Abstract
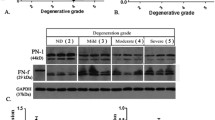
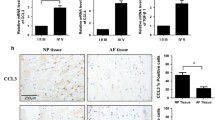
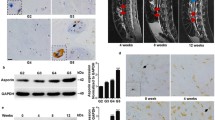
We aim at determining the changes in the expression of NF-kB signaling pathway in degenerative intervertebral discs. We collected normal and degenerated intervertebral discs tissues. The normal and degenerated cells were cultivated and their histopathology and immunofluoresence studies were used to observe the position of NF-kB p65 in the cell. We also treated the nucleus pulposus cells with inflammatory factors and inhibitors. Western blot was used to analyze the expression of different proteins. Real time fluorescence-based quantitative PCR was used for observation of NF-kB regulation of change in gene expression. Immunofluorescence showed that in the non-degenerative group the p65 was found in the cytoplasm of the nucleus pulposus cell while in the degenerated cell group the p65 protein was found in the nucleus of the cell. The expression of p65 increased with increase in the degree of degenerative change of the nucleus pulposus cell. RT-PCR showed that the expression of matrix metalloproteinases, aggrecanases and IL-6 was higher in the degenerative group. The amount of aggrecan and type II collagen was significantly decreased in the degenerative group. IL-1β was able to upregulate the activation of NF-kB and the expression of MMP-13 and ADAMTS-4 was also significantly increased. The effect of these proteins can be inhibited by the NF-kB inhibitor, BAY11-7082. The activation of the NK-kB signaling pathway in a degenerative intervertebral disc is gradually increased, regulating the over-expression of matrix-degrading enzymes. It plays an important role in the degradation of extracellular matrix.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hayden, M. S., & Ghosh, S. (2008). Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell, 132(3), 344–362.
Hayden, M. S., West, A. P., & Ghosh, S. (2006). NF-kappaB and the immune response. Oncogene, 25(51), 6758–6780.
Lee, J. I., & Burckart, G. J. (1998). Nuclear factor kappa B: Important transcription factor and therapeutic target. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 38(11), 981–993.
Pfirrmann, C. W., Metzdorf, A., Zanetti, M., et al. (2001). Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine, 26(17), 1873–1878.
Livak, K. J., & Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods, 25(4), 402–408.
Berenbaum, F. (2004). Signaling transduction: Target in osteoarthritis. Current Opinion in Rheumatology, 16(5), 616–622.
Kim, H. J., Chang, E. J., Kim, H. M., et al. (2006). Antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid inhibits osteoclast differentiation by reducing nuclear factor-kappaB DNA binding and prevents in vivo bone resorption induced by receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 40(9), 1483–1493.
Dai, S., Hirayama, T., Abbas, S., et al. (2004). The IkappaB kinase (IKK) inhibitor, NEMO-binding domain peptide, blocks osteoclastogenesis and bone erosion in inflammatory arthritis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279(36), 37219–37222.
Acharyya, S., Villalta, S. A., Bakkar, N., et al. (2007). Interplay of IKK/NF-kappaB signaling in macrophages and myofibers promotes muscle degeneration in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 117(4), 889–901.
Wuertz, K., Quero, L., Sekiguchi, M., et al. (2011). The red wine polyphenol resveratrol shows promising potential for the treatment of nucleus pulposus-mediated pain in vitro and in vivo. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 36(21), E1373–E1384.
Yu, Z. G., Xu, N., Wang, W. B., et al. (2009). Interleukin-1 inhibits Sox9 and collagen type II expression via nuclear factor-kappaB in the cultured human intervertebral disc cells. Chinese Medical Journal, 122(20), 2483–2488.
Wang, J., Markova, D., Anderson, D. G., et al. (2011). TNF-α and IL-1β promote a disintegrin-like and metalloprotease with thrombospondin type I motif-5-mediated aggrecan degradation through syndecan-4 in intervertebral disc. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286(46), 39738–39749.
