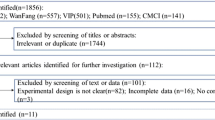
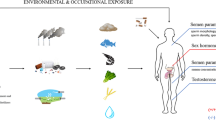
Abstract
It is known that cadmium induces damage to the testis. However, the significant cadmium impact on the testicular architecture and the mechanisms involved in this process are not clear. Besides, the relationship between dose, route, and time of exposure and injuries remains poorly understood. Thus, we aimed to assess whether cadmium exposure in any dose, route, and time of exposure causes significant alteration in the testicular tissue of murine models, as well as the main mechanisms involved. We performed a structured search on the Medline/PubMed and Scopus databases to retrieve studies published until September 2018. The results were organized into an Adverse Outcome Pathway (AOP) framework. Also, a bias analysis of included studies was performed. We included 37 studies, and most of them identified significant histopathologies in both tubule and intertubule regarding routes, in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The damages were observed after the first hours of exposure, mainly vascular damages suggesting that vasculature failure is the primary mechanism. The AOP showed that potential molecular initiating events may mimic and interfere with essential elements disrupting proteins (structural and antioxidants), change in the oxidative phosphorylation enzyme activities, and gene expression alteration, which lead to reproductive failure (adverse outcome). Analysis of methodological quality showed that the current evidence is at high risk of bias. Despite the high risk of bias, cadmium triggers significant lesions in the testis of murine models, regarding routes, in a dose- and time-dependent manner, mainly due to vascular changes. Therefore, cadmium is a risk factor for male reproductive health.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Duffus J (2002) Heavy metals – a meaningless term? (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem 74(5):793–807
Martiniakova M, Omelka R, Jancova A, Formicki G, Stawarz R, Bauerova M (2012) Accumulation of risk elements in kidney, liver, testis, uterus and bone of free-living wild rodents from a polluted area in Slovakia. J Environ Sci Health A 47(9):1202–1206
WHO World Health Organization (2017) Guidelines for drinking-water quality: fourth edition incorporating the first addendum. https://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/publications/drinking-water-quality-guidelines-4-including-1st-addendum/en/. Accessed 05 May 2020
ATSDR Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2012) Toxicological profile for cadmium. Mailstop F-62, Atlanta
Bernard A, Lauwerys R (1984) Cadmium in human population. Experientia 40:143–152
Nishijo M, Nakagawa H, Suwazono Y, Nogawa K, Kido T (2017) Causes of death in patients with Itai-itai disease suffering from severe chronic cadmium poisoning: a nested case-control analysis of a follow-up study in Japan. BMJ Open 7:1–7
Barratt C, Bjӧrndahl L, De Jonge C, Lamb D, Martini F, Mclachlan R et al (2017) The diagnosis of male infertility: an analysis of the evidence to support the development of global WHO guidance-challenges and future research opportunities. Hum Reprod Update 23(6):660–680
Leaver R (2017) Male infertility: an overview of causes and treatment options. Br J Nurs 25(18):35–40
Guzikowski W, Szynkowska MI, Motak-Pochrzęst H, Pawlaczyk A, Sypniewski S (2015) Trace elements in seminal plasma of men from infertile couples. Arch Med Sci 11(3):591–598
Zafar A, Eqani S, Bostan N, Cincinelli A, Tahir F, Shah S et al (2015) Toxic metals signature in the human seminal plasma of Pakistani population and their potential role in male infertility. Environ Geochem Health 37(3):515–527
Satarug S (2018) Dietary cadmium intake and its effects on kidneys. Toxics 6(15):1–23
Egger AE, Grabmann G, Gollmann-Tepeöylü C, Pechriggl EJ, Artner C, Türkcan A et al (2019) Chemical imaging and assessment of cadmium distribution in the human body. Metallomics 11(12):2010–2019
Wu X, Guo X, Wang H, Zhou S, Li L, Chen X et al (2017) A brief exposure to cadmium impairs Leydig cell regeneration in the adult rat testis. Sci Rep 7(6337):1–11
Santana V, Salles É, Correa D, Gonçalves B, Campos S, Justulin L et al (2016) Long-term effects of perinatal exposure to low doses of cadmium on the prostate of adult male rats. Int J Exp Pathol 97(4):310–316
Siu E, Mruk D, Porto C, Cheng C (2009) Cadmium-induced testicular injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238(3):240–249
