Abstract
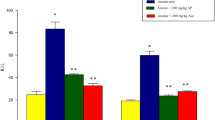
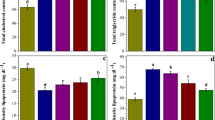
Ellagic acid (EA) is a phenolic constituent in certain fruits and nuts with wide range of biological activities, including potent antioxidant, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, anticancer and antimutagen properties. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of EA on sodium arsenic (SA)-induced cardio- and hematotoxicity in rats. Animals were divided into five groups. The first group was used as control. Group 2 was orally treated with sodium arsenite (SA, 10 mg/kg) for 21 days. Group 3 was orally treated with EA (30 mg/kg) for 14 days. Groups 4 and 5 were orally treated with SA for 7 days prior to EA (10 and 30 mg/kg, respectively) treatment and continued up to 21 days simultaneous with SA administration. Various biochemical, histological and molecular biomarkers were assessed in blood and heart. The results indicate that SA-intoxicated rats display significantly higher levels of plasma cardiac markers (AST, CK-MB, LDH and cTnI) than normal control animals. Moreover, an increase in MDA and NO with depletion of GSH and activities of CAT, SOD and GPx occurred in the heart of rats treated with SA. Furthermore, SA-treated rats showed significantly lower WBC, RBC, HGB, HCT and PLT and significantly higher MCV and MCH. Administration of EA (30 mg/kg) resulted in a significant reversal of hematological and cardiac markers in arsenic-intoxicated rats. These biochemical disturbances were supported by histopathological observations of the heart. In conclusion, the results of this study suggest that EA treatment exerts a significant protective effect on SA-induced cardio- and hematotoxicity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang, J. Q., Ashekuzzaman, S. M., Jiang, A., Sharifuzzaman, S. M., & Chowdhury, S. R. (2012). Arsenic contaminated groundwater and its treatment options in Bangladesh. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 10, 18–46.
Anetor, J. I., Wanibuchi, H., & Fukushima, S. (2007). Arsenic exposure and its health effects and risk of cancer in developing countries: Micronutrients as host defence. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention: APJCP, 8, 13–23.
Hughes, M. F. (2002). Arsenic toxicity and potential mechanisms of action. Toxicology Letters, 133, 1–16.
Jalaludeen, A. M., Ha, W. T., Lee, R., Kim, J. H., Do, J. T., Park, C., et al. (2016). Biochanin a ameliorates arsenic-induced hepato- and hematotoxicity in rats. Molecules, 21, 69.
Shi, H., Shi, X., & Liu, K. J. (2004). Oxidative mechanism of arsenic toxicity and carcinogenesis. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 255, 67–78.
Pachauri, V., & Flora, S. (2013). Effect of nicotine pretreatment on arsenic-induced oxidative stress in male Wistar rats. Human and Experimental Toxicology, 32, 972–982.
Chen, C., Jiang, X., Hu, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2013). The protective role of resveratrol in the sodium arsenite-induced oxidative damage via modulation of intracellular GSH homeostasis. Biological Trace Element Research, 155, 119–131.
Abu El-Saad, A. M., Al-Kahtani, M. A., & Abdel-Moneim, A. M. (2016). N-acetylcysteine and meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid alleviate oxidative stress and hepatic dysfunction induced by sodium arsenite in male rats. Drug Design, Development and Therapy, 10, 3425–3434.
Saha, S. S., & Ghosh, M. (2010). Ameliorative role of conjugated linolenic acid isomers against oxidative DNA damage induced by sodium arsenite in rat model. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 48, 3398–3405.
Soong, Y.-Y., & Barlow, P. J. (2006). Quantification of gallic acid and ellagic acid from longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) seed and mango (Mangifera indica L.) kernel and their effects on antioxidant activity. Food Chemistry, 97, 524–530.
Garcia-Nino, W. R., & Zazueta, C. (2015). Ellagic acid: Pharmacological activities and molecular mechanisms involved in liver protection. Pharmacological Research, 97, 84–103.
Doyle, B., & Griffiths, L. A. (1980). The metabolism of ellagic acid in the rat. Xenobiotica, 10, 247–256.
Priyadarsini, K. I., Khopde, S. M., Kumar, S. S., & Mohan, H. (2002). Free radical studies of ellagic acid, a natural phenolic antioxidant. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50, 2200–2206.
Pari, L., & Sivasankari, R. (2008). Effect of ellagic acid on cyclosporine A-induced oxidative damage in the liver of rats. Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology, 22, 395–401.
El-Shitany, N. A., El-Bastawissy, E. A., & El-desoky, K. (2014). Ellagic acid protects against carrageenan-induced acute inflammation through inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B, inducible cyclooxygenase and proinflammatory cytokines and enhancement of interleukin-10 via an antioxidant mechanism. International Immunopharmacology, 19, 290–299.
Al-Kharusi, N., Babiker, H. A., Al-Salam, S., Waly, M. I., Nemmar, A., Al-Lawati, I., et al. (2013). Ellagic acid protects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: A dose-dependent study. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 17, 299–310.
