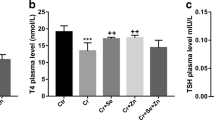
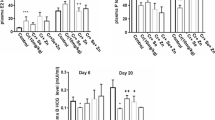
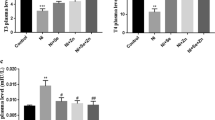
Abstract
Hexavalent chromium (CrVI) compounds are potent toxicants commonly used in numerous industries. Thus, potential toxic effects and health hazards are of high relevance. Selenium (Se) and zinc (Zn) are known for their antioxidant and chemoprotective properties. However, little is known about their protective effects against CrVI-induced renal damage during pregnancy. In this context, the present study aimed to investigate the protective efficacy of these two essential elements against potassium dichromate-induced nephrotoxicity in pregnant Wistar Albino rats. Female rats were divided into control and four treated groups of six each receiving subcutaneously on the 3rd day of pregnancy, K2Cr2O7 (10 mg/kg, s.c. single dose) alone, or in association with Se (0.3 mg/kg, s.c. single dose), ZnCl2 (20 mg/kg, s.c. single dose) or both of them simultaneously. The nephrotoxic effects were monitored by the evaluation of plasma renal parameters, oxidative stress biomarkers, DNA damage, and renal Cr content. The obtained results showed that K2Cr2O7 disturbed renal biochemical markers, induced oxidative stress and DNA fragmentation in kidney tissues, and altered renal histoarchitecture. The co-administration of Se and/or ZnCl2 has exhibited pronounced chelative, antioxidant, and genoprotective effects against K2Cr2O7-induced renal damage and attenuated partially the histopathological alterations. These results suggest that Se and Zn can be used as efficient nephroprotective agents against K2Cr2O7-induced toxicity in pregnant Wistar Albino rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Alvarez CC, Bravo Gómez ME, Hernández Zavala A (2021) Hexavalent chromium: regulation and health effects. J Trace Elem Med Biol 65:126729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2021.126729
Renu K, Chakraborty R, Myakala H et al (2021) Molecular mechanism of heavy metals (lead, chromium, arsenic, mercury, nickel and cadmium) - induced hepatotoxicity – a review. Chemosphere 271:129735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.Chemosphere129735
Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M (2006) Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact 160(1):1–40
Mishra S, Bharagava RN (2016) Toxic and genotoxic effects of hexavalent chromium in environment and its bioremediation strategies. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev 34(1):1–32
Winczura A, Zdzalik D, Tudek B (2012) Damage of DNA and proteins by major lipid peroxidation products in genome stability. Free Radic Res 46(4):442–459
Salah I, Adjroud O, Elwej A (2021) Protective effects of selenium and zinc against nickel chloride–induced hormonal changes and oxidative damage in thyroid of pregnant rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02815-x
Krim M, Messaadia A, Maidi I, Aouacheri O, Saka S (2013) Protective effect of ginger against toxicity induced by chromate in rats. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 71(2):165–173
Fedala A, Adjroud O, Saouli A, Salah I, Abid-Essefi S, Timoumi R (2021) Zinc alleviates potassium dichromate induced-hepatotoxicity in pregnant Wistar rats. Malays J Biochem Mol Biol 2:10–16
Banu SK, Samuel JB, Arosh JA, Burghardt RC, Aruldhas MM (2008) Lactational exposure to hexavalent chromium delays puberty by impairing ovarian development, steroidogenesis and pituitary hormone synthesis in developing Wistar rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 232:180–189
Fedala A, Adjroud O, Abid-Essefi S, Timoumi R (2021) Protective effects of selenium and zinc against potassium dichromate–induced thyroid disruption, oxidative stress, and DNA damage in pregnant Wistar rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(18):22563–22576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12268-9
Stanley JA, Sivakumar KK, Nithy TK et al (2013) Postnatal exposure to chromium through mother’s milk accelerates follicular atresia in F1 offspring through increased oxidative stress and depletion of antioxidant enzymes. Free Radic Biol Med 61:179–196
Hegazy R, Mansour D, Salama A, Hassan A, Saleh D (2021) Exposure to intranasal chromium triggers dose and time-dependent behavioral and neurotoxicological defects in rats. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 216: 112220.
