M. Shichiri, H. Kishikawa, Y. Ohkubo, N. Wake, Long-term results of the Kumamoto Study on optimal diabetes control in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 23, B21–B29 (2000)
UK Propective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group, Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 352, 837–853 (1998)
N. Emanuele, R. Klein, C. Abraira, J. Colwell, J. Comstock, W.G. Henderson, S. Levin, F. Nuttall, C. Sawin, C. Silbert, H.S. Lee, N. Johnson-Nagel, Evaluations of retinopathy in the VA Cooperative Study on Glycemic Control and Complications in Type II Diabetes (VA CSDM). A feasibility study. Diabetes Care 19, 1375–1381 (1996)
W. Duckworth, C. Abraira, T. Moritz, D. Reda, N. Emanuele, P.D. Reaven, F.J. Zieve, J. Marks, S.N. Davis, R. Hayward, S.R. Warren, S. Goldman, M. McCarren, M.E. Vitek, W.G. Henderson, G.D. Huang, VADT investigators, glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes. N. Eng. J. Med. 360, 129–139 (2009)
O. Brinchmann-Hansen, K. Dahl-Jørgensen, L. Sandvik, K.F. Hanssen, Blood glucose concentrations and progression of diabetic retinopathy: the seven year results of the Oslo study. BMJ 304, 19–22 (1992)
P. Reichard, B.Y. Nilsson, U. Rosenqvist, The effect of long-term intensified insulin treatment on the development of microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 329, 304–309 (1993)
N.H. White, W. Sun, P.A. Cleary, R.P. Danis, M.D. Davis, D.P. Hainsworth, L.D. Hubbard, J.M. Lachin, D.M. Nathan, Prolonged effect of intensive therapy on the risk of retinopathy complications in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: 10 years after the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Arch. Ophthalmol. 126, 1707–1715 (2008)
J.P.T. Higgins, S. Green, Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of intervention 5.1.0 (2011) Cochrane Collaboration. [Online] Available from http://handbook.cochrane.org. Accessed 20 December 2013
D. Moher, A. Liberati, J. Tetzlaff, D.G. Altman, PRISMA Group, Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339, b2535 (2009)
T. Zhao, J. Zhao, Association of the apolipoprotein A5 gene -1131 T > C polymorphism with fasting blood lipids: a meta-analysis in 37859 subjects. BMC Med. Genet. 11, 120 (2010)
J.P. Higgins, S.G. Thompson, J.J. Deeks, D.G. Altman, Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327, 557–560 (2003)
E.Y. Chew, W.T. Ambrosius, M.D. Davis, R.P. Danis, S. Gangaputra, C.M. Greven, L. Hubbard, B.A. Esser, J.F. Lovato, L.H. Perdue, D.C. Goff, W.C. Cushman, H.N. Ginsberg, M.B. Elam, S. Genuth, H.C. Gerstein, U. Schubart, L.J. Fine, ACCORD Study Group, ACCORD Eye Study Group, Effects of medical therapies on retinopathy progression in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med 363, 233–244 (2010)
J.W. Beulens, A. Patel, J.R. Vingerling, J.K. Cruickshank, A.D. Hughes, A. Stanton, J. Lu, S.A. McG Thom, D.E. Grobbee, R.P. Stolk, Effects of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control on the incidence and progression of retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetologia 52, 2027–2036 (2009)
UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group, Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet 352, 854–865 (1998)
Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group, Grading diabetic retinopathy from stereoscopic color fundus photographs-an extension of the modified Airlie House classification. ETDRS report number 10. Ophthalmology 98, 786–806 (1991)
Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group, Fundus photographic risk factors for progression of diabetic retinopathy. ETDRS report number 12. Ophthalmology 98, 823–833 (1991)
P.H. Wang, J. Lau, T.C. Chalmers, Metaanalysis of the effects of intensive glycemic control on late complications of type I diabetes mellitus. Lancet 341, 1306–1309 (1993)
L.P. Aiello, DCCT/EDIC Research Group, Diabetic retinopathy and other ocular findings in the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study. Diabetes Care 37, 17–23 (2014)
A.M. Buehler, A.B. Cavalcanti, O. Berwanger, M. Figueiro, L.N. Laranjeira, A.D. Zazula, B. Kioshi, D.G. Bugano, E. Santucci, G. Sbruzzi, H.P. Guimaraes, V.O. Carvalho, S.A. Bordin, Effect of tight blood glucose control versus conventional control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review with meta-analysis of RCTs. Cardiovasc. Ther. 31, 147–160 (2013)
B. Hemmingsen, S.S. Lund, C. Gluud, A. Vaag, T. Almdal, C. Hemmingsen, J. Wetterslev, Intensive glycaemic control for patients with T2DM: systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of randomised clinical trials. BMJ 343, d6898 (2011)
The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group, Early worsening of diabetic retinopathy in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Arch. Ophthalmol. 116, 874–886 (1998)
