Abstract
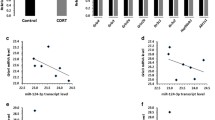
Depression is a major social and health concern, and ketamine exerts a quick, remarkable and persistent anti-depressive effect. microRNAs (miRNAs) show remarkable potential in the treatment of clinical depression. Here, we determined the expression profile of miRNAs in the hippocampus of rats treated with ketamine (15 mg/kg). The results suggest that multiple miRNAs were aberrantly expressed in rat hippocampus after ketamine injection (18 miRNAs were significantly reduced, while 22 miRNAs were significantly increased). Among them, miR-206 was down-regulated in ketamine-treated rats. In both cultured neuronal cells in vitro and hippocampus in vivo, we identified that the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) was a direct target gene of miR-206. Via this target gene, miR-206 strongly modulated the expression of BDNF. Moreover, overexpression of miR-206 significantly attenuated ketamine-induced up-regulation of BDNF. The results indicated that miRNA-206 was involved in novel therapeutic targets for the anti-depressive effect of ketamine.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao, Y. P., Yang, Y. I., Peng, L. L., Fang, J., Liu, K. B., Li, W. Z., et al. (2013). Roles of microRNA-206 in osteosarcoma pathogenesis and progression. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 14, 3751–3755.
Berman, R. B., Cappielo, A., Anand, A., Oren, D. A., Heninger, G. R., Charney, D. S., et al. (2000). Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biological Psychiatry, 47, 351–354.
Brunig, I., Kaech, S., Brinkhaus, H., Oertner, T. G., & Matus, A. (2004). Influx of extracellular calcium regulates actin-dependent morphological plasticity in dendritic spines. Neuropharmacology, 47, 669–676.
Chaturvedi, H. K., Bapna, J. S., & Chandra, D. (2001). Effect of fluvoxamine and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists on shock-induced depression in mice. Indian Journal of Physiology Pharmacology, 45, 199–207.
Chen, K., & Rajewsky, N. (2007). The evolution of gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Nature Review, 8, 93–103.
Chen, X., Yan, Q., Li, S., Zhou, L., Yang, H., Yang, Y., et al. (2012). Expression of the tumor suppressor miR-206 is associated with cellular proliferative inhibition and impairs invasion in ERalpha-positive endometrioid adenocarcinoma. Cancer Letters, 314, 41–53.
Cohen, M. L., Chan, S. L., Way, W. L., & Trevor, A. J. (1973). Distribution in the brain and metabolism of ketamine in the rat after intravenous administration. Anesthesiology, 39, 370–376.
Correll, G. E., & Futter, G. E. (2006). Two case studies of patients with major depressive disorder given low-dose (subanesthetic) ketamine infusions. Pain Medicine, 7, 92–95.
Duman, R. S., & Monteggia, L. M. (2006). A neurotrophic model for stress-related mood disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 59, 1116–1127.
Dwivedi, Y. (2011). Evidence demonstrating role of microRNAs in the etiopathology of major depression. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy, 42, 142–156.
Fath, T., Ke, Y. D., Gunning, P., Götz, J., & Ittner, L. M. (2009). Primary support cultures of hippocampal and substantia nigra neurons. Nature Protocols, 4, 78–85.
Frey, B. N., Andreazza, A. C., Ceresér, K. M., Martins, M. R., Valvassori, S. S., & Réus, G. Z. (2006). Effects of mood stabilizers on hippocampus BDNF levels in an animal model of mania. Life Science, 79, 281–286.
Garcia, L. S., Comim, C. M., Valvassori, S. S., Réus, G. Z., Andreazza, A. C., Stertz, L., et al. (2008a). Chronic administration of ketamine elicits antidepressant-like effects in rats without affecting hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein levels. Basic Clinical Pharmacology Toxicology, 103, 502–516.
Garcia, L. S., Comim, C. M., Valvassori, S. S., Réus, G. Z., Barbosa, L. M., Andreazza, A. C., et al. (2008b). Acute administration of ketamine induces antidepressant-like effects in the forced swimming test and increases BDNF levels in the rat hippocampus. Progress in Neuropsychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 32, 140–144.
Gardier, A. M. (2009). Mutant mouse models and antidepressant drug research: Focus on serotonin and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Behavioural Pharmacology, 20, 18–32.
Guo, A. Y., Sun, J., Jia, P., & Zhao, Z. (2010). A novel microRNA and transcription factor mediated regulatory network in schizophrenia. BMC Systems Biology, 4, 10.
Hansen, K. F., & Obrietan, K. (2013). MicroRNA as therapeutic targets for treatment of depression. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 9, 1011–1021.