Goodarzi Z, Karami E, Ahmadizadeh M (2017) Simvastatin attenuates chromium-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Nephropathol 6(1):5–9
Patel JG, Joshi DV, Patel BJ, Raval SH (2017) Pathology of experimentally induced acute toxicity of potassium dichromate in Wistar rats (Rattus norvegicus). Indian J Vet Pathol 41(1):75–77
Soudani N, Sefi M, Ben Amara I, Boudawara T, Zeghal N (2010) Protective effects of Selenium (Se) on Chromium (VI) induced nephrotoxicity in adult rats. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73(4):671–678
Barrera D, Maldonado PD, Medina-Campos ON, Hernández-Pando R, Ibarra-Rubio ME, Pedraza-Chaverrí J (2003) HO-1 induction attenuates renal damage and oxidative stress induced by K2Cr2O7. Free Radic Biol Med 34(11):1390–1398
Yeung AWK, Tzvetkov NT, El-Tawil OS, Bungǎu SG, Abdel-Daim MM, Atanasov AG (2019) Antioxidants: scientific literature landscape analysis. Oxid Med Cell Longev 8278454. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8278454
Mehany HA, Abo-youssef AM, Ahmed LA, Arafa EA, Abd El-Latif HA (2013) Protective effect of vitamin E and atorvastatin against potassium dichromate-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 2(2):96–102
Tabassum A, Bristow RG, Venkateswaran V (2010) Ingestion of selenium and other antioxidants during prostate cancer radiotherapy: a good thing? Cancer Treat Rev 36:230–234
Kim H, Park S, Suh JM, Chung HK, Shong M, Kwon OY (2001) Thyroid- stimulating hormone transcriptionally regulates the thiol-specific antioxidant gene. Cell Physiol Biochem 11:247–252
Sengul E, Gelen V, Yildirim S, Tekin S, Dag Y (2021) The Effects of selenium in acrylamide-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: roles of oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and DNA damage. Biol Trace Elem Res 199(1):173–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02111-0
Mandour AS, Samir H, El-Beltagy MA et al (2020) Effect of supra-nutritional selenium-enriched probiotics on hematobiochemical, hormonal, and Doppler hemodynamic changes in male goats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27(16):19447–19460
Barceloux DG. Zinc (1999) J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 37: 279- 292.
Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc R, Baltaci SB (2019) The role of zinc in the endocrine system. Pak J Pharm Sci 32:231–239
Marreiro DD, Cruz KJ, Morais JB, Beserra JB, Severo JS, de Oliveira AR (2017) Zinc and oxidative stress: current mechanisms. Antioxidants (Basel) 6(2):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox6020024
Wang X, Anl Y, Jiao W et al (2018) Selenium protects against lead-induced apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress in chicken kidneys. Biol Trace Elem Res 182:354–363
Messarah M, Klibet F, Boumendjel A et al (2012) Hepatoprotective role and antioxidant capacity of selenium on arsenic-induced liver injury in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 64:167–174
Messaoudi I, El Heni J, Hammouda F, Saïd K, Kerkeni A (2009) Protective effects of selenium, zinc, or their combination on cadmium-induced oxidative stress in rat kidney. Biol Trace Elem Res 130:152–161
Adjroud O (2009) Effects of potassium dichromate on haematological parametrs in female and male wistar albino rats. Ass univ Bull environ Res 12:2
Adjroud O (2010) Protective effects of selenium against potassium dichromate-induced hematotoxicity in female and male Wistar albino rats. Ann Toxicol Anal 22:165–172
Käkelä R, Käkelä A, Hyvärinen H (1999) Effects of nickel chloride on reproduction of the rat and possible antagonistic role of selenium. Comp Biochem Physiol C Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 123:27–37
Adjroud O, Mouffok S (2009) Effects of nickel chloride on hematological and developmental parameters in Wistar albino pregnant rats. Ass Univ Bull Environ Res 12(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.21608/auber.2009.149529.
Paksy K, Varga B, Lázár P (1996) Zinc protection against cadmium-induced infertility in female rats. Effect of zinc and cadmium on the progesterone production of cultured granulosa cells. Biometals 10:27–36
Nasiry Zarrin Ghabaee D, Talebpour Amiri F, Esmaeelnejad Moghaddam A, Khalatbary AR, Zargari M (2017) Administration of zinc against arsenic-induced nephrotoxicity during gestation and lactation in rat model. J Nephropathol 6(2):74–80
Fransion MA (1981) Standard methods for determination of wastes and waste water. Method No. 32(D), 15th ed. 225
Bradford M (1979) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay of lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Mercier Y, Gatellier P, Renerre M (2004) Lipid and protein oxidation in vivo, and antioxidant potential in meat from Charolais cows finished on pasture or mixed die. Meat Sci 66:467–473
Collins AR, Dusinská M, Gedik CM, Stĕtina R (1996) Oxidative damage to DNA: do we have a reliable biomarker? Environ Health Perspect 104:465–469
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Beauchamp C (1971) Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44:276–287
Clairbone A (1985) Catalase activity. Handbook of methods for oxygen radical research. CRC, Press Boca Rton FL 283- 284.
