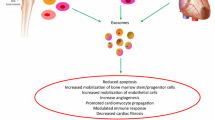
Abstract
Exosomes are spherical bilayer membrane vesicles with an average diameter of 40–100 nm. These particles perform a wide range of biological activities due to their contents, including proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, lncRNA, and miRNA. Exosomes are involved in inflammation induction, oxidative stress and apoptosis, which can be effective in endothelial dysfunction. Due to the induction of mentioned processes in the endothelial cells, the intercellular connections are destroyed, cell permeability increases and finally cell efficiency decreases and functional defects occur. Cardiovascular disease (CVDs) are of consequences of endothelial dysfunction. Thus by identifying the exosome signaling pathways, which induce inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis, endothelial dysfunction and subsequently CVDs can be reduced; exosomes can be used for appropriate target therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are a wide range of disorders, that affect vascular system, heart, brain and other vital organs. CVD is a chronic disease, that begins in childhood, even if the first symptoms appear in the middle age [1]. According to researches, these disorders are more common in patients with chronic kidney disease than general population [2]. A wide range of evidence supports the important role of inflammatory responses in the pathogenesis of CVD through endothelial cell (ECs) dysfunction [3, 4].
In fact, the endothelium creates a barrier due to cell-to-cell attachments, that selectively restricts macromolecules movement [5]. It also has protective effects, anti-apoptotic activity, anti-myocardial fibrosis, as well as vasodilation and immune system regulation [6, 7]. However, ECs with an inflammatory phenotype cause inflammation in the blood vessels, resulting in cardiac dysfunction [8, 9]. In addition, exosome increases the permeability and disrupts the joints by increasing the expression of adhesion molecules; they also decrease nitric oxide (NO) synthesis in ECs, that causes ECs dysfunction and thus increases CVD risk [10, 11].
In fact, exosome is a largely unknown "cell-to-cell" communication system, that is now increasingly considered for diagnostic and therapeutic use in CVD [12]. As a new type of treatment and diagnostic tool, they are involved in non-invasive assessment of limb response to injury, or in the treatment and development of a reliable treatment method [13,14,15]. The aim of this study was to evaluate exosomes for the incidence of ECs dysfunction in CVD.
Structure and Function of Exosome
Exosomes are spherical vesicles with a bilayer membrane with an average diameter of 40–100 nm [16]. They form inside secretory cells in endosomal chambers called multivesicular endosomes (MVEs), with a series of precise regulatory processes such as "endocytosis-fusion-efflux" process [17]. Exosomes are secreted out of the cell via exocytosis process; it has three steps, including: exosome biogenesis, transportation of multivesicular bodies ( MVBs) to the plasma membrane and MVBs fusion with the plasma membranes. The exosome secretion stage is closely monitored by molecules, such as Rab27a/b, Rab7, Contractin, SNARE and Synaptotagmin-7. Therefore, exosome secretion is monitored by physiological signaling, but some diseases and cancers can affect these regulatory mechanisms and alter exosome secretion [18, 19].
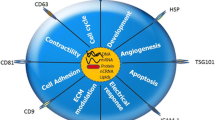
Exosomes can be found in all living cells, especially dendritic, lymphocyte, epithelial and endothelial cells [20]. They do not contain a random array of intracellular proteins, but a specific set of several protein families derived from plasma membranes, intracellular pathways, and cytosols [21]. In fact, exosomes usually contain a variety of biomolecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, lncRNA and miRNA and even viruses [15, 22]. These particles communicate with recipient cells by three mechanisms; they are absorbed by them. These three mechanisms include: 1- binding of transmembrane proteins from exosome to the existing receptors on the surface of recipient cells, 2-plasma membrane fusion of exosomes with plasma membrane of recipient cells and transfer of their contents to the cytosol of target cells and 3- internalization of exosomes into recipient cells [16].
Exosomes can play an important role in intercellular communications [23]. They are described as new particles in contact with neighboring or distant cells, and binding to membrane proteins, cytoplasm, lipids and nucleotides [24]. Transmission microscopy, possessing a cup-shaped morphology after negative staining and density gradient are used to identify exosomes. CD63, CD9, CD81 and tetraspanin protein markers can also be used to detect exosomes by monoclonal antibodies. Ultracentrifugation, ultrafiltration, size-exclusion chromatography, magnetic beads immunoaffinity, size-based microfluidic, microfluidics separation and dynamic microfluidics techniques are also used to separate exosomes [25].
Nowadays, exosomes are used for diagnosis and treatment of many diseases, including Alzheimer, Parkinson, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes mellitus and infectious diseases such as bacterial infections, sepsis, and COVID-19; they are also used for some cancers, such as breast, cervical, prostate and lung. Therapeutic use of exosomes is based on drug delivery or effective factors on signaling pathways, which are associated with patient's recovery. For example, in the treatment of cancer patients, exosomes can be used to deliver chemotherapeutic drugs such as paclitaxel, cisplatin and doxorubicin. Also, by transmitting chimeric agents such as CAR-T Cell and inducing an effect on the signaling of effector T cells, it is possible to increase exosomes function to eliminate tumor agents; thus, it helps the process of recovery in patients with cancer.
The use of exosomes in the treatment of infectious diseases is another example of the therapeutic use of these particles. In bacterial infections, exosomes can be used to treat patients by transmitting antimicrobial peptides, Hepcidin and beta-defincin-2 to increase the antibacterial function of immune cells. Exosomes containing super-repressor IκB can also be used in people with septic shock; they suppress the induction of septic shock due to IL-6, IL-1 and TNF cytokines by suppressing the NF-Kβ signaling pathway. In addition, recent studies have shown the effective role of exosomes in CVD treating by regulating cellular condition in cardio myocytes [26].
Also due to the transport of protein and functional RNA, exosomes are involved in the pathogenesis of many human malignancies, infectious and degenerative diseases, oncogenesis and tumor metastasis [27].Tumor cells can significantly release more exosomes than healthy ones; this fact suggests, that selective regulation of tumor-derived exosomes (TEXs) is based on their structure and function. TEXs also facilitate tumor growth and metastasis through exosome cross-section [28]. Also in the cardiovascular system, exosomes are related to ECs, cardiac myocytes, vascular cells and stem cells; they play a key role in growth and damage of cardiac muscle and CVD [29]. In fact, lncRNAs and miRNAs contents of exosome provide a potential source of new diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for CVD. They have many beneficial effects in preventing CVD, and heart repairing [30]. Most importantly, stem cell-derived exosomes will be more effective and safer than stem cell-based alternative therapies for CVDs treatment [31].
