Abstract
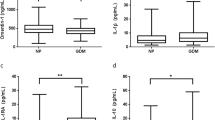
To assess maternal serum and cord blood apelin-36 and nesfatin-1 concentrations in pregnant women with and without gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). Thirty pregnant women with GDM and 30 gestational age matched healthy pregnant subjects participated to the study. Maternal serum and cord blood nesfatin-1 and apelin-36 levels were measured with ELISA, at the time of birth. The relationships between maternal serum and cord blood nesfatin-1 and apelin-36 levels, anthropometric and metabolic parameters were also assessed. Maternal serum apelin-36 levels were found higher (13.5 ± 8.3 vs. 9.6 ± 5.9 ng/ml, P = 0.001) and nesfatin-1 levels were found lower (5.5 ± 8.1 vs. 8.1 ± 23.9 ng/ml, P = 0.001) in patients with GDM compared with control pregnant women. However, the cord blood apelin-36 levels (8.8 ± 4.3 and 8.2 ± 1.9 ng/ml, P = 0.618) and nesfatin-1 levels (5.4 ± 4.0 and 6.2 ± 10.3 ng/ml, P = 0.688) were similar in the GDM and control groups, respectively. Maternal serum apelin-36 and nesfatin-1 levels correlated positively with their respective cord blood levels. Maternal serum and cord blood apelin-36 levels correlated negatively with the gestational age and birth weight. Similarly maternal serum and cord blood nesfatin-1 levels correlated negatively with the gestational age, but there was no correlation with the birth weight. We did not find a correlation between maternal serum apelin-36 and nesfatin-1 levels, maternal age, BMI, fasting glucose, fasting insulin, and HOMA-IR. Also cord blood apelin-36 and nesfatin-1 levels did not correlate with the maternal age, BMI, HOMA-IR, cord blood glucose, and cord blood insulin levels. Our results indicate that apelin-36 concentrations increase and nesfatin-1 concentrations decrease in maternal serum of women with GDM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.E. Metzger, D.R. Coustan, Summary and recommendations of the fourth ınternational workshop-conference on gestational diabetes mellitus. The Organizing Committee. Diabet. Care 21(Suppl 2), B161–B167 (1998)
American Diabetes Association, Gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Care 26(Suppl 1), S103–S105 (2003)
D.R. Coustan, Making the diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 43(1), 99–105 (2000)
B. Masri, N. Morin, L. Pedebernade, B. Knibiehler, Y. Audigier, The apelin receptor is coupled to Gi1 or Gi2 protein and is differentially desensitized by apelin fragments. J. Biol. Chem. 281(27), 18317–18326 (2006). doi:10.1074/jbc.M600606200
K. Tatemoto, M. Hosoya, Y. Habata, R. Fujii, T. Kakegawa, M.X. Zou, Y. Kawamata, S. Fukusumi, S. Hinuma, C. Kitada, T. Kurokawa, H. Onda, M. Fujino, Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous peptide ligand for the human APJ receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 251(2), 471–476 (1998). doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.9489
Y. Kawamata, Y. Habata, S. Fukusumi, M. Hosoya, R. Fujii, S. Hinuma, N. Nishizawa, C. Kitada, H. Onda, O. Nishimura, M. Fujino, Molecular properties of apelin: tissue distribution and receptor binding. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1538(2–3), 162–171 (2001)
A.M. O’Carroll, T.L. Selby, M. Palkovits, S.J. Lolait, Distribution of mRNA encoding B78/apj, the rat homologue of the human APJ receptor, and its endogenous ligand apelin in brain and peripheral tissues. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1492(1), 72–80 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0167-4781(00)00072-5
A.S. Hekmat, H. Najafipour, A.A. Nekooian, S. Esmaeli-Mahani, K. Javanmardi, Cardiovascular responses to apelin in two-kidney-one-clip hypertensive rats and its receptor expression in ischemic and non-ischemic kidneys. Regul. Pept. 172(1–3), 62–68 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2011.08.010
L. Li, G. Yang, Q. Li, Y. Tang, M. Yang, H. Yang, K. Li, Changes and relations of circulating visfatin, apelin, and resistin levels in normal, impaired glucose tolerance, and type 2 diabetic subjects. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabet. 114(10), 544–548 (2006). doi:10.1055/s-2006-948309
J. Boucher, B. Masri, D. Daviaud, S. Gesta, C. Guigne, A. Mazzucotelli, I. Castan-Laurell, I. Tack, B. Knibiehler, C. Carpene, Y. Audigier, J.S. Saulnier-Blache, P. Valet, Apelin, a newly identified adipokine up-regulated by insulin and obesity. Endocrinology 146(4), 1764–1771 (2005). doi:10.1210/en.2004-1427
F. Soriguer, L. Garrido-Sanchez, S. Garcia-Serrano, J.M. Garcia-Almeida, J. Garcia-Arnes, F.J. Tinahones, E. Garcia-Fuentes, Apelin levels are increased in morbidly obese subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Obes. Surg. 19(11), 1574–1580 (2009). doi:10.1007/s11695-009-9955-y