Flohe L, Gunzler W (1984) Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 105:114–121
Bancroft JD, Gamble M (2008) Theory and practice of histological techniques. China. Churchill Livingstone, Elsevier
Kotyzova D, Hodkova A, Bludovska M, Eybl V (2015) Effect of chromium (VI) exposure on antioxidant defense status and trace element homeostasis in acute experiment in rat. Toxicol Ind Health 31(11):1044–1050
Wedeen RP, Qian LF (1991) Chromium-induced kidney disease. Environ Health Perspect 92:71–74
Saïd L, Banni M, Kerkeni A, Saïd K, Messaoudi I (2010) Influence of combined treatment with zinc and selenium on cadmium induced testicular pathophysiology in rat. Food Chem Toxicol 48(10):2759–2765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.07.003
Hammouda F, Messaoudi I, El Hani J, Baati T, Saïd K, Kerkeni A (2008) Reversal of cadmium-induced thyroid dysfunction by selenium, zinc, or their combination in rat. Biol Trace Elem Res 126:194–203
Girotti AW, Thomas JP, Jordan JE (1985) Inhibitory effect of zinc (II) on free radical lipid peroxidation in erythrocyte membranes. J Free Radic Biol Med 1:395–401
Zhang D, Liu J, Gao J, Shahzad M, Han Z et al (2014) Zinc supplementation protects against cadmium accumulation and cytotoxicity in Madin-Darby bovine kidney cells. PLoS ONE 9(8):e103427. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0103427
Yin J et al (2021) Pretreatment with selenium prevented the accumulation of hexavalent chromium in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and reduced the potential health risk of fish consumption. Food Control 122:107817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107817
Badiello R, Feroci G, Fini A (1996) Interaction between trace elements: selenium and cadmium ions. J Trace Elem Med Bio 10:156–162
Zwolak I (2020) The role of selenium in arsenic and cadmium toxicity: an updated review of scientific literature. Biol Trace Elem Res 193(1):44–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01691-w
El-Demerdash FM, El-Sayed RA, Abdel-Daim MM (2021) Rosmarinus officinalis essential oil modulates renal toxicity and oxidative stress induced by potassium dichromate in rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol 67: 126791
Arreola-Mendoza L, Reyes J et al (2006) Alpha-tocopherol protects against the renal damage caused by potassium dichromate. Toxicology 218:237–246
Salama A, Elmalt HA (2021) Aescin ameliorates acute kidney injury induced by potassium dichromate in rat: involvement of TLR 4/ TNF-α pathway. Egypt J Chem 64(4):2067–2074
Hegazy R, Salama A, Mansour D, Hassan A (2016) Renoprotective effect of lactoferrin against chromium-induced acute kidney injury in rats: involvement of IL-18 and IGF-1 inhibition. PLoS One 11 (3)
Bashandy SA, Salama A, Fayed AHM et al (2020) Protective effect of mandarin (Citrus Reticulata) peel extract on potassium dichromate induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats. Plant Archives 20(1):2231–2242
Adi PJ, Burra SP, Vataparti AR, Matcha B (2016) Calcium, zinc and vitamin E ameliorate cadmium-induced renal oxidative damage in albino Wistar rats. Toxicol Rep 29(3):591–597
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D, Hassoun E, Bagchi M (2000) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of chromium and cadmium ions. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 19(3):201–213
Valko M, Morris H, Cronin MT (2005) Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem 12(10):1161–1208
Chandra KA, Chatterjee A, Ghosh R, Sarkar M (2007) Effect of curcumin on chromium-induced oxidative damage in male reproductive system. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 24(2):160–166
Travacio M, Polo JM, Llesuy S (2000) Chromium (VI) induces oxidative stress in the mouse brain. Toxicology 150(1–3):137–146
Saber TM, Farag MR, Cooper RG (2015) Ameliorative effect of extra virgin olive oil on hexavalent chromium induced nephrotoxicity and genotoxicity in rats. Revue de Médecine Vétérinaire 166(1–2):11–19
Sumner ER, Shanmuganathan A, Sideri TC, Willetts SA, Houghton JE, Avery SV (2005) Oxidative protein damage causes chromium toxicity in yeast. Microbiology 151:1939–1948
Mattagajasingh SN, Misra BR, Misra HP (2008) Carcinogenic chromium (VI)-induced protein oxidation and lipid peroxidation: implications in DNA–protein crosslinking. J Appl Toxicol 28:987–997
Ahmad MK, Syma S, Mahmood R (2011) Cr (VI) Induces lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation and alters the activities of antioxidant enzymes in human erythrocytes. Biol Trace Elem Res 144:426–435
Pedraza-Chaverri J, Yam-Canul P, Chirino YI et al (2008) Protective effects of garlic powder against potassium dichromate-induced oxidative stress and nephrotoxicity. Food Chem Toxicol 46(2):619–627