The Role of Exosome in Inflammation
Studies show, that inflammatory process induced by exosomes can lead to ECs dysfunction and subsequently CVD. The exosome containing miR-155 can lead to endothelial dysfunction by inducing inflammation in endothelial cells. miR-155 causes inflammation in ECs by activating the NF-Kβ transcription factor, and subsequently increasing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α). The result is a defect in the function of these cells. On the other hand, miR-155 expression in ECs can also induce inflammation by targeting the two molecules of Src homology 2 (SH2) domain-containing inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase 1 (SHIP1) and Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) [32,33,34]. Thus, miR-155 increases the JNK signaling pathway activity by suppressing the SHIP1 molecule activity; the product of this pathway is inflammation induction in ECs through the production of IL-8.
In addition, miR-155 can induce MAPK/STAT1/SATAT3 signaling pathway by suppressing the SOCS1 molecule activity, which can also cause inflammation in ECs by producing Pro-inflammatory cytokines. Subsequently, inflammation in ECs increases cell permeability, which leads to endothelial dysfunction through damage to intercellular connections [35, 36]. Exosome containing Diacyl glycerol (DAG) suppresses the endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS molecule activity, and increases the Egr1 and MMP2 molecules activity in the downstream of PKC-β stimulation pathway, by increasing the level of protein kinase C beta (PKC-β in EC; it results in inflammation induction in EC, endothelial dysfunction and finally CVD [37].
eNOS enzyme incites IL-10 production by producing NO, and induces the HO-1/CO pathway; due to the anti-inflammatory role of this cytokine, it can prevent inflammation. NO-induced HO-1/CO pathway also inhibits signal transmission in the downstream of Toll-like Receptor (TLR), which can also induce an anti-inflammatory effect in ECs [38, 39]. Due to the anti-inflammatory role of eNOS enzyme by NO production, the inflammatory process occurs in ECs by suppressing this enzyme; it results in increased permeability of cells, loss of intercellular connections and consequent defects in EC function.
In addition, PKC-β can upregulate the CD11c, CCL2 and IL-1β inflammatory markers in ECs by activating the ERK1/2 enzyme, thereby inducing inflammation in cells [40]. Expression of CD11c at the ECs level, and then binding to its ligand (ICAM-1) at the immune cell surface results in ERK/c-fos and JNK/C-JUN signaling pathways production in the downstream of this binding; the outcome is IL-8 production [41]. Expressed CCL2 on the ECs surface can also lead to IL-8 production via JNK signaling pathway, which occurs in its downstream in ECs [42]. The produced IL-8 can also induce inflammation through the above pathways and by activating the NF-Kβ transcription factor [43, 44].
Exosome containing C-Reactive Protein (CRP) molecule can also increase the activity of COX1/2 enzymes in ECs by activating the NF-Kβ transcription factor. By producing TXA2/PGH2 in ECs, inflammation and endothelial dysfunction are induced [45]. TXA2 induces inflammation in ECs via the Ca + 2/cnA/NFAT pathway. Prostaglandin (PG) molecule can also induce inflammation in ECs through the G protein-dependent pathway, and induction of the EPAC/Rap signaling pathway [46]. Following the onset of inflammation, by increasing the permeability of ECs, intercellular connections of these cells are destroyed, and consequently ECs malfunction occurs.
Also, exosomes produced from monocytes through Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4)/Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response gene 88 (Myd88) pathway can lead to inflammation in ECs and subsequent endothelial dysfunction, which can result in CVD induction [47]. Exosomes containing HMGB1 can also induce a signal in the downstream of the receptor signaling pathway by connecting to its receptor called RAGE. CDC42/RAC1/RH0A/GSK3β/AKT/ROCK signaling in the downstream of RAGE receptor is induced by DIAPH1 mediator, which activates production of SRF transcription factor by increasing the expression of Egr1/C-fos/Tagln genes; finally, it induces inflammation and endothelial dysfunction, and may also contribute to CVD [48].
Downstream activated AKT of exosome containing HMGB can also lead to inflammation in ECs via the mTORC1/4EBP1/P70S6K pathway [49]. In addition, in another pathway induced by AKT, the FOXO1 molecule can induce inflammation in ECs by activating the NF-Kβ transcription factor [50, 51]. Downstream activated GSK3β of this exosome can also activate the TCF transcription factor via the β-Catenin/APC/Axin/CK pathway, which translates IL-1β gene to produce the cytokine; subsequently it generates inflammation [52]. On the other hand, GSK3β can also induce inflammation in ECs via Nrf2/HO1 pathway [53].
Some other pathways induced in the downstream of exosomes containing HMGB1 can have anti-inflammatory effects in ECs. Thus, the Rac1/NADPH oxidase/ROS/p38 signaling pathway in the downstream of this exosome inhibits inflammation in ECs by upregulating the hemeoxygenase-1 (HO-1) molecule. Also in the other pathway, that occurs by RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway in the downstream of this exosome, it can prevent inflammation by inhibiting TNF-α function; thus it prevents permeability increment in ECs, and consequent endothelial dysfunction. So, HMGB1 exosome can have dual effects on ECs following the onset or absence of inflammation [54,55,56].
Exosome containing Free Fatty acid (FFA) can lead to inflammation in ECs via the NF-Kβ and JNK pathways. This exosome can also induce endothelial dysfunction by reducing NOS enzyme activity, and consequently reducing NO production. This defect in the function of ECs along with causing an inflammatory condition in these cells causes CVD [57, 58]. The NF-Kβ transcription factor, in addition to inflammation induce endothelial dysfunction by inducing miR-31-5P, and subsequently inhibiting the eNOS enzyme; the result is an increased risk of developing CVD [59].
Contrary to the above findings, some other studies have shown that exosomes can prevent inflammation induction in endothelial cells and subsequent endothelial dysfunction, so these exosomes can be used as therapeutic targets in CVD [60]. Thus, exosomes containing Small Nuclear RNA host gene 9 (SNHG9) lncRNA act as a CeRNA by targeting mRNA of TNF receptor type-1 associated death domain protein (TRADD); it can prevent inflammation in ECs and subsequently endothelial dysfunction [61]. Some exosomes can also reduce NF-Kβ acetyl P65 transcription factor activity by increasing the SIRT1 expression in ECs, which in turn reduces inflammation. Finally, it increases ECs function and reduces CVD incidence [62].
