Abstract
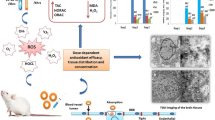
Aluminum nanoparticles (AlNPs) are among the most abundantly produced nanosized particles in the market. There is limited information about the potential harmful effects of aluminum oxide due to its particle size on human health. Considering the toxic effects of Al on brain as its target tissue, in this study, the toxicity of nanoparticles, microparticles, and ionic forms of Al on rat brain and isolated mitochondria was evaluated. Sixty male Wistar rats were divided into ten groups (six rats each), in which group I was the control, and the other groups were administered different doses of Al nanoparticles, Al microparticles (AlMP), and Al ionic forms (2, 4, and 8 mg/kg, i.p.) for 28 days. After 24 h, the animals were killed, brain tissue was separated, the mitochondrial fraction was isolated, and oxidative stress markers were measured. Also, mitochondrial function was assayed by MTT test. The results showed that all forms of Al particles induced ROS formation, lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation, glutathione depletion, mitochondrial dysfunction, and gait abnormalities in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, Al particles decreased mitochondrial membrane potential. These data indicated that oxidative stress might contribute to the toxicity effects of Al. Comparison of oxidative stress markers between all forms of Al revealed that the toxic effect of AlNP on brain tissue was substantially more than that caused by AlMP and bulk form. This study showed more neurotoxicity of AlNPs compared to other forms on brain oxidative damage that probably is due to more penetration into the brain.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park E-J, Lee G-H, J-h S, Cho M-H, Lee B-S, Kim Y-B, Kim J-H, Kim Y, Kim D-W (2015) Comparison of the toxicity of aluminum oxide nanorods with different aspect ratio. Arch Toxicol 89(10):1771–1782
Yan L, Zheng YB, Zhao F, Li S, Gao X, Xu B, Weiss PS, Zhao Y (2012) Chemistry and physics of a single atomic layer: strategies and challenges for functionalization of graphene and graphene-based materials. Chem Soc Rev 41(1):97–114
Amelia M, Lincheneau C, Silvi S, Credi A (2012) Electrochemical properties of CdSe and CdTe quantum dots. Chem Soc Rev 41(17):5728–5743
Joh DY, Kinder J, Herman LH, Ju S-Y, Segal MA, Johnson JN, Chan GK-L, Park J (2011) Single-walled carbon nanotubes as excitonic optical wires. Nat Nanotechnol 6(1):51–56
Tang F, Li L, Chen D (2012) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: synthesis, biocompatibility and drug delivery. Adv Mater 24(12):1504–1534
Laurent S, Forge D, Port M, Roch A, Robic C, Vander Elst L, Muller RN (2008) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem Rev 108(6):2064–2110
Doudi M, Setorki M (2014) Acute effect of nano-copper on liver tissue and function in rat. Nanomedicine J 1 (5): 331-338
Oesterling E, Chopra N, Gavalas V, Arzuaga X, Lim EJ, Sultana R, Butterfield DA, Bachas L, Hennig B (2008) Alumina nanoparticles induce expression of endothelial cell adhesion molecules. Toxicol Lett 178(3):160–166
Kumar V, Gill KD (2014) Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in aluminium neurotoxicity and its amelioration: a review. Neurotoxicology 41:154–166
Perry CC, Keeling-Tucker T (1998) Aspects of the bioinorganic chemistry of silicon in conjunction with the biometals calcium, iron and aluminium. J Inorg Biochem 69(3):181–191
Becaria A, Campbell A, Bondy S (2002) Aluminum as a toxicant. Toxicol Ind Health 18(7):309–320
Lal B, Gupta A, Murthy R, Ali MM, Chandra S (1993) Aluminum ingestion alters behaviour and some neurochemicals in rats. Indian J Exp Biol 31(1):30–35
Julka D, Gill K (1996) Effect of aluminum on regional brain antioxidant defense status in Wistar rats. Res Exp Med 196(1):187–194
Kaur A, Joshi K, Minz RW, Gill KD (2006) Neurofilament phosphorylation and disruption: a possible mechanism of chronic aluminium toxicity in Wistar rats. Toxicology 219(1):1–10
Sánchez-Iglesias S, Soto-Otero R, Iglesias-Gonzalez J, Barciela-Alonso MC, Bermejo-Barrera P, Méndez-Álvarez E (2007) Analysis of brain regional distribution of aluminium in rats via oral and intraperitoneal administration. J Trace Elem Med Biol 21:31–34