Ozturk A, Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc R et al (2003) Effects of zinc deficiency and supplementation on malondialdehyde and glutathione levels in blood and tissues of rats performing swimming exercise. Biol Trace Elem Res 94(2):157–166
Yildiz A, Kaya Y, Tanriverdi O (2019) Effect of the interaction between selenium and zinc on DNA repair in association with cancer prevention. J Cancer Prev 24(3):146–154
Cogun HY, Fırat O, Fırat O, Yüzereroǧlu TA (2012) Protective effect of selenium against mercury-induced toxicity on hematological and biochemical parameters of Oreochromis niloticus. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 26(3):117–122
Levis AG, Bianchi V (1982) Mutagenic and cytogenetic effects of chromium compounds. In: Langard S (ed) Biological and Environmental Aspect of Chromium. Elsevier Biomedical Press, New York, pp 171–207
Khorsandi K, Rabbani-Chadegani A (2013) Studies on the genotoxic effect of chromium oxide (Cr VI): interaction with deoxyribonucleic acid in solution. Mutat Res 750(1–2):105–110
Monteiro C, Conceição S, Bastos V, Oliveira H (2019) Cr (VI)‐induced genotoxicity and cell cycle arrest in human osteoblast cell line MG‐63. J Appl Toxicol 1-9
García-Rodríguez MDC, Carvente-Juárez MM, Altamirano-Lozano MA (2013) Antigenotoxic and apoptotic activity of green tea polyphenol extracts on hexavalent chromium-induced DNA damage in peripheral blood of CD-1 mice: analysis with differential acridine orange/ ethidium bromide staining. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/486419
Patlolla AK, Barnes C, Yedjou C, Velma VR, Tchounwou PB (2009) Oxidative stress, DNA damage, and antioxidant enzyme activity induced by hexavalent chromium in Sprague-Dawley rats. Environ Toxicol 24(1):66–73
Ho E (2004) Zinc deficiency, DNA damage and cancer risk. J Nutr Biochem 15:572–578
Bera S, De Rosa V, Rachidi W, Diamond AM (2013) Does a role for selenium in DNA damage repair explain apparent controversies in its use in chemoprevention? Mutagenesis 28:127–134
Kubrak OI, Lushchak OV, Lushchak JV, Torous IM, Storey JM, Storey KB et al (2010) Chromium effects on free radical processes in goldfish tissues: comparison of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) exposures on oxidative stress markers, glutathione status and antioxidant enzymes. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C 152:360–370
Kim JH, Kang JC (2016) Oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, and metallothionein (MT) gene expression in juvenile rock fish Sebastes schlegelii under the different levels of dietary chromium(Cr6+) exposure. Ecotox Environ Safe 125:78–84
Travacio M, Llesuy S (1996) Antioxidant enzymes and their modification under oxidative stress conditions. J Br Assoc Adv Sci 48:9–13
Othman AI, El Missiry MA (1999) Role of selenium against lead toxicity in male rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 12(6):345–349
Atteia HH, Arafa MH, Prabahar K (2018) Selenium nanoparticles prevent lead acetate-induced hypothyroidism and oxidative damage of thyroid tissues in male rats through modulation of selenoenzymes and suppression of miR-224. Biomed Pharmacother 99:486–491
Flora SJS (2002) Nutritional components modify metal absorption, toxic response and chelation therapy. J Nutr Environ Med 12(1):53–67
Whanger PD (1992) Selenium in the treatment of heavy metal poisoning and chemical carcinogenesis. J Trace Elem Electrolytes Health Dis 6(4):209–221
Šulinskienė J, Bernotienė R, Baranauskienė D, Naginiene R, Staneviciene I, Kasauskas A et al (2019) Effect of zinc on the oxidative stress biomarkers in the brain of nickel-treated mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8549727
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the DGRSDT/ MESRS (code: N ° E2212600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Anfal Fedala and Ounassa Adjroud designed the experiement; Anfal Fedala, Rim Timoumi, and Foughalia Abdelhamid performed the experiment; Anfal Fedala, Ounassa Adjroud, Omar Bennoune, Salwa Abid-Essefi, and Rim Timoumi analyzed the data; Anfal Fedala and Ounassa Adjroud wrote the manuscript; Ounassa Adjroud, Salwa Abid Essefi, and Omar Bennoune revised the manuscript, and all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Batna University.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fedala, A., Adjroud, O., Bennoune, O. et al. Nephroprotective Efficacy of Selenium and Zinc Against Potassium Dichromate-Induced Renal Toxicity in Pregnant Wistar Albino Rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 200, 4782–4794 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-03069-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-03069-3