Abstract
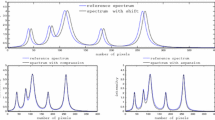
A simple analytical approximation to an inhomogeneously-broadened dispersion signal is proposed and tested with resonance lines broadened by unresolved hyperfine structure. Spectral parameters may be rapidly and accurately extracted using a nonlinear least-squares fitting algorithm. Combining the new approximation to a dispersion signal with a well-known approximation to the absorption signal allows dispersion-absorption admixtures, a problem of growing importance, to be analyzed quickly and accurately. For pure dispersion signals, the maximum difference between the fit and the signal for unresolved lines is 1.1 % of the maximum intensity. For pure absorption, the difference is 0.33 % of the peak-to-peak intensity, and for admixtures up to 40 % dispersion (maximum intensity/peak-to-peak intensity), the difference is 0.7 %. The accuracy of the recovered spectral parameters depends on the degree of inhomogeneously-broadened and the percentage admixture, but they are generally about 1 % at most. A significant finding of the work is that the parameters pertinent to the dispersion or the absorption are insignificantly different when fitting isolated lines vs. fitting admixtures. Admixtures with added noise or an unsuspected extraneous line are investigated.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
To simplify the presentation, we abbreviate the Voigt, Lorentzian, Gaussian, and sum-function line shape functions as simply the Voigt, Lorentzian, Gaussian, and sum-function, respectively. To distinguish between the absorption and dispersion, we refer, to the Voigt absorption or the Lorentzian dispersion, etc. Furthermore, we shall write that “\(\Delta H_{pp}^0\) increases …” rather than “the value of \(\Delta H_{pp}^0\) increases …,” etc.
Sigma-Aldrich, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany.
References
Portis, A. M. (1953). Electronic Structure of F Centers: Saturation of the Electron Spin Resonance. Physical Review, 91, 1071.
Wertheim, G. K., Butler, M. A., West, K. W., & Buchanan, D. N. E. (1974). Determination of the Gaussian and Lorentzian Content of Experimental Line Shapes. Review of Scientific instruments, 45, 1369–1371.
v.d. Hulst, H. C., & Reesinck, J. J. M. (1947). Lin Breadths and Voigt Profiles. Astronomical Journal, 106, 121–127.
Westberg, J., Wang, J., & Axner, O. (2012). Fast and non-approximate methodology for calculation of wavelength-modulated Voigt lineshap functions suitable for real-time curve fitting. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer, 113, 2049–2057.
Westberg, J., Wang, J., & Axner, O. (2014). Methodology for fast curve fitting to modulated Voigt dispersion lineshape functions. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer, 133, 244–250.
Bales, B. L. (1989). Inhomogeneously Broadened Spin-Label Spectra. In L. J. Berliner, J. Reuben (Ed.). Biological Magnetic Resonance (pp. 77–130). New York: Plenum.
Bales, B. L., Peric, M., & Lamy-Freund, M. T. (1998). Gaussian line broadening induced by unresolved proton hyperfine structure and by field modulation into the EPR spectrum of the proxyl spin probe. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 132, 279–286.
Halpern, H. J., Peric, M., Yu, C., & Bales, B. L. (1993). Rapid Quantitation of Parameters from Inhomogeneously Broadened EPR Spectra. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 103, 13–22.
Bales, B. L., & Willett, D. (1984). EPR investigation of the intermediate spin exchange regime. Journal of Chemical Physics, 80, 2997–3004.
De Tommasi, E., Castrillo, A., Casa, G., & Gianfrani, L. (2008). An efficient approximation for a wavelength-modulated 2nd harmonic lineshape from a Voigt absorption profile. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 109, 168–175.
Smirnov, A. I., & Belford, R. L. (1995). Rapid Quantitation from Inhomogeneously Broadened EPR Spectra by a Fast Convolution Algorithm. Journal of Magnetic Resonance A, , 113, 65–73.
Liu, Y., Lin, J., Huang, G., Guo, Y., & Duan, C. (2001). Simple empirical analytical approximation to the Voigt profile. Journal of Optical Society of America B, 18, 666–672.
Kielkopf, J. F. (1973). New approximation to the Voigt function with applications to spectral-line analysis. Journal of Optical Society of America, 63, 987–995.
Shin, B. (2016). An analytical method for the deconvolution of Voigtian profiles. Applied Magnetic Resonance, 47, 429–452.
Klug, C. S., Camenisch, T. G., Hubbell, W. L., & Hyde, J. S. (2005). Multiquantum EPR spectroscopy of spin-labled Arrestin K267c at 35 GHz. Biophysical Journal, 88, 3641–3647.
Fajer, P., & Marsh, D. (1983). Analysis of dispersion-mode saturation transfer ESR spectra. Application of model membranes. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 55, 205–215.