E. Moskalets, G. Galstyan, E. Starostina, M. Antsiferov, E. Chantelau, Association of blindness to intensification of glycemic control in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Complications 8, 45–50 (1994)
M. Henricsson, A. Nilsson, L. Janzon, L. Groop, The effect of glycaemic control and the introduction of insulin therapy on retinopathy in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Med. 14, 123–131 (1997)
M. Henricsson, K. Berntorp, E. Berntorp, P. Fernlund, G. Sundkvist, Progression of retinopathy after improved metabolic control in type 2 diabetic patients. Relation to IGF-1 and hemostatic variables. Diabetes Care 22, 1944–1949 (1999)
J. Tovi, S.O. Ingemansson, P. Engfeldt, Insulin treatment of elderly type 2 diabetic patients: effects on retinopathy. Diabetes Metab. 24, 442–447 (1998)
S. Savage, R.O. Estacio, B. Jeffers, R.W. Schrier, Increased complications in noninsulin-dependent diabetic patients treated with insulin versus oral hypoglycemic agents: a population study. Proc. Assoc. Am. Physicians 109, 181–189 (1997)
E. Chantelau, E.M. Kohner, Why some cases of retinopathy worsen when diabetic control improves. BMJ 315, 1105–1106 (1997)
M. Paques, P. Massin, A. Gaudric, Growth factors and diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Metab. 23, 125–130 (1997)
R. Simó, J.M. Sundstrom, D.A. Antonetti, Ocular anti-VEGF therapy for diabetic retinopathy: the role of VEGF in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 37, 893–899 (2014)
The Kroc Collaborative Study Group, Follow-up of the Kroc Collaborative Study, Diabetic retinopathy after two years of intensified insulin treatment. JAMA 260, 37–41 (1988)
E.Y. Chew, W.T. Ambrosius, R.P. Danis, Retinopathy progression in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 25, 2173–2174 (2010)
Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group, Progression of retinopathy with intensive versus conventional treatment in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Ophthalmology 102, 647–661 (1995)
R.R. Holman, S.K. Paul, M.A. Bethel, D.R. Matthews, H.A. Neil, 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N. Eng. J. Med. 359, 1577–1589 (2008)
Diabetes Control and Complications Trail Research Group, The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Eng. J. Med. 329, 977–986 (1993)
N. Cheung, P. Mitchell, T.Y. Wong, Diabetic retinopathy. Lancet 376, 124–136 (2010)
V.S. Jeganathan, J.J. Wang, T.Y. Wong, Ocular association of diabetes other than diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 31, 1905–1912 (2008)
C. Rotimi, H. Daniel, J. Zhou, A. Obisesan, G. Chen, Y. Chen, A. Amoah, V. Opoku, J. Acheampong, K. Agyenim-Boateng, B.A. Eghan, J. Oli, G. Okafor, E. Ofoegbu, B. Osotimehin, F. Abbiyesuku, T. Johnson, O. Fasanmade, A. Doumatey, T. Aje, F. Collins, G. Dunston, Prevalence and determinants of diabetic retinopathy and cataracts in West African type 2 diabetes patients. Ethn. Dis. 13, S110–S117 (2003)
B. Sonmez, B. Bozkurt, A. Atmaca, M. Irkec, M. Orhan, U. Aslan, Effect of glycemic control on refractive changes in diabetic patients with hyperglycemia. Cornea 24, 531–537 (2005)
S. Kato, T. Oshika, J. Numaga, H. Kawashima, S. Kitano, T. Kaiya, Influence of rapid glycemic control on lens opacity in patients with diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 130, 354–355 (2000)
K. Skarbez, Y. Priestley, M. Hoepf, S.B. Koevary, Comprehensive review of the effects of diabetes on ocular health. Expert Rev. Ophthalmol. 5, 557–577 (2010)
American Diabetes Association, Executive summary: standards of medical care in diabetes-2009. Diabetes Care 32, S6–S12 (2009)
P.S. Jellinger, J.A. Davidson, L. Blonde, D. Einhorn, G. Grunberger, Y. Handelsman, R. Hellman, H. Lebovitz, P. Levy, V.L. Roberts, ACE/AACE Diabetes Road MapTask Force, Road maps to achieve glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus: ACE/AACE Diabetes Road Map Task Force. Endocr. Pract. 13, 260–268 (2007)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Xiaoyan Wang from Guangdong Institute of Gastroenterology for her kind instruction and advice in statistical analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest associated with this manuscript.
Funding
The authors have no funding to report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1
Flow chart of literature search and selection (TIFF 587 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Zhao, J., Zhao, T. et al. Effects of intensive glycemic control in ocular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Endocrine 49, 78–89 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0459-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0459-8