Ohba, T., Haro, H., Ando, T., et al. (2009). TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB signaling reverses age-related declines in VEGF induction and angiogenic activity in intervertebral disc tissues. Journal of Orthopaedic Research, 27(2), 229–235.
Nasto, L. A., Seo, H. Y., Robinson, A. R., et al. (2012). Inhibition of NF-KB activity ameliorates age-associated disc degeneration in a mouse model of accelerated aging. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 37, 1819–1825.
Oliver, K. M., Garvey, J. F., Ng, C. T., et al. (2009). Hypoxia activates NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression through the canonical signaling pathway. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 11(9), 2057–2064.
Studer, R. K., Vo, N., Sowa, G., et al. (2011). Human nucleus pulposus cells react to IL-6: independent actions and amplification of response to IL-1 and TNF-α. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 36(8), 593–599.
Solovieva, S., Kouhia, S., Leino-Arjas, P., et al. (2004). Interleukin 1 polymorphisms and intervertebral disc degeneration. Epidemiology, 15(5), 626–633.
Ponnappan, R. K., Markova, D. Z., Antonio, P. J., et al. (2011). An organ culture system to model early degenerative changes of the intervertebral disc. Arthritis Research & Therapy, 13(5), R171.
Smith, L. J., Chiaro, J. A., Nerurkar, N. L., et al. (2011). Nucleus pulposus cells synthesize a functional extracellular matrix and respond to inflammatory cytokine challenge following long term agarose culture. European Cells & Materials, 22, 291–301.
Poveda, L., H, M., Boos, N., & Wuertz, K. (2009). Peroxynitrite induces gene expression in intervertebral disc cells. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 34(11), 1127–1133.
Roberts, S., Caterson, B., Menage, J., et al. (2000). Matrix metalloproteinases and aggrecanase: their role in disorders of the human intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 25(23), 3005–3013.
Millward-Sadler, S. J., Costello, P. W., Freemont, A. J., et al. (2009). Regulation of catabolic gene expression in normal and degenerate human intervertebral disc cells: Implications for the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Research & Therapy, 11(3), R65.
Ellman, M. B., Kim, J. S., An, H. S., et al. (2012). The pathophysiologic role of the protein kinase Cδ pathway in the intervertebral discs of rabbits and mice: in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo studies. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 64(6), 1950–1959.
Liacini, A., Sylvester, J., Li, W. Q., et al. (2002). Inhibition of interleukin-1-stimulated MAP kinases, activating protein-1 (AP-1) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B) transcription factors down-regulates matrix metalloproteinase gene expression in articular chondrocytes. Matrix Biology, 21(3), 251–262.
Little, C. B., Flannery, C. R., Hughes, C. E., et al. (1999). Aggrecanase versus matrix metalloproteinases in the catabolism of the interglobular domain of aggrecan in vitro. Biochemical Journal, 344(1), 61–68.
Ross, T. N., Kisiday, J. D., Hess, T., et al. (2012). Evaluation of the inflammatory response in experimentally induced synovitis in the horse: A comparison of recombinant equine interleukin 1 beta and lipopolysaccharide. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 20(12), 1583–1590.
Ellman, M. B., Kim, J. S., An, H. S., et al. (2012). Toll-like receptor adaptor signaling molecule MyD88 on intervertebral disk homeostasis: In vitro, ex vivo studies. Gene, 505(2), 283–290.
Singh, K., Masuda, K., Thonar, E. J., et al. (2009). Age-related changes in the extracellular matrix of nucleus pulposus and anulus fibrosus of human intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 34(1), 10–16.
Roughley, P. J. (2006). The structure and function of cartilage proteoglycans. European Cells and Materials, 12, 92–101.
Martin, J. A., & Buckwalter, J. A. (2001). Roles of articular cartilage aging and chondrocyte senescence in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Iowa Orthopaedic Journal, 21, 1–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhongyi Sun and Zhanmin Yin contributed equally to this work and should be considered as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Yin, Z., Liu, C. et al. The Changes in the Expression of NF-KB in a Degenerative Human Intervertebral Disc model. Cell Biochem Biophys 72, 115–122 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0417-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0417-3