Angelis C, Galdiero M, Pivonello C, Salzano C, Gianfrilli D, Piscitelli P (2017) The environment and male reproduction: the effect of cadmium exposure on reproductive function and its implication in fertility. Reprod Toxicol 73:105–127
Othman A, Abdel-Hamid M (2017) Curcumin mitigates fethion-induced testicular toxicity in rats: histopathological and immunohistochemical study. Afr Zool 52(4):209–215
Kumar S, Sharma A (2019) Cadmium toxicity: effects on human reproduction and fertility. Rev Environ Health 34(4):327–338
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA group (2009) Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7):1–6
Hoojimans CR, Tilema A, Leenaars M, Ritskes-Hoitinga M (2010) Enhancing search efficiency by means of a search filter for finding all studies on animal experimentation. Lab Anim 44(3):170–175
Villeneuve DL, Crump D, Garcia-Reyero N, Hecker M, Hutchinson TH, LaLone CA, Landesmann B, Lettieri T, Munn S, Nepelska M, Ottinger MA, Vergauwen L, Whelan M (2014) Adverse Outcome Pathway (AOP) development I: strategies and principles. Toxicol Sci 142(2):312–320
Hoojimans CR, Rovers MM, Vries R, Leenaars M, Ritskes-Hoitinga M, Lagendam W (2014) SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med Res Methodol 14(43):1–9
Allanson M, Deanesly R (1962) Observations on cadmium damage and repair in rat testes and the effects on the pituitary gonadotrophs. J Endocrinol 24:453–462
Aoyagi T, Ishikawa H, Miyaji K, Hayakawa K, Hata M (2002) Cadmium-induced testicular damage in a rat model of subchronic intoxication. Reprod Med Biol 1(2):59–63
Berliner A, Jones-Witters P (1975) Early effects of a lethal cadmium dose on Gerbil testis. Biol Reprod 13(2):240–247
Blanco A, Moyano M, Molina A, Blanco C, Flores-Acuña R, García-Flores J et al (2010) Preneoplastic and neoplastic changes in the Leydig cells population in mice exposed to low doses of cadmium. Toxicol Ind Health 26(8):451–457
Blanco A, Moyano M, Molina A, Blanco C, Flores-Acuña R, García-Flores J et al (2009) Quantitative study of Leydig cell populations in mice exposed to low doses of cadmium. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82(6):756–760
Blanco A, Moyano M, Vivo J, Flores-Acuña R, Molina A, Blanco C et al (2007) Quantitative changes in the testicular structure in mice exposed to low doses of cadmium. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 23(1):96–101
Bomhard E, Vogel O, Löser E (1987) Chronic effects on single and multiple oral and subcutaneous cadmium administration on the testes of Wistar rats. Cancer Lett 36(3):307–315
Cupertino M, Novaes R, Santos E, Bastos D, Santos D, Fialho M et al (2017) Cadmium-induced testicular damage is associated with mineral imbalance, increased antioxidant activity and protein oxidation in rats. Life Sci 175:23–30
Cupertino M, Novaes R, Santos E, Neves A, Silva E, Oliveira J et al (2017) Differential susceptibility of germ and Leydig cells to cadmium-mediated toxicity: impact on testis structure, adiponectin levels, and steroidogenesis. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2017:1–11
Davis J, Goniglio J (1967) The effect of cryptorchidism, cadmium and anti-spermatogenic drugs on fatty acid composition of rat testis. J Reprod Fertil 14(3):407–413
Favino A, Baillie A, Griffiths K (1966) Androgen synthesis by the testes and adrenal glands of rats poisoned with cadmium chloride. J Endocrinol 35(2):185–192
Hew K, Ericson W, Welsh M (1993) A single low cadmium dose causes failure of spermiation in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 121(1):15–21
Ito T, Sawauchi K (1966) Inhibitory effects on cadmium-induced testicular damage by pretreatment with smaller cadmium dose. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn 42(2-3):107–117
Kar A, Das R (1962) Sterilization of males by intratesticular administration of cadmium chloride. Acta Endocrinol 40:321–331
Krasovskii G, Varshavskaya S, Borisov A (1976) Toxic and gonadotropic effects of cadmium and boron relative to standards for these substances in drinking water. Environ Health Perspect 13:69–75
Leite R, Peloso E, Gadelha F, Dolder M (2015) Environmentally realistic doses of cadmium as a possible etiologic agent for idiopathic pathologies. Biol Trace Elem Res 168(1):133–140
Li X, Yang X, Yuwen L, Yang W, Weng L, Teng Z, Wang L (2016) Evaluation of toxic effects of CdTe quantum dots on the reproductive system in adult male mice. Biomaterials 96:24–32
Marettová E, Legáth J (2010) Changes in the peritubular tissue of rat testis after cadmium treatment. Biol Trace Elem Re 134(3):288–295