The Role of Exosome in Oxidative Stress Induction
Studies show that exosomes can lead to ECs dysfunction through oxidative stress and induce CVD [63]. The exosome can activate the ROS/NOS signaling pathway by suppressing miR-223 in ECs. Downstream of this activated pathway, Grb/shc/MAPK/ET1 signaling leads to endothelial dysfunction and subsequently induces CVD [63, 64]. Other exosomes can also suppress eNOS enzyme by increasing Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) production and consequently reducing NO production [65]. Since, the produced NO by eNOS enzyme can be Guanylate enzyme cofactor to produce cGMP, and the produced cGMP molecule through RAC-1/CORTACTIN/ARP2/3 signaling pathway leads to ECs function maintenance, the NO molecule by affecting cGMP production, indirectly affects ECs performance [66]. Therefore, with the reduction of NO production by ROS, ECs function is impaired; one of the consequences can be CVD development [67, 68].
In addition, exosome-induced oxidative stress with ROS production can activate NF-Kβ signaling pathway in ECs. Epigenetic changes resulting from activation of NF-Kβ transcription factor in the downstream of this pathway, increase the expression of VCAM, MCP-1, VEGF and MMP molecules on the ECs surface. Increased expression of these molecules reduces endothelium-dependent vasodilation, which can impair ECs structure and affects CVD development [69,70,71]. MCP-1/ICAM-1 molecules, which are expressed by increasing ROS production and subsequent epigenetic changes are associated with NF-Kβ signaling on ECs surface; they can alter ECs structure by increasing monocyte-endothelial adhesion, and subsequently induce atherosclerosis and other CVDs [72, 73].
Exosome-induced ROS can also increase contraction in ECs by activating the two signaling pathways of MLCK/MYPT1/MLC and Rho/Rho Kinase. By inducing this action in ECs, the structure of these cells is altered and lead to CVD, such as aortic aneurysm [74]. As it was mentioned before, exosomes are involved in endothelial dysfunction, and CVD induction by inducing oxidative stress by RNS. Thus, RNS molecules can lead to up regulation of endothelin-1 molecules. Following this action, Protein Kinase C is activated and the signaling pathway resulting from PKC activation can lead to vasoconstriction, thereby inducing a number of CVDs such as coronary spasm [75].
Also, exosomes containing High-Mobility Group Protein-1 (HMGP-1), miR-15-b-5p and miR 378-3P, which are produced from active platelets can induce Neutrophil Extracellular Trap (NET) formation by activating the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway [76]. Subsequently, the Rac2 molecule from the NET network can activate NADPH oxidase enzyme via the MAPK signaling pathway. This enzyme can also produce a type of ROS by converting O2 to its free radical (O2−), which leads to endothelial dysfunction by damaging endothelial cells [77]. In addition, HMGB1 binding to TLR4 can activate the RIPK3/p-DRP1 signaling pathway, which results in ROS production by mitochondrial fission [78]. On the other hand, miR-15b can also regulate ROS production via Sirtuin 4 Pathway [79]. Therefore, produced exosomes from platelets can have different effects on ROS production and regulation.
Despite the role of some exosomes in inducing oxidative stress and subsequent endothelial dysfunction and CVD, some studies have shown that these exosomes can have adverse effects on oxidative stress; they prevent CVD, and can be used as a treatment strategy [80]. Thus, SRT 1720 exosome can increase antioxidant enzymes production by expressing SIRT1 molecule in ECs, and subsequently suppress oxidative stress in ECs; it results in homeostasis induction in ECs, cell function increment, and finally reduces CVD incidence.
In addition, the aforementioned exosomes through the expression of SIRT1 molecule can increase COX-2 expression, and induce homeostasis in ECs by increasing COX2-mediated vasodilation; this homeostasis can also neutralize the adverse effects of ROS and RNS molecules, that are involved in oxidative stress [62].
The Role of Exosome in Apoptosis
In addition to inflammation and oxidative stress induction, exosomes can induce endothelial dysfunction by causing apoptosis in ECs, and subsequently induce CVDs. Thus, the exosome containing HMGB1 can induce apoptosis in ECs via RAGE/Bax/Bcl-2/Caspase 3 pathway; it results in cell apoptosis, endothelial dysfunction and ultimately CVD induction [81,82,83]. In addition, another study showed that an exosome treated with Advanced Glycation End products (AGEs) could lead to apoptosis in ECs via the RAGE/NADPH/ROS/p-JNK pathway [84, 85]. Exosomes containing Protein Disulfide Isomerase (PDI), which is produced from active platelets can also activate Bip molecules in ECs by binding to Calnexin. This molecule can also induce apoptosis in ECs through the ASK 1/TRAF 2/JNK/Caspase 3 pathway, and subsequently induces endothelial dysfunction [50, 51, 63]. In addition, the Bip molecule, which is activated in downstream of the PDI exosome activation pathway, can lead to Cytochrome C exit from the mitochondria via the eIF2/ATF4/CHOP/Bcl 2/Bax/Bak pathway [86].
On the other hand, the exosome containing Amyloid-β (Aβ) can send out Cytochrome C to the mitochondria by binding to the DR4/5 receptor in ECs via the FADD/Caspase 8/Bid/Bax/Bak signaling pathway; by cytochrome C removal from the mitochondria, apoptosis is induced in ECs [87]. The exosome containing TNF-α can also induce apoptosis in ECs via the FADD/Caspase 8/Bid/Cytochrome C and TRAF2/TRADD/Caspase 1/Caspase 3,6,7 signaling pathways [88]. On the other hand, exosomes containing FFA can also induce apoptosis in ECs via GSK-3β/Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway and p38MAPK [89, 90].
In addition, exosomes containing ox-LDL induce apoptosis in ECs by inducing the NADPH oxidase/ROS/p38 MAPK signaling pathway, thereby causing endothelial dysfunction [91]. Defect in ECs performance may lead to CVDs creation.