Jack R, Rabin PL, McKinney TD (1984) Dialysis encephalopathy: a review. Int J Psychiatry Med 13(4):309–326
Neri L, Hewitt D (1991) Aluminium, Alzheimer’s disease, and drinking water. Lancet 338(8763):390
Gauthier E, Fortier I, Courchesne F, Pepin P, Mortimer J, Gauvreau D (2000) Aluminum forms in drinking water and risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Environ Res 84(3):234–246
Flaten TP (2001) Aluminium as a risk factor in Alzheimer’s disease, with emphasis on drinking water. Brain Res Bull 55(2):187–196
Jones CF, Grainger DW (2009) In vitro assessments of nanomaterial toxicity. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61(6):438–456
Landsiedel R, Kapp MD, Schulz M, Wiench K, Oesch F (2009) Genotoxicity investigations on nanomaterials: methods, preparation and characterization of test material, potential artifacts and limitations—many questions, some answers. Mutation Res/Reviews in Mutation Res 681(2):241–258
Møller P, Jacobsen NR, Folkmann JK, Danielsen PH, Mikkelsen L, Hemmingsen JG, Vesterdal LK, Forchhammer L, Wallin H, Loft S (2009) Role of oxidative damage in toxicity of particulates. Free radical research
Oberdörster G, Stone V, Donaldson K (2007) Toxicology of nanoparticles: a historical perspective. Nanotoxicology 1(1):2–25
Niu P, Niu Q, Zhang Q, Wang L, He S, Wu T, Conti P, Di Gioacchino M, Boscolo P (2005) Aluminum impairs rat neural cell mitochondria in vitro. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 18(4):683–689
Kumar V, Bal A, Gill KD (2008) Impairment of mitochondrial energy metabolism in different regions of rat brain following chronic exposure to aluminium. Brain Res 1232:94–103
Kumar V, Gill KD (2009) Aluminium neurotoxicity: neurobehavioural and oxidative aspects. Arch Toxicol 83(11):965–978
Liang F-Q, Godley BF (2003) Oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial DNA damage in human retinal pigment epithelial cells: a possible mechanism for RPE aging and age-related macular degeneration. Exp Eye Res 76(4):397–403
Halliwell B (1992) Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous system. In: Free radicals in the brain. Springer, pp 21–40
Chaves S, Lacava L, Lacava Z, Silva O, Pelegrini F, Buske N, Gansau C, Morais P, Azevedo R (2002) Light microscopy and magnetic resonance characterization of a DMSA-coated magnetic fluid in mice. Magnetics, IEEE Transactions on 38(5):3231–3233
Shaki F, Hosseini M-J, Ghazi-Khansari M, Pourahmad J (2012) Toxicity of depleted uranium on isolated rat kidney mitochondria. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects 1820(12):1940–1950
Lambowitz AM (1979) [34] Preparation and analysis of mitochondrial ribosomes. Methods Enzymol 59:421–433
Mehri S, Karami HV, Hassani FV, Hosseinzadeh H (2014) Chrysin reduced acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in both in vitro and in vivo assessments. Iran Biomed J 18(2):101
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Gao X, Zheng CY, Yang L, Tang XC, Zhang HY (2009) Huperzine A protects isolated rat brain mitochondria against β-amyloid peptide. Free Radic Biol Med 46(11):1454–1462
Sadegh C, Schreck RP (2003) The spectroscopic determination of aqueous sulfite using Ellman’s reagent. MURJ 8:39–43
Zhang S, Fu J, Zhou Z (2004) In vitro effect of manganese chloride exposure on reactive oxygen species generation and respiratory chain complexes activities of mitochondria isolated from rat brain. Toxicol in Vitro 18(1):71–77
Lee YW, Hennig B, Yao J, Toborek M (2001) Methamphetamine induces AP-1 and NF-κB binding and transactivation in human brain endothelial cells. J Neurosci Res 66(4):583–591
Ghazi-Khansari M, Mohammadi-Bardbori A, Hosseini MJ (2006) Using Janus green B to study paraquat toxicity in rat liver mitochondria. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1090(1):98–107
Hosseini M-J, Shaki F, Ghazi-Khansari M, Pourahmad J (2013) Toxicity of vanadium on isolated rat liver mitochondria: a new mechanistic approach. Metallomics 5(2):152–166
Yang S-T, Wang T, Dong E, Chen X-X, Xiang K, Liu J-H, Liu Y, Wang H (2012) Bioavailability and preliminary toxicity evaluations of alumina nanoparticles in vivo after oral exposure. Toxicology Res 1(1):69–74