Medina M, Arrieta M, Villafañe M, Klyver S, Odstrcil I, González M (2017) Early signs of toxicity in testes and sperm of rats exposed to low cadmium doses. Toxicol Ind Health 33(7):576–587
Meek E (1959) Cellular changes induced by cadmium in mouse testis and liver. Br J Exp Pathol XL(5):503-507
Niknafs B, Salehnia M, Kamkar M (2015) Induction and determination of apoptotic and necrotic cell death by cadmium chloride in testis tissue of mouse. J Reprod Infertil 16(1):24–29
Oliveira H, Lopes T, Almeida T, Pereira M, Santos C (2012) Cadmium-induced genetic instability in mice testis. Hum Exp Toxicol 31(12):1228–1236
Predes F, Diamante M, Dolder H (2010) Testis response to low doses of cadmium in Wistar rats. Int J Exp Pathol 91(2):125–131
Reddy J, Svoboda D, Azarnoff D, Dawar R (1973) Cadmium-induced Leydig cell tumors of rat testis: morphology and cytochemical study. J Natl Cancer Inst 51(3):891–903
Saygi Ş, Deniz G, Kutsal O, Vural N (1991) Chronic effects of cadmium on kidney, liver, testis, and fertility of male rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 31(3):209–214
Selypes A, Serényi P, Boldog L, Bokros F, Takács S (1992) Acute and “long-term” genotoxic effects of CdCl2 on testes of mice. J Toxicol Environ Health 36(4):401–409
Sharma S, Kaur S (2012) Histopathological effects of acute and chronic doses of cadmium on testes of albino mice. J Exp Zool India 15(1):107–111
Singh K, Mathur S (1968) Action of cadmium on some testicular enzymes of the desert gerbil Meriones hurrianae Jerdon. J Reprod Fertil 17(3):509–513
Waalkes M, Rehm S, Riggs C, Bare R, Devor D, Poirier L et al (1988) Cadmium carcinogenesis in male Wistar [Crl:(WI)BR] rats: dose-response analysis of tumor induction in the prostate and testes and at injection site. Cancer Res 48(15):4656–4663
Wang Y, Yan J, Yin F, Li L, Qin Y, Meng C et al (2016) Role of autophagy in cadmium-induced testicular injury. Hum Exp Toxicol 36(10):1039–1048
Wong K, Klaassen C (1980) Age difference in the susceptibility to cadmium-induced testicular damage in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 55(3):456–466
Wong K, Cachia R, Klaassen C (1980) Comparison of the toxicity and tissue distribution of cadmium in newborn and adult rats after repeated administration. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 56(3):317–325
Zenick H, Hastings L, Goldsmith M, Niewennhuis R (1982) Chronic cadmium exposure: relation to male reproductive toxicity and subsequent fetal outcome. J Toxicol Environ Health 9(3):377–387
Zhou T, Jia X, Chapin R, Maronpot R, Harris M, Liu J et al (2004) Cadmium at a non-toxic dose alters gene expression in mouse testes. Toxicol Lett 154(3):191–200
Zielinska-Psuja B, Lukaszyk A, Senczuk W (1979) The anti-reproductive effects of long term oral administration of cadmium on the adult male rats. Int J Androl 8(2):150–161
Zschauer A, Hodel C (1980) Drug-induced histological changes in rat seminiferous tubular epithelium. Arch Toxicol 4:466–470
Ӧner H, Karatepe M, Karatas F, Ӧner J, Yilmaz I, Cukurovali A (2005) Effects on rat testes of the thiosemicarbazone derivative Schiff base (4-(1-phenylmethylcyclobutane-3-yl)-2-(2-hydroxybenzylidenehydrazino)thiazole) and its cadmium(II) complex. Cell Biochem Funct 23(6):427–433
Gad SC (2016) Animals models in toxicology, 3rd edn. CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton
Kratchamn J, Wang B, Gray G (2018) Which is most sensitive? Assessing responses of mice and rats toxicity bioassays. J Toxicol Environ Health A 81(7):173–183
Catlin NR, Willson CJ, Creasy DM, Rao DB, Kissling GE, Mclntyre BS et al (2018) Differentiating between testicular toxicity and sexual immaturity in ortho-phthalaldehyde inhalation toxicity studies in rats and mice. Toxicol Pathol 46(7):753–763
King L, Banks W, George W (1999) Differences in cadmium transport to the testis, epididymis, and brain in cadmium-sensitive and -resistant murine strains 129/J and A/J. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289(2):825–830
Shimada H, Narumi R, Nagano M, Yasutake A, Waalkes M, Imamura Y et al (2009) Strain difference of cadmium-induced testicular toxicity in inbred Wistar-Imamichi and Fisher 344 rats. Arch Toxicol 83(7):647–652
Wei T, Jia J, Wada Y, Kapron CM, Liu J (2017) Dose dependent effects of cadmium on tumor angiogenesis. Oncotarget 8(27):44944–44959
Mouro VGS, Siman VA, Silva J, Dias FCR, Damasceno EM, Cupertino MC et al (2019) Cadmium-induced testicular toxicity in mice: subacute and subchronic route-dependent effects. Biol Trace Elem Res 193(2):466–482