Some studies have shown that exosomes containing Growth Factor (GF) can also activate NADPH oxidase via the PKC/PI3K/Src/MAP Kinase/PAK signaling pathway. This enzyme can lead to ROS production. ROS is produced by NADPH oxidase, which is induced through the exosome containing GF; it can induce Redox signaling event by inhibiting PTEN, MKP-1 and PTP proteins. This signaling pathway contains Akt, c-Src, p38 MAPK, JNK, SAPK, ERK, PKC and ASK-1 signaling, which can activate Redox sensitive transcription factors such as NF-Kβ, AP-1, P53, Ets and HIF-1α. Consequently, these transcription factors can lead to ECs apoptosis by transcribing genes, called Redox sensitive genes, which include P21, SOD, and TRPM 2 [92]. On the other hand, exosomes containing GF can lead to Cytochrome C removal from the mitochondria via the PI3K/AKT/BAD/BAX pathway. Consequently, Caspase 3 and Caspase 9 are activated, which start apoptosis in ECs [93].
In addition, the exosome containing Rac-1 via the NOX 2/ROS/P38MAPK signaling pathway can lead to mitochondrial dysfunction, which is followed by caspase activation; it can induce apoptosis in ECs [94]. The exosome containing miR-122 can also play effective role in apoptosis induction in ECs by regulating the XIAP/ERK/Caspase8/Caspase3, GATA4/Bax/Bcl-2 and PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathways [95].
Therefore, exosomes microRNAs are effective in CVDs; by designing appropriate target therapies, these exosomes can be used as a treatment strategy (Table 1). As explained in the text, in addition to miRNA, exosomes also contain other contents such as proteins, lipids and enzymes, which can be effective in inducing CVD or cardioprotection. Therefore, identifying the signals resulting from these contents can also be effective for CVD treating, by designing appropriate target therapies (Table 2).
As explained above, endothelial dysfunction occurs by apoptosis induction in ECs, which can be effective in causing CVD. Therefore, by identifying the effective signaling pathways, in which exosomes can induce apoptosis in ECs, endothelial dysfunction and CVDs can reduce mentioned consequences.
Conclusion
Studies have shown that exosomes can lead to endothelial dysfunction by inducing inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in ECs. With the induction of dysfunction in ECs, one of the consequences of this event is CVDs occurrence. Thus, by identifying signaling pathways, in which exosomes induce inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis in ECs, can prevent endothelial dysfunction and CVDs; CVDs can be reduced by designing appropriate target therapies and can be used as a treatment strategy (Table 3).
References
Jokinen, E. (2014). Obesity and cardiovascular disease. Minerva Pediatrica, 67(1), 25–32.
Foley, R. N., Parfrey, P. S., & Sarnak, M. J. (1998). Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: JASN, 9(12 Suppl), S16-23.
Carter, A. M. (2012). Complement activation: An emerging player in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease. Scientifica. https://doi.org/10.6064/2012/402783
Farsad, B. F., Alavi, S. M., Ghorbanian, G., Fahimi, F., Ghaemmaghami, Z., Mehr, A. Z., & Bakhshandeh, H. (2019). The therapeutic efficnecy of ranolazine in comparison with conventional therapy in diabetic individuals with ischemic heart disease; a randomized clinical trial. Journal of Renal Injury Prevention, 9(1), e04–e04.
Rahimi, N. (2017). Defenders and challengers of endothelial barrier function. Frontiers in Immunology, 8, 1847.
Zhang, J., Tecson, K. M., & McCullough, P. A. (2020). Endothelial dysfunction contributes to COVID-19-associated vascular inflammation and coagulopathy. Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine, 21(3), 315–319.
Zhang, Y., Murugesan, P., Huang, K., & Cai, H. (2020). NADPH oxidases and oxidase crosstalk in cardiovascular diseases: Novel therapeutic targets. Nature Reviews Cardiology, 17(3), 170–194.
Momtaz, H. E., Tanasan, A., & Godini, M. (2020). Evaluation of urinary NGAL level in children with congenital heart disease as a possible early indicator of nephropathy. Journal of Nephropharmacology, 10(2), e14–e14.
Ooi, B. K., Chan, K.-G., Goh, B. H., & Yap, W. H. (2018). The role of natural products in targeting cardiovascular diseases via Nrf2 pathway: Novel molecular mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9, 1308.
Bhattacharjee, R., Khalyfa, A., Khalyfa, A. A., Mokhlesi, B., Kheirandish-Gozal, L., Almendros, I., et al. (2018). Exosomal cargo properties, endothelial function and treatment of obesity hypoventilation syndrome: A proof of concept study. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 14(5), 797–807.
Haybar, H., Shahrabi, S., Rezaeeyan, H., Jodat, H., & Saki, N. (2019). Strategies to inhibit arsenic trioxide-induced cardiotoxicity in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 234(9), 14500–14506.
Zhang, Y., Hu, Y.-W., Zheng, L., & Wang, Q. (2017). Characteristics and roles of exosomes in cardiovascular disease. DNA and Cell Biology, 36(3), 202–211.
Terrasini, N., & Lionetti, V. (2017). Exosomes in critical illness. Critical Care Medicine, 45(6), 1054–1060.
Zadeh, F. J., Akbari, T., Samimi, A., Davari, N., & Rezaeeyan, H. (2020). The role of molecular mechanism of Ten-Eleven Translocation2 (TET2) family proteins in pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). Molecular Biology Reports, 47(7), 5503–5509.
Zadeh, F. J., Ghasemi, Y., Bagheri, S., Maleknia, M., Davari, N., & Rezaeeyan, H. (2020). Do exosomes play role in cardiovascular disease development in hematological malignancy? Molecular Biology Reports. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05453-z
Zhang, J., Li, S., Li, L., Li, M., Guo, C., Yao, J., & Mi, S. (2015). Exosome and exosomal microRNA: Trafficking, sorting, and function. Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics, 13(1), 17–24.
Zhang, C., Ji, Q., Yang, Y., Li, Q., & Wang, Z. (2018). Exosome: Function and role in cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment, 17, 1533033818763450.
Asgarpour, K., Shojaei, Z., Amiri, F., Ai, J., Mahjoubin-Tehran, M., Ghasemi, F., et al. (2020). Exosomal microRNAs derived from mesenchymal stem cells: Cell-to-cell messages. Cell Communication and Signaling, 18(1), 1–16.
Hessvik, N. P., & Llorente, A. (2018). Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 75(2), 193–208.
Zhang, H., Wang, L., Li, C., Yu, Y., Yi, Y., Wang, J., & Chen, D. (2019). Exosome-induced regulation in inflammatory bowel disease. Frontiers in Immunology, 10, 1464.
Ostrowski, M., Carmo, N. B., Krumeich, S., Fanget, I., Raposo, G., Savina, A., et al. (2010). Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nature Cell Biology, 12(1), 19–30.