Huang, Y., Kesselman, D., Kizub, D., Guerrero-Preston, R., & Ratovitski, E. A. (2013). Phospho-ΔNp63α/microRNA feedback regulation in squamous carcinoma cells upon cisplatin exposure. Cell Cycle, 12, 684–697.
Hunsberger, J. G., Austin, D. R., Chen, G., & Manji, H. K. (2009). MicroRNAs in mental health: From biological underpinnings to potential therapies. NeuroMolecular Medicine, 2009(11), 173–182.
Ibla, J. C., Hayashi, H., Bajic, D., & Soriano, S. G. (2009). Prolonged exposure to ketamine increases brain derived neurotrophic factor levels in developing rat brains. Current Drug Safety, 4, 11–16.
Jacobson, I., Hamberger, A., & Richards, C. D. (1990). Ketamine and MK801 attenuate paired pulse inhibition in the olfactory bulb of the rat. Experimental Brain Research, 80, 409–414.
Karege, F., Perret, G., & Bondolfi, G. (2002). Decreased serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in major depressed patients. Psychiatry Research, 109, 143–148.
Kohrs, R., & Durieux, M. E. (1998). Ketamine: Teaching an old drug new tricks. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 87, 1186–1193.
Kos, T., Popik, P., Pietraszek, M., Schäfer, D., Danysz, W., Dravolina, O., et al. (2006). Effect of 5-HT3 receptor antagonist MDL 72222 on behaviors induced by ketamine in rats and mice. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 16, 297–310.
Lee, S. T., Chu, K., Jung, K. H., Kim, J. H., Huh, J. Y., Yoon, H., et al. (2007). miR-206 regulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Alzheimer disease model. Annals of Neurology, 72, 269–277.
Lewis, B. P., Burge, C. B., & Bartel, D. P. (2005). Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell, 120, 15–20.
Liu, X. R., Tan, X. Q., Yang, Y., Zeng, X. R., & Tang, X. L. (2012). Propofol increases the Ca2+ sensitivity of BKCa in the cerebral arterial smooth muscle cells of mice. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 33, 19–26.
Majer, A., Medina, S. J., Niu, Y., Abrenica, B., Manguiat, K. J., Frost, K. L., et al. (2012). Early mechanisms of pathobiology are revealed by transcriptional temporal dynamics in hippocampal CA1 neurons of prion infected mice. PLoS Pathogens, 8, e1003002.
Missiaglia, E., Shepherd, C. J., Patel, S., Thway, K., Pierron, G., Pritchard-Jones, K., et al. (2010). MicroRNA-206 expression levels correlate with clinical behaviour of rhabdomyosarcomas. British Journal of Cancer, 102, 1769–1777.
Miura, P., Amirouche, A., Clow, C., Réus, G. Z., Barbosa, L. M., et al. (2012). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression is repressed during myogenic differentiation by miR-206. Journal of Neurochemistry, 120, 230–238.
Mouillet-Richard, S., Baudry, A., Launay, J. M., & Kellermann, O. (2012). MicroRNAs and depression. Neurobiology Disease, 46, 272–278.
Numakawa, T., Richards, M., Adachi, N., Kishi, S., Kunugi, H., & Hashido, K. (2011). MicroRNA function and neurotrophin BDNF. Neurochemistry International, 59, 551–558.
O’Connor, R. M., Dinan, T. G., & Cryan, J. F. (2012). Little things on which happiness depends: MicroRNAs as novel therapeutic targets for the treatment of anxiety and depression. Molecular Psychiatry, 17, 359–376.
Perrine, S. A., Ghoddoussi, F., Michaels, M. S., Sheikh, I. S., McKelvey, G., & Galloway, M. P. (2014). Ketamine reverses stress-induced depression-like behavior and increased GABA levels in the anterior cingulate: An 11.7T (1)H-MRS study in rats. Progress in Neuropsychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 51, 9–15.
Rajasethupathy, P., Fiumara, F., Sheradan, R., Betel, D., Puthanveettil, S. V., Russo, J. J., et al. (2009). Characterization of small RNAs in Aplysia reveals a role for miR-124 in constraining synaptic plasticity through CREB. Neuron, 63, 803–807.
Réus, G. Z., Stringari, R. B., Ribeiro, K. F., Ferraro, A. K., Vitto, M. F., Cesconetto, P., et al. (2011). Ketamine plus imipramine treatment induces antidepressant-like behavior and increases CREB and BDNF protein levels and PKA and PKC phosphorylation in rat brain. Behavioural Brain Research, 221, 166–171.