Menon A, Chang J, Kim J (2016) Mechanism of divalent metal toxicity in affective disorders. Toxicol 339:58–72
Wang H, Chang M, Peng T, Yang Y, Li N, Luo T et al (2017) Exposure to cadmium impairs sperm functions by reducing CatSper in mice. Cell Physiol Biochem 42:44–54
Ankley GT, Edwards SW (2018) The adverse outcome pathway: a multifaceted framework supporting 21st century toxicology. Curr Opin Toxicol 1(7):1–7
Knapen D, Vergauwen L, Villeneuve DL, Ankley GT (2015) The potential of AOP networks for reproductive and developmental toxicity assay development. Reprod Toxicol 56:52–55
Matović V, Buha A, Bulat Z, Đukić-Ćosić D, Miljković M, Ivanišević J et al (2012) Route-dependent effects of cadmium/cadmium and magnesium acute treatment on parameters of oxidative stress in rat liver. Food Chem Toxicol 50(3-4):552–557
Rinaldi M, Micali A, Marini H, Adamo EB, Puzzolo D, Pisani A et al (2017) Cadmium, organ toxicity and therapeutic approaches: a review on brain, kidney and testis damage. Curr Med Chem 24(35):3879–3893
Ge J, Zhang C, Sun Y, Zhang Q, Lv M, Guo K et al (2019) Cadmium exposure triggers mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in chicken (Gallus gallus) kidney via mitochondrial UPR inhibition and Nrf2-mediated antioxidant defense activation. Sci Total Environ 689:1160–1171
Brix KV, Schlekat CE, Garman ER (2016) The mechanisms of nickel toxicity in aquatic environments: an adverse outcome pathway analysis. Environ Toxicol Chem 36(5):1128–1137
El-Shahat A, Gabr A, Meki A, Mehana E (2009) Altered testicular morphology and oxidative stress induced by cadmium in experimental rats and protective effect of simultaneous green tea extract. Int J Morphol 27(3):757–764
Aitken R, Roman S (2008) Antioxidant systems and oxidative stress in the testes. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 1(1):15–24
Bauer R, Demeter I, Hasemann V, Johansen J (1980) Structural properties of the zinc site in Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase; perturbed angular correlation of gamma ray spectroscopy on the Cu, 111Cd-superoxide dismutase derivative. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 94(4):1296–1302
Wąsowicz W, Gromadzińska J, Rydzyński K (2001) Blood concentration of essential trace elements and heavy metals in workers exposed to lead and cadmium. Int J Occup Med Environ Health 14(3):223–229
Riaz M, Mahmood Z, Shahid U, Saeed M, Tahir I, Shah A et al (2015) Impact of reactive oxygen species on antioxidant capacity of male reproductive system. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 29(3):421–425
Prozialeck W, Edwards J, Nebert D, Woods J, Barchowsky A, Atchison W (2008) The vascular system as a target of metal toxicity. Toxicol Sci 102(2):207–218
Kim K (1995) Apoptosis and calcification. Scanning Microsc 9(4):1137–1178
Xie Z, Zhang Y, Li A, Li P, Ji W, Huang D (2010) Cd-induced apoptosis was mediated by the release of Ca2+ from intracellular Ca storage. Toxicol Lett 192(2):115–118
Mouro VGS, Menezes TP, Lima GDA, Domingues RR, Souza AC, Oliveira JA et al (2018) How bad is aluminum exposure to reproductive parameters in rats? Biol Trace Elem Res 183(2):314–324
Morgan DL (1998) Practical strategies for combining qualitative and quantitative methods: applications to health research. Qual Health Res 8(3):362–376
Onwuegbuzie AJ, Leech NL (2007) On becoming a pragmatic researcher: the importance of combining quantitative and qualitative research methodologies. Int J Soc Res Methodol 8(5):375–387
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Amanda Alves de Melo for English assistance, the support provided by Fundação do Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG, processes PPM-00687-17 and PPM-00077-18), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, processes 303972/2017-3, 423594/2018-4, 305093/2017-7, and MCTIC 408503/2018-1), and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES, finance code 001). Also, we thank CAPES for the PhD scholarship provided to Silva J.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 434 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva, J., Gonçalves, R.V., de Melo, F.C.S.A. et al. Cadmium Exposure and Testis Susceptibility: a Systematic Review in Murine Models. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 2663–2676 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02389-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02389-0