Van Niel, G., d’Angelo, G., & Raposo, G. (2018). Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 19(4), 213–228.
Seo, N., Akiyoshi, K., & Shiku, H. (2018). Exosome-mediated regulation of tumor immunology. Cancer Science, 109(10), 2998–3004.
Bobrie, A., Colombo, M., Raposo, G., & Théry, C. (2011). Exosome secretion: Molecular mechanisms and roles in immune responses. Traffic, 12(12), 1659–1668.
Zhu, L., Sun, H.-T., Wang, S., Huang, S.-L., Zheng, Y., Wang, C.-Q., et al. (2020). Isolation and characterization of exosomes for cancer research. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 13(1), 1–24.
Mosquera-Heredia, M. I., Morales, L. C., Vidal, O. M., Barceló, E., Silvera-Redondo, C., Vélez, J. I., & Garavito-Galofre, P. (2021). Exosomes: Potential disease biomarkers and new therapeutic targets. Biomedicines, 9(8), 1061.
Li, P., Kaslan, M., Lee, S. H., Yao, J., & Gao, Z. (2017). Progress in exosome isolation techniques. Theranostics, 7(3), 789.
Jiang, K., Dong, C., Yin, Z., Li, R., Mao, J., Wang, C., et al. (2020). Exosome-derived ENO1 regulates integrin α6β4 expression and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis. Cell Death & Disease, 11(11), 1–20.
Zamani, P., Fereydouni, N., Butler, A. E., Navashenaq, J. G., & Sahebkar, A. (2019). The therapeutic and diagnostic role of exosomes in cardiovascular diseases. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine, 29(6), 313–323.
Liang, B., He, X., Zhao, Y.-X., Zhang, X.-X., & Gu, N. (2020). Advances in exosomes derived from different cell sources and cardiovascular diseases. BioMed Research International. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7298687
Yuan, Y., Du, W., Liu, J., Ma, W., Zhang, L., Du, Z., & Cai, B. (2018). Stem cell-derived exosome in cardiovascular diseases: Macro roles of micro particles. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9, 547.
Jiang, K., Yang, J., Guo, S., Zhao, G., Wu, H., & Deng, G. (2019). Peripheral circulating exosome-mediated delivery of miR-155 as a novel mechanism for acute lung inflammation. Molecular Therapy, 27(10), 1758–1771.
Roohaninasab, M., Goodarzi, A., Ghassemi, M., Sadeghzadeh-Bazargan, A., Behrangi, E., & Najar Nobari, N. (2021). Systematic review of platelet-rich plasma in treating alopecia: Focusing on efficacy, safety, and therapeutic durability. Dermatologic Therapy, 34(2), e14768.
Zheng, B., Yin, W.-N., Suzuki, T., Zhang, X.-H., Zhang, Y., Song, L.-L., et al. (2017). Exosome-mediated miR-155 transfer from smooth muscle cells to endothelial cells induces endothelial injury and promotes atherosclerosis. Molecular Therapy, 25(6), 1279–1294.
Kuo, Y.-C., Li, Y.-S.J., Zhou, J., Shih, Y.-R.V., Miller, M., Broide, D., et al. (2013). Human mesenchymal stem cells suppress the stretch–induced inflammatory miR-155 and cytokines in bronchial epithelial cells. PLoS ONE, 8(8), e71342.
Wu, X., Li, Q., Feng, Y., & Ji, Q. (2018). Antitumor research of the active ingredients from traditional Chinese medical plant Polygonum cuspidatum. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2313021
Sun, H.-J., Wu, Z.-Y., Nie, X.-W., & Bian, J.-S. (2020). Role of endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: The link between inflammation and hydrogen sulfide. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 10, 1568.
Chung, H.-T., Choi, B.-M., Kwon, Y.-G., & Kim, Y.-M. (2008). Interactive relations between nitric oxide (NO) and carbon monoxide (CO): Heme oxygenase-1/CO pathway is a key modulator in NO-mediated antiapoptosis and anti-inflammation. Methods in Enzymology, 441, 329–338.
Khademi, M., Roohaninasab, M., Goodarzi, A., Seirafianpour, F., Dodangeh, M., & Khademi, A. (2021). The healing effects of facial BOTOX injection on symptoms of depression alongside its effects on beauty preservation. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 20(5), 1411–1415.
Kong, L., Shen, X., Lin, L., Leitges, M., Rosario, R., Zou, Y. S., & Yan, S. F. (2013). PKCβ promotes vascular inflammation and acceleration of atherosclerosis in diabetic ApoE null mice. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 33(8), 1779–1787.
Rahman, A., & Fazal, F. (2009). Hug tightly and say goodbye: Role of endothelial ICAM-1 in leukocyte transmigration. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 11(4), 823–839.
Harrell, C. R., Djonov, V., & Volarevic, V. (2021). The cross-talk between mesenchymal stem cells and immune cells in tissue repair and regeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(5), 2472.
Mostofa, A., Punganuru, S. R., Madala, H. R., Al-Obaide, M., & Srivenugopal, K. S. (2017). The process and regulatory components of inflammation in brain oncogenesis. Biomolecules, 7(2), 34.
Roohaninasab, M., Sadeghzadeh-Bazargan, A., & Goodarzi, A. (2021). Effects of laser therapy on periorbital hyperpigmentation: A systematic review on current studies. Lasers in Medical Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-020-03241-6
Melnikov, I., Kozlov, S., Saburova, O., Zubkova, E., Guseva, O., Domogatsky, S., et al. (2020). CRP is transported by monocytes and monocyte-derived exosomes in the blood of patients with coronary artery disease. Biomedicines, 8(10), 435.
Cheng, C.-F., & Lian, W.-S. (2013). Prooxidant mechanisms in iron overload cardiomyopathy. BioMed Research International. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/740573
Dalvi, P., Sun, B., Tang, N., & Pulliam, L. (2017). Immune activated monocyte exosomes alter microRNAs in brain endothelial cells and initiate an inflammatory response through the TLR4/MyD88 pathway. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1–12.
Egaña-Gorroño, L., López-Díez, R., Yepuri, G., Ramirez, L. S., Reverdatto, S., Gugger, P. F., et al. (2020). Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities in diabetes and cardiovascular disease: Insights from human subjects and animal models. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, 7, 37.