Rinard, G. A., Quine, R. W., Ghim, B. T., Eaton, S. S., & Eaton, G. R. (1996). Dispersion and superheterodyne EPR using a bimodal resonator. Journal of Magnetic Resonance A, 122, 58–63.
Hyde, J. S., Froncisz, W., & Kusumi, A. (1982). Dispersion electron spin resonance with the loop gap resonator.. Review of Scientific Instruments, 53, 1934–1937.
Bales, B. L., & Peric, M. (1997). EPR Line Shifts and Line Shape Changes Due to Spin Exchange of Nitroxide Free Radicals in liquids. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 101, 8707–8716.
Bales, B. L., & Peric, M. (2002). EPR Line Shifts and Line Shape Changes Due to Spin Exchange of Nitroxide Free Radicals in Liquids 2. Extension to High Spin Exchange Frequencies and Inhomogeneously Broadened Spectra. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 106, 4846–4854.
Bales, B. L., Peric, M., & Dragutan, I. (2003). EPR Line Shifts and Line Shape Changes Due to Spin Exchange of Nitroxide Free Radicals in Liquids 3. Extension to Five Hyperfine Lines. Additional Line Shifts Due to Re-encounters. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 107, 9086–9098.
Bales, B. L., Meyer, M., Smith, S., & Peric, M. (2008). EPR Line Shifts and Line Shape Changes Due to Spin Exchange of Nitroxide-Free Radicals in Liquids 4. Test of a Method to Measure Re-encounter Rates in Liquids Employing 15N and 14N Nitroxide Spin Probes. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 112, 2177–2181.
Bales, B. L., Meyer, M., Smith, S., & Peric, M. (2009). EPR Line Shifts and Line Shape Changes Due to Spin Exchange of Nitroxide-Free Radicals in Liquids 6. Separating Line Broadening due to Spin Exchange and Dipolar Interactions. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 113, 4930–4940.
Bales, B. L., Harris, F. L., Peric, M., & Peric, M. (2009). EPR Line Shifts and Line Shape Changes Due to Spin Exchange of Nitroxide-Free Radicals in Liquids 7. Singly Charged Surfactant Nitroxide. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 113, 9295–9303.
Bales, B. L., Meyer, M., & Peric, M. (2014). EPR Line Shifts and Line Shape Changes Due to Heisenberg Spin Exchange and Dipole–Dipole Interactions of Nitroxide Free Radicals in Liquids: 9. An Alternative Method to Separate the Effects of the Two Interactions Employing 15N and 14N. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 118, 6154–6162.
Salikhov, K. M. (2010). Contributions of Exchange and Dipole-Dipole Interactions to the Shape of EPR Spectra of Free Radicals in Diluted Sollutions. Applied Magnetic Resonance, 38, 237–256.
Salikhov, K. M., Mambetov, A. Y., Bakirov, M. M., Khairuzhdinov, I. T., Galeev, R. T., Zaripov, R. B., & Bales, B. L. (2014). Spin Exchange Between Charged Paramagnetic Paritcles in Dilute Solutions. Applied Magnetic Resonance, 45, 911–940.
Peric, M., Bales, B. L., & Peric, M. (2012). Electron Paramagnetic Line Shifts and Line Shape Changes Due to Heisenberg Spin Exchange and Dipole-Dipole Interactions of Nitroxide Free Radicals in Liquids 8. Further Experimental and Theoretical Efforts to Separate the Effects of the Two Interactions. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 116, 2855–2866.
Kurban, M. R., Peric, M., & Bales, B. L. (2008). Nitroxide spin exchange due to re-encounter collisions in a series of n-alkanes. Journal of Chemical Physics, 129, 064501–064510.
Reif, F. (1965). Fundamentals of Statistical and Thermal Physics. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Dobryakov, S. N., & Lebedev, Y. S. (1969). Analysis of Spectral Lines whose Profile is Describe by a Composition of Gaussian and Lorentz Profiles. Soviet Physics-Doklady, 13, 873.
Ludowise, P., Eaton, S. S., & Eaton, G. R. (1991). A Convenient Monitor of EPR Automatic Frequency Control (AFC) Function. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 93, 410–412.
Smirnov, A. I. (2008). Post-processing of EPR spectra by convolution filtering: Calculation of a harmonics’ series and automatic separation of fast-motion components from spin label EPR spectra. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 190, 154–159.
Tseitlin, M., Quine, R. W., Rinard, G. A., Eaton, S. S., & Eaton, G. R. (2010). Combining absorption and dispersion signals to improve singal-to-noise for rapid scan EPR imaging. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 203, 305–310.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12013-017-0805-6.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bales, B.L. A Simple Analytical Approximation to an Inhomogeneously-Broadened Dispersion Spectrum. Application to Absorption-Dispersion Admixtures. Cell Biochem Biophys 75, 171–184 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-016-0760-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-016-0760-7