Yuce, A., Atessahin, A., Ceribasi, A. O., & Aksakal, M. (2007). Ellagic acid prevents cisplatin-induced oxidative stress in liver and heart tissue of rats. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology, 101, 345–349.
Gul, M., Aliosmanoglu, I., Uslukaya, O., Firat, U., Yuksel, H., Gumus, M., et al. (2013). The protective effect of ellagic acid on lung damage caused by experimental obstructive jaundice model. Acta Chirurgica Belgica, 113, 285–289.
Al-Hasan, A. K. J. (2017). Effects of low-and high-level pulsed Nd: YAG laser irradiation on red blood cells and platelets indices of albino rats in vitro. Iraq Medical Journal, 1, 10–19.
Saha, S. S., & Ghosh, M. (2009). Comparative study of antioxidant activity of alpha-eleostearic acid and punicic acid against oxidative stress generated by sodium arsenite. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 47, 2551–2556.
Celik, G., Semiz, A., Karakurt, S., Arslan, S., Adali, O., & Sen, A. (2013). A comparative study for the evaluation of two doses of ellagic acid on hepatic drug metabolizing and antioxidant enzymes in the rat. BioMed Research International, 2013, 358945.
Reitman, S., & Frankel, S. (1957). In vitro determination of transaminase activity in serum. American Journal of Clinical Pathology, 28, 56–63.
Bishop, C., Chu, T., & Shihabi, Z. (1971). Single stable reagent for creatine kinase assay. Clinical Chemistry, 17, 548–550.
Whitaker, J. (1969). A general colorimetric procedure for the estimation of enzymes which are linked to the NADH/NAD + system. Clinica Chimica Acta, 24, 23–37.
Ghosh, A., & Sil, P. C. (2008). A protein from Cajanus indicus Spreng protects liver and kidney against mercuric chloride-induced oxidative stress. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 31, 1651–1658.
Buege, J. A., & Aust, S. D. (1978). Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymology, 52, 302–310.
Tracey, W. R., Linden, J., Peach, M. J., & Johns, R. A. (1990). Comparison of spectrophotometric and biological assays for nitric oxide (NO) and endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF): Nonspecificity of the diazotization reaction for NO and failure to detect EDRF. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 252, 922–928.
Jalaludeen, A. M., Lee, W. Y., Kim, J. H., Jeong, H. Y., Ki, K. S., Kwon, E. G., et al. (2015). Therapeutic efficacy of biochanin a against arsenic-induced renal and cardiac damage in rats. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 39, 1221–1231.
Adil, M., Kandhare, A. D., Visnagri, A., & Bodhankar, S. L. (2015). Naringin ameliorates sodium arsenite-induced renal and hepatic toxicity in rats: Decisive role of KIM-1, Caspase-3, TGF-β, and TNF-α. Renal Failure, 37, 1396–1407.
Dwivedi, N., Flora, G., Kushwaha, P., & Flora, S. J. (2014). Alpha-lipoic acid protects oxidative stress, changes in cholinergic system and tissue histopathology during co-exposure to arsenic-dichlorvos in rats. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 37, 7–23.
Archer, S. (1993). Measurement of nitric oxide in biological models. The FASEB Journal, 7, 349–360.
Priyamvada, S., Priyadarshini, M., Arivarasu, N., Farooq, N., Khan, S., Khan, S. A., et al. (2008). Studies on the protective effect of dietary fish oil on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative damage in rat kidney. Prostaglandins Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids, 78, 369–381.
Singh, K., Khanna, A., Visen, P., & Chander, R. (1999). Protective effect of ellagic acid on t-butyl hydroperoxide induced lipid peroxidation in isolated rat hepatocytes. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 37, 939–940.
Ding, Y., Zhang, B., Zhou, K., Chen, M., Wang, M., Jia, Y., et al. (2014). Dietary ellagic acid improves oxidant-induced endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis: Role of Nrf2 activation. International Journal of Cardiology, 175, 508–514.
Song, L.-L., Tu, Y.-Y., Xia, L., Wang, W.-W., Wei, W., Ma, C.-M., et al. (2014). Targeting catalase but not peroxiredoxins enhances arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis in k562 cells. PLoS ONE, 9, e104985.
Modi, M., Kaul, R. K., Kannan, G. M., & Flora, S. J. (2006). Co-administration of zinc and n-acetylcysteine prevents arsenic-induced tissue oxidative stress in male rats. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 20, 197–204.
Hemmati, A. A., Olapour, S., Varzi, H. N., Khodayar, M. J., Dianat, M., Mohammadian, B., and Yaghooti, H. (2017). Ellagic acid protects against arsenic trioxide-induced cardiotoxicity in rat. Human & Experimental Toxicology 960327117701986.
Ahad, A., Ganai, A. A., Mujeeb, M., & Siddiqui, W. A. (2014). Ellagic acid, an NF-κB inhibitor, ameliorates renal function in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 219, 64–75.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Deputy of Research of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran (Grant Number 95s35).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest related to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goudarzi, M., Fatemi, I., Siahpoosh, A. et al. Protective Effect of Ellagic Acid Against Sodium Arsenite-Induced Cardio- and Hematotoxicity in Rats. Cardiovasc Toxicol 18, 337–345 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-018-9446-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-018-9446-2