Xie, Q.-B., Liang, Y., Yang, M., Yang, Y., Cen, X.-M., & Yin, G. (2017). DEPTOR-mTOR signaling is critical for lipid metabolism and inflammation homeostasis of lymphocytes in human PBMC culture. Journal of Immunology Research. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5252840
Liu, L., Wang, W., Zhao, Z., Hu, C., Tao, L., & Zhang, X. (2019). Pholidonone, an active stilbene derivative from Pholidota cantonensis, exhibits pro-apoptotic effect via induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress in human gastric cancer. Food & Nutrition Research. https://doi.org/10.29219/fnr.v63.3553
Liu, Y., Tong, C., Xu, Y., Cong, P., Liu, Y., Shi, L., et al. (2019). CD28 deficiency ameliorates blast exposure-induced lung inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and T cell accumulation in the lungs via the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 signaling pathway. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4848560
Dohare, P., Cheng, B., Ahmed, E., Yadala, V., Singla, P., Thomas, S., et al. (2018). Glycogen synthase kinase-3β inhibition enhances myelination in preterm newborns with intraventricular hemorrhage, but not recombinant Wnt3A. Neurobiology of Disease, 118, 22–39.
Li, Y., Zhao, Y., Tan, X., Liu, J., Zhi, Y., Yi, L., et al. (2020). Isoorientin inhibits inflammation in macrophages and endotoxemia mice by regulating glycogen synthase kinase 3β. Mediators of Inflammation. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8704146
Hong, H.-Y., Jeon, W.-K., & Kim, B.-C. (2008). Up-regulation of heme oxygenase-1 expression through the Rac1/NADPH oxidase/ROS/p38 signaling cascade mediates the anti-inflammatory effect of 15-deoxy-Δ12, 14-prostaglandin J2 in murine macrophages. FEBS Letters, 582(6), 861–868.
Kafi, F., Bolourian, A., Mojtahedi, Z., & Pouramini, A. (2021). High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) in COVID-19. Journal of Preventive Epidemiology, 6(1), e11.
Wei, F., Liu, S. Y., Luo, L., Gu, N. N., Zeng, Y., Chen, X. Y., et al. (2017). Anti-inflammatory mechanism of ulinastatin: Inhibiting the hyperpermeability of vascular endothelial cells induced by TNF-α via the RhoA/ROCK signal pathway. International Immunopharmacology, 46, 220–227.
Wang, C. C. L., Hess, C. N., Hiatt, W. R., & Goldfine, A. B. (2016). Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and heart failure in type 2 diabetes–mechanisms, management, and clinical considerations. Circulation, 133(24), 2459.
Wang, X., Sun, Y., Yang, H., Lu, Y., & Li, L. (2016). Oxidized low-density lipoprotein induces apoptosis in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes by modulating the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 1–8.
Kim, S., Lee, K.-S., Choi, S., Kim, J., Lee, D.-K., Park, M., et al. (2018). NF-κB–responsive miRNA-31-5p elicits endothelial dysfunction associated with preeclampsia via down-regulation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 293(49), 18989–19000.
Ko, K.-W., Yoo, Y.-I., Kim, J. Y., Choi, B., Park, S.-B., Park, W., et al. (2020). Attenuation of tumor necrosis factor-α induced inflammation by umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cell derived exosome-mimetic nanovesicles in endothelial cells. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, 17(2), 155–163.
Song, Y., Li, H., Ren, X., Li, H., & Feng, C. (2020). SNHG9, delivered by adipocyte-derived exosomes, alleviates inflammation and apoptosis of endothelial cells through suppressing TRADD expression. European Journal of Pharmacology, 872, 172977.
Gano, L. B., Donato, A. J., Pasha, H. M., Hearon, C. M., Jr., Sindler, A. L., & Seals, D. R. (2014). The SIRT1 activator SRT1720 reverses vascular endothelial dysfunction, excessive superoxide production, and inflammation with aging in mice. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 307(12), H1754–H1763.
Ailawadi, S., Wang, X., Gu, H., & Fan, G.-C. (2015). Pathologic function and therapeutic potential of exosomes in cardiovascular disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease, 1852(1), 1–11.
Ping, Z., Peng, Y., Lang, H., Xinyong, C., Zhiyi, Z., Xiaocheng, W., et al. (2020). Oxidative stress in radiation-induced cardiotoxicity. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3579143
Lü, J.-M., Jiang, J., Jamaluddin, M. S., Liang, Z., Yao, Q., & Chen, C. (2019). Ginsenoside Rb1 blocks ritonavir-induced oxidative stress and eNOS downregulation through activation of estrogen receptor-beta and upregulation of SOD in human endothelial cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(2), 294.
Wilkerson, B. A., & Argraves, K. M. (2014). The role of sphingosine-1-phosphate in endothelial barrier function. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 1841(10), 1403–1412.
Gioscia-Ryan, R. A., LaRocca, T. J., Sindler, A. L., Zigler, M. C., Murphy, M. P., & Seals, D. R. (2014). Mitochondria-targeted antioxidant (MitoQ) ameliorates age-related arterial endothelial dysfunction in mice. The Journal of Physiology, 592(12), 2549–2561.
Lee, V. V., Muravlyova, L. E., Bakirova, R. Y., Kiziltunc, A., Turkhanova, Z. Z., & Ashirbekova, B. D. (2021). Molecular patterns of oxidative stress in drug-induced nephropathy. Journal of Nephropathology, 10(3).
Gurunathan, S., Kang, M.-H., Jeyaraj, M., & Kim, J.-H. (2021). Platinum nanoparticles enhance exosome release in human lung epithelial adenocarcinoma cancer cells (A549): Oxidative stress and the ceramide pathway are key players. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 16, 515.
Matheus, A. S. D. M., Tannus, L. R. M., Cobas, R. A., Palma, C. C. S., Negrato, C. A., & Gomes, M. D. B. (2013). Impact of diabetes on cardiovascular disease: An update. International Journal of Hypertension, 1, 1. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/653789
Parsaee, M., Akiash, N., Azarkeivan, A., Alizadeh Sani, Z., Amin, A., Pazoki, M., et al. (2018). The correlation between cardiac magnetic resonance T2* and left ventricular global longitudinal strain in people with β-thalassemia. Echocardiography, 35(4), 438–444.
Amiri, M. (2018). Oxidative stress and free radicals in liver and kidney diseases; an updated short-review. Journal of Nephropathology, 7(3).
Kanikarla-Marie, P., & Jain, S. K. (2016). 1, 25 (OH) 2D3 inhibits oxidative stress and monocyte adhesion by mediating the upregulation of GCLC and GSH in endothelial cells treated with acetoacetate (ketosis). The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 159, 94–101.