I.S. Oh, H. Shimizu, T. Satoh, S. Okada, S. Adachi, K. Inoue, H. Eguchi, M. Yamamoto, T. Imaki, K. Hashimoto, T. Tsuchiya, T. Monden, K. Horiguchi, M. Yamada, M. Mori, Identification of nesfatin-1 as a satiety molecule in the hypothalamus. Nature 443(7112), 709–712 (2006). doi:10.1038/nature05162
K.S. Foo, H. Brismar, C. Broberger, Distribution and neuropeptide coexistence of nucleobindin-2 mRNA/nesfatin-like immunoreactivity in the rat CNS. Neuroscience 156(3), 563–579 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.07.054
A. Stengel, M. Goebel, Y. Tache, Nesfatin-1: a novel inhibitory regulator of food intake and body weight. Obes. Rev. 12(4), 261–271 (2011). doi:10.1111/j.1467-789X.2010.00770.x
Q.C. Li, H.Y. Wang, X. Chen, H.Z. Guan, Z.Y. Jiang, Fasting plasma levels of nesfatin-1 in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus and the nutrient-related fluctuation of nesfatin-1 level in normal humans. Regul. Pept. 159(1–3), 72–77 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2009.11.003
I. Castan-Laurell, C. Dray, C. Attane, T. Duparc, C. Knauf, P. Valet, Apelin, diabetes, and obesity. Endocrine 40(1), 1–9 (2011). doi:10.1007/s12020-011-9507-9
ACOG Practice Bulletin. Clinical management guidelines for obstetrician-gynecologists No. 30: September 2001 (replaces Technical Bulletin Number 200, December 1994). Gestational diabetes. Obstet Gynecol 98(3), 525–538 (2001)
D.R. Matthews, J.P. Hosker, A.S. Rudenski, B.A. Naylor, D.F. Treacher, R.C. Turner, Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28(7), 412–419 (1985)
B. Telejko, M. Kuzmicki, N. Wawrusiewicz-Kurylonek, J. Szamatowicz, A. Nikolajuk, A. Zonenberg, D. Zwierz-Gugala, W. Jelski, P. Laudanski, J. Wilczynski, A. Kretowski, M. Gorska, Plasma apelin levels and apelin/APJ mRNA expression in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Res. Clin. Pract. 87(2), 176–183 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2009.10.018
L. Wei, X. Hou, K. Tatemoto, Regulation of apelin mRNA expression by insulin and glucocorticoids in mouse 3T3–L1 adipocytes. Regul. Pept. 132(1–3), 27–32 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2005.08.003
T. Van Mieghem, R. van Bree, E. Van Herck, R. Pijnenborg, J. Deprest, J. Verhaeghe, Maternal apelin physiology during rat pregnancy: the role of the placenta. Placenta 31(8), 725–730 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2010.06.001
A. Kourtis, A. Gkiomisi, M. Mouzaki, K. Makedou, A.D. Anastasilakis, K.A. Toulis, S. Gerou, E. Gavana, T. Agorastos, Apelin levels in normal pregnancy. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf) 75(3), 367–371 (2011). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04061.x
L. Cobellis, M. De Falco, A. Mastrogiacomo, D. Giraldi, D. Dattilo, C. Scaffa, N. Colacurci, A. De Luca, Modulation of apelin and APJ receptor in normal and preeclampsia-complicated placentas. Histol. Histopathol. 22(1), 1–8 (2007)
T. Josephs, H. Waugh, I. Kokay, D. Grattan, M. Thompson, Fasting-induced adipose factor identified as a key adipokine that is up-regulated in white adipose tissue during pregnancy and lactation in the rat. J. Endocrinol. 194(2), 305–312 (2007). doi:10.1677/JOE-07-0158
R. Gonzalez, A. Tiwari, S. Unniappan, Pancreatic beta cells colocalize insulin and pronesfatin immunoreactivity in rodents. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 381(4), 643–648 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.02.104
K.S. Foo, H. Brauner, C.G. Ostenson, C. Broberger, Nucleobindin-2/nesfatin in the endocrine pancreas: distribution and relationship to glycaemic state. J. Endocrinol. 204(3), 255–263 (2010). doi:10.1677/JOE-09-0254
R. Gonzalez, B.K. Reingold, X. Gao, M.P. Gaidhu, R.G. Tsushima, S. Unniappan, Nesfatin-1 exerts a direct, glucose-dependent insulinotropic action on mouse islet beta- and MIN6 cells. J. Endocrinol. 208(3), R9–R16 (2011). doi:10.1530/JOE-10-0492
Y. Su, J. Zhang, Y. Tang, F. Bi, J.N. Liu, The novel function of nesfatin-1: anti-hyperglycemia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 391(1), 1039–1042 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.12.014
B.E. Metzger, S.G. Gabbe, B. Persson, T.A. Buchanan, P.A. Catalano, P. Damm, A.R. Dyer, A. Leiva, M. Hod, J.L. Kitzmiler, L.P. Lowe, H.D. McIntyre, J.J. Oats, Y. Omori, M.I. Schmidt, International association of diabetes and pregnancy study groups recommendations on the diagnosis and classification of hyperglycemia in pregnancy. Diabet. Care 33(3), 676–682 (2010). doi:10.2337/dc09-1848
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The experiments used comply with the current laws of our country in which the study was conducted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aslan, M., Celik, O., Celik, N. et al. Cord blood nesfatin-1 and apelin-36 levels in gestational diabetes mellitus. Endocrine 41, 424–429 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-011-9577-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-011-9577-8