Shimizu, E., Hashimoto, K., Okamura, N., Koike, K., Komatsu, N., Kumakiri, C., et al. (2003). Alterations of serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in depressed patients with or without antidepressants. Biological Psychiatry, 54, 70–75.
Siuciak, J. A., Lewis, D. R., & Wiegand, S. J. (1997). Antidepressant-like effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 56, 131–137.
Soriano, S. G., Liu, Q., Li, J., Liu, J. R., Han, X. H., Kanter, J. L., et al. (2010). Ketamine activates cell cycle signaling and apoptosis in the neonatal rat brain. Anesthesiology, 2010(112), 1155–1163.
Wahid, F., Shehzad, A., Khan, T., & Kim, Y. Y. (2010). MicroRNAs: Synthesis, mechanism, function, and recent clinical trials. Biochimica Biophysica Acta, 1803, 1231–1243.
Wang, X., Chen, Y., Zhou, X., Liu, F., Zhang, T., & Zhang, C. (2012). Effects of propofol and ketamine as the combined anesthesia for electroconvulsive therapy in patients with depressive disorder. The Journal of ECT, 28, 128–132.
Wang, X. B., Cheng, Y. H., Liu, X. J., Yang, J., & Zhang, C. (2011a). Unexpected pro-injury effect of propofol on vascular smooth muscle cells with increased oxidative stress. Critical Care Medicine, 39, 738–745.
Wang, X., Ling, C., Bai, Y., & Zhao, J. (2011b). MicroRNA-206 is associated with invasion and metastasis of lung cancer. Anatomical Record, 294, 88–92.
Wang, X. B., Yang, Y. L., Zhou, X., Wu, J. L., Li, J. L., Jiang, X., et al. (2011c). Propofol pretreatment increases antidepressant-like effects induced by acute administration of ketamine in rats receiving forced swimming test. Psychiatry Research, 185, 248–253.
Wang, N., Zhang, G. F., Liu, X. Y., Sun, H. L., Wang, X. M., Qiu, L. L., et al. (2014). Downregulation of neuregulin 1-ErbB4 signaling in parvalbumin interneurons in the rat brain may contribute to the antidepressant properties of ketamine. Journal of Molecule Neuroscience. doi:10.1007/s12031-014-0277-8.
Xu, S. X., Zhou, Z. Q., Li, X. M., Ji, M. H., Zhang, G. F., & Yang, J. J. (2013). The activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase in rat hippocampus contributes to the rapid antidepressant effect of ketamine. Behavior Brain Research, 253, 305–319.
Yu, S. P., Farhangrazi, Z. S., Ying, H. S., Yeh, C. H., & Choi, D. W. (1998). Enhancement of outward potassium current may participate in beta-amyloid peptide-induced cortical neuronal death. Neurobiology Disease, 5, 81–88.
Yu, S. P., Yeh, C. H., Sensi, S. L., Gwag, B. J., Canzoniero, L. M., Farhangrazi, Z. S., et al. (1997). Mediation of neuronal apoptosis by enhancement of outward potassium current. Science, 278, 114–117.
Yuluğ, B., Ozan, E., Gönül, A. S., & Kilic, E. (2009). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, stress and depression: A minireview. Brain Research Bull, 78, 267–269.
Zarate, C. A., Singh, J. B., Carson, P. J., Brutsche, N. E., Ameli, R., Luckenbaugh, D. A., et al. (2006). A randomized trial of an N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Archives of General Psychiatry, 63, 856–864.
Zhou, W., Wang, N., Yang, C., Li, X. M., Zhou, Z. Q., & Yang, J. J. (2013). Ketamine-induced antidepressant effects are associated with AMPA receptors-mediated upregulation of mTOR and BDNF in rat hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. European Psychiatry, 13, 00428–00488.
Zhou, R., Yuan, P., Wang, Y., Hunsberger, J. G., Elkahloun, A., Wei, Y., et al. (2009). Evidence for selective microRNAs and their effectors as common long-term targets for the actions of mood stabilizers. Neuropsychopharmacology, 34, 1395–1405.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 8127147) and International Cooperation, Department of Science & Technology of Sichuan Province (Grant No. 2011HH0031) to X. Wang. The authors acknowledge Yong Pu and Haidong Wu Ph.D. from Saier Biotechnology Inc. for their laboratory support and Tingjing Gong Ph.D. from Tianjing Kangchen Biotechnology Inc. for his support and encouragement with this research project.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest in this matter.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Yang, Q., Wang, X. et al. MicroRNA Expression Profile and Functional Analysis Reveal that miR-206 is a Critical Novel Gene for the Expression of BDNF Induced by Ketamine. Neuromol Med 16, 594–605 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-014-8312-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-014-8312-z