Touyz, R. M., Anagnostopoulou, A., Camargo, L. L., Rios, F. J., & Montezano, A. C. (2019). Vascular biology of superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase 5—implications in hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 30(7), 1027–1040.
Sabbatino, F., Conti, V., Liguori, L., Polcaro, G., Corbi, G., Manzo, V., et al. (2021). Molecules and mechanisms to overcome oxidative stress inducing cardiovascular disease in cancer patients. Life, 11(2), 105.
Jiao, Y., Li, W., Wang, W., Tong, X., Xia, R., Fan, J., et al. (2020). Platelet-derived exosomes promote neutrophil extracellular trap formation during septic shock. Critical Care, 24(1), 1–18.
Pei, H., Zhang, J., Nie, J., Ding, N., Hu, W., Hua, J., et al. (2017). RAC2-P38 MAPK-dependent NADPH oxidase activity is associated with the resistance of quiescent cells to ionizing radiation. Cell Cycle, 16(1), 113–122.
Boytard, L., Hadi, T., Silvestro, M., Qu, H., Kumpfbeck, A., Sleiman, R., et al. (2020). Lung-derived HMGB1 is detrimental for vascular remodeling of metabolically imbalanced arterial macrophages. Nature Communications, 11(1), 1–17.
Lang, A., Grether-Beck, S., Singh, M., Kuck, F., Jakob, S., Kefalas, A., et al. (2016). MicroRNA-15b regulates mitochondrial ROS production and the senescence-associated secretory phenotype through sirtuin 4/SIRT4. Aging (Albany NY), 8(3), 484.
Luo, G., Jian, Z., Zhu, Y., Zhu, Y., Chen, B., Ma, R., et al. (2019). Sirt1 promotes autophagy and inhibits apoptosis to protect cardiomyocytes from hypoxic stress. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 43(5), 2033–2043.
Jin, Y., Guan, Z., Wang, X., Wang, Z., Zeng, R., Xu, L., & Cao, P. (2018). ALA-PDT promotes HPV-positive cervical cancer cells apoptosis and DCs maturation via miR-34a regulated HMGB1 exosomes secretion. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy, 24, 27–35.
Seif, F., Kheirollah, A., & Babaahmadi-Rezaei, H. (2020). Efficient isolation and identification of primary endothelial cells from bovine aorta by collagenase P. Immunopathologia Persa, 6(2), e15–e15.
Zheng, P., Tang, Z., Xiong, J., Wang, B., Xu, J., Chen, L., et al. (2021). RAGE: A potential therapeutic target during FGF1 treatment of diabetes-mediated liver injury. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 25(10), 4776–4785.
Chen, J., Jing, J., Yu, S., Song, M., Tan, H., Cui, B., & Huang, L. (2016). Advanced glycation endproducts induce apoptosis of endothelial progenitor cells by activating receptor RAGE and NADPH oxidase/JNK signaling axis. American Journal of Translational Research, 8(5), 2169.
Chen, L., Wang, J., Wang, B., Yang, J., Gong, Z., Zhao, X., et al. (2016). MiR-126 inhibits vascular endothelial cell apoptosis through targeting PI3K/Akt signaling. Annals of Hematology, 95(3), 365–374.
Yang, S., Wu, M., Li, X., Zhao, R., Zhao, Y., Liu, L., & Wang, S. (2020). Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in atherosclerosis and its potential as a therapeutic target. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/9270107
Parodi-Rullán, R., Sone, J. Y., & Fossati, S. (2019). Endothelial mitochondrial dysfunction in cerebral amyloid angiopathy and Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 72(4), 1019–1039.
Jayaraman, T., Paget, A., Shin, Y. S., Li, X., Mayer, J., Chaudhry, H. W., et al. (2008). TNF-α-mediated inflammation in cerebral aneurysms: A potential link to growth and rupture. Vascular Health and Risk Management, 4(4), 805.
Hajsadeghi, S., Mirshafiee, S., Pazoki, M., Moradians, V., Mansouri, P., Kianmehr, N., & Iranpour, A. (2020). The relationship between global longitudinal strain and pulmonary function tests in patients with scleroderma and normal ejection fraction and pulmonary artery pressure: A case–control study. The International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-020-01788-7.pdf
Zhang, H., Dellsperger, K. C., & Zhang, C. (2012). The link between metabolic abnormalities and endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: An update. Basic Research in Cardiology, 107(1), 1–11.
Zuniga, F. A., Ormazabal, V., Gutierrez, N., Aguilera, V., Radojkovic, C., Veas, C., et al. (2014). Role of lectin-like oxidized low density lipoprotein-1 in fetoplacental vascular dysfunction in preeclampsia. BioMed Research International. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/353616
Frey, R. S., Ushio-Fukai, M., & Malik, A. B. (2009). NADPH oxidase-dependent signaling in endothelial cells: Role in physiology and pathophysiology. Antioxidants & redox signaling, 11(4), 791–810.
Colombo, E., Signore, A., Aicardi, S., Zekiy, A., Utyuzh, A., Benedicenti, S., & Amaroli, A. (2021). Experimental and clinical applications of red and near-infrared photobiomodulation on endothelial dysfunction: A review. Biomedicines, 9(3), 274.
Veluthakal, R., Kumar, B., Mohammad, G., Kowluru, A., & Kowluru, R. A. (2015). Tiam1-Rac1 axis promotes activation of p38 MAP kinase in the development of diabetic retinopathy: Evidence for a requisite role for protein palmitoylation. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 36(1), 208–220.
Liu, Y., Song, J.-W., Lin, J.-Y., Miao, R., & Zhong, J.-C. (2020). Roles of microRNA-122 in cardiovascular fibrosis and related diseases. Cardiovascular Toxicology, 20(5), 463–473.
Geng, T., Song, Z.-Y., Xing, J.-X., Wang, B.-X., Dai, S.-P., & Xu, Z.-S. (2020). Exosome derived from coronary serum of patients with myocardial infarction promotes angiogenesis through the miRNA-143/IGF-IR pathway. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 15, 2647.
Samiei, N., Akiash, N., Naeini, S. D., Nikpajouh, A., & Pazoki, M. (2020). The presence of patent foramen ovale in the superior type of sinus venosus atrial septal defect. The Journal of Tehran University Heart Center, 15(3), 98.
Ling, H., Guo, Z., Shi, Y., Zhang, L., & Song, C. (2020). Serum exosomal MicroRNA-21, MicroRNA-126, and PTEN are novel biomarkers for diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome. Frontiers in Physiology, 11, 654.
Bang, C., Batkai, S., Dangwal, S., Gupta, S. K., Foinquinos, A., Holzmann, A., et al. (2014). Cardiac fibroblast–derived microRNA passenger strand-enriched exosomes mediate cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. The Journal of clinical investigation, 124(5), 2136–2146.
Sun, W., Zhao, L., Song, X., Zhang, J., Xing, Y., Liu, N., et al. (2017). MicroRNA-210 modulates the cellular energy metabolism shift during H2O2-induced oxidative stress by repressing ISCU in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 43(1), 383–394.
Wang, L., Jia, Q., Xinnong, C., Xie, Y., Yang, Y., Zhang, A., et al. (2019). Role of cardiac progenitor cell-derived exosome-mediated microRNA-210 in cardiovascular disease. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 23(11), 7124–7131.
Yang, Y., Li, Y., Chen, X., Cheng, X., Liao, Y., & Yu, X. (2016). Exosomal transfer of miR-30a between cardiomyocytes regulates autophagy after hypoxia. Journal of Molecular Medicine, 94(6), 711–724.
Aoyagi, T., & Matsui, T. (2011). Phosphoinositide-3 kinase signaling in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 17(18), 1818–1824.
Ranek, M. J., Stachowski, M. J., Kirk, J. A., & Willis, M. S. (2018). The role of heat shock proteins and co-chaperones in heart failure. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 373(1738), 20160530.
Zhang, Y., Jiang, D. S., Yan, L., Cheng, K. J., Bian, Z. Y., & Lin, G. S. (2011). HSP75 protects against cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 112(7), 1787–1794.
Kang, K., Ma, R., Cai, W., Huang, W., Paul, C., Liang, J., et al. (2015). Exosomes secreted from CXCR4 overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells promote cardioprotection via Akt signaling pathway following myocardial infarction. Stem Cells International. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/659890
Barile, L., Cervio, E., Lionetti, V., Milano, G., Ciullo, A., Biemmi, V., et al. (2018). Cardioprotection by cardiac progenitor cell-secreted exosomes: Role of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A. Cardiovascular research, 114(7), 992–1005.
Guo, D., Xu, Y., Ding, J., Dong, J., Jia, N., Li, Y., & Zhang, M. (2020). Roles and clinical applications of exosomes in cardiovascular disease. BioMed Research International. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5424281
Hu, J., Wang, S., Xiong, Z., Cheng, Z., Yang, Z., Lin, J., et al. (2018). Exosomal Mst1 transfer from cardiac microvascular endothelial cells to cardiomyocytes deteriorates diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease, 1864(11), 3639–3649.
Hervera, A., De Virgiliis, F., Palmisano, I., Zhou, L., Tantardini, E., Kong, G., et al. (2018). Reactive oxygen species regulate axonal regeneration through the release of exosomal NADPH oxidase 2 complexes into injured axons. Nature Cell Biology, 20(3), 307–319.
Yang, T.-C., Chen, Y.-J., Chang, S.-F., Chen, C.-H., Chang, P.-Y., & Lu, S.-C. (2014). Malondialdehyde mediates oxidized LDL-induced coronary toxicity through the Akt-FGF2 pathway via DNA methylation. Journal of Biomedical Science, 21(1), 1–12.
Yao, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., & Liu, C. (2017). Klotho ameliorates oxidized low density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced oxidative stress via regulating LOX-1 and PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathways. Lipids in Health and Disease, 16(1), 1–10.
Shang, X., Lin, K., Yu, R., Zhu, P., Zhang, Y., Wang, L., et al. (2019). Resveratrol protects the myocardium in sepsis by activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PI3K)/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway and inhibiting the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway. Medical Science Monitor: International Medical Journal of Experimental and Clinical Research, 25, 9290.
Yan, Y., Song, D., Song, X., & Song, C. (2020). The role of lncRNA MALAT1 in cardiovascular disease. IUBMB Life, 72(3), 334–342.
Mao, Q., Liang, X.-L., Zhang, C.-L., Pang, Y.-H., & Lu, Y.-X. (2019). LncRNA KLF3-AS1 in human mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorates pyroptosis of cardiomyocytes and myocardial infarction through miR-138-5p/Sirt1 axis. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 10(1), 1–14.
Arslan, F., Lai, R. C., Smeets, M. B., Akeroyd, L., Choo, A., Aguor, E. N., et al. (2013). Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes increase ATP levels, decrease oxidative stress and activate PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance myocardial viability and prevent adverse remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Research, 10(3), 301–312.
Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Li, Y., Chen, L., Wang, X., Guo, W., et al. (2015). Exosomes/microvesicles from induced pluripotent stem cells deliver cardioprotective miRNAs and prevent cardiomyocyte apoptosis in the ischemic myocardium. International Journal of Cardiology, 192, 61–69.
Barile, L., Lionetti, V., Cervio, E., Matteucci, M., Gherghiceanu, M., Popescu, L. M., et al. (2014). Extracellular vesicles from human cardiac progenitor cells inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis and improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Cardiovascular Research, 103(4), 530–541.
Ibrahim, A.G.-E., Cheng, K., & Marbán, E. (2014). Exosomes as critical agents of cardiac regeneration triggered by cell therapy. Stem Cell Reports, 2(5), 606–619.
Vicencio, J. M., Yellon, D. M., Sivaraman, V., Das, D., Boi-Doku, C., Arjun, S., et al. (2015). Plasma exosomes protect the myocardium from ischemia-reperfusion injury. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 65(15), 1525–1536.
Zheng, L., Li, Z., Ling, W., Zhu, D., Feng, Z., & Kong, L. (2018). Exosomes derived from dendritic cells attenuate liver injury by modulating the balance of Treg and Th17 cells after ischemia reperfusion. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 46(2), 740–756.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank all our colleagues in Iran, Tehran and Ahwaz University of Medical Sciences and also in Iranian Blood Transfusion Organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.A has conceived the manuscript and revised it. F.N, M.P, M.M and M.K.A wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Vittorio Fineschi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikdoust, F., Pazoki, M., Mohammadtaghizadeh, M. et al. Exosomes: Potential Player in Endothelial Dysfunction in Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovasc Toxicol 22, 225–235 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-021-09700-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-021-09700-y