Kawahara M, Kato-Negishi M (2011) Link between aluminum and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: the integration of the aluminum and amyloid cascade hypotheses. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011
Lukiw WJ, Pogue AI (2007) Induction of specific micro RNA (miRNA) species by ROS-generating metal sulfates in primary human brain cells. J Inorg Biochem 101(9):1265–1269
Wu Z, Du Y, Xue H, Wu Y, Zhou B (2012) Aluminum induces neurodegeneration and its toxicity arises from increased iron accumulation and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Neurobiology Aging 33(1):199.e1–199.e12
Youdim M (1988) Iron in the brain: implications for Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases. Mount Sinai J medicine, New York 55(1):97–101
Sethi P, Jyoti A, Hussain E, Sharma D (2009) Curcumin attenuates aluminium-induced functional neurotoxicity in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 93(1):31–39
Shaligram S, Campbell A (2013) Toxicity of copper salts is dependent on solubility profile and cell type tested. Toxicol in Vitro 27(2):844–851
Ray PC, Yu H, Fu PP (2009) Toxicity and environmental risks of nanomaterials: challenges and future needs. J Environ Sci Health Part C 27(1):1–35
Nel A, Xia T, Mädler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311(5761):622–627
Xia T, Kovochich M, Brant J, Hotze M, Sempf J, Oberley T, Sioutas C, Yeh JI, Wiesner MR, Nel AE (2006) Comparison of the abilities of ambient and manufactured nanoparticles to induce cellular toxicity according to an oxidative stress paradigm. Nano Lett 6(8):1794–1807
Wang S, Lu W, Tovmachenko O, Rai US, Yu H, Ray PC (2008) Challenge in understanding size and shape dependent toxicity of gold nanomaterials in human skin keratinocytes. Chem Phys Lett 463(1):145–149
Lu W, Senapati D, Wang S, Tovmachenko O, Singh AK, Yu H, Ray PC (2010) Effect of surface coating on the toxicity of silver nanomaterials on human skin keratinocytes. Chem Phys Lett 487(1):92–96
He C, Hu Y, Yin L, Tang C, Yin C (2010) Effects of particle size and surface charge on cellular uptake and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. Biomaterials 31(13):3657–3666
Wang S-H, Lee C-W, Chiou A, Wei P-K (2010) Size-dependent endocytosis of gold nanoparticles studied by three-dimensional mapping of plasmonic scattering images. J Nanobiotechnol 8(1):33
Campbell A, Prasad KN, Bondy SC (1999) Aluminum-induced oxidative events in cell lines: glioma are more responsive than neuroblastoma. Free Radic Biol Med 26(9):1166–1171
Strong MJ, Garruto RM, Joshi JG, Mundy WR, Shafer TJ (1996) Can the mechanisms of aluminum neurotoxicity be integrated into a unified scheme? J Toxicology Environ Health Part A 48(6):599–614
Prakash NT, Rao KJ (1995) Modulations in antioxidant enzymes in different tissues of marine bivalve Perna viridis during heavy metal exposure. Mol Cell Biochem 146(2):107–113
Kaiser R, Correa M, Spanevello R, Morsch V, Mazzanti C, Goncalves J, Schetinger M (2005) Acetylcholinesterase activation and enhanced lipid peroxidation after long-term exposure to low levels of aluminium on different mouse brain regions. J Inorg Biochem 99:1865–1870
Candan N, Tuzmen N (2008) Very rapid quantification of malondialdehyde (MDA) in rat brain exposed to lead, aluminium and phenolic antioxidants by high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. Neurotoxicology 29(4):708–713
Golub MS, Han B, Keen CL, Gershwin ME (1992) Effects of dietary aluminum excess and manganese deficiency on neurobehavioral endpoints in adult mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 112(1):154–160
Dong E, Wang Y, Yang S-T, Yuan Y, Nie H, Chang Y, Wang L, Liu Y, Wang H (2011) Toxicity of nano gamma alumina to neural stem cells. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 11(9):7848–7856
Lewinski N, Colvin V, Drezek R (2008) Cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. Small 4(1):26–49
Kowaltowski AJ, Castilho RF, Vercesi AE (2001) Mitochondrial permeability transition and oxidative stress. FEBS Lett 495(1–2):12–15
Garrido C, Galluzzi L, Brunet M, Puig P, Didelot C, Kroemer G (2006) Mechanisms of cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Cell Death & Differentiation 13(9):1423–1433
Karlsson HL, Gustafsson J, Cronholm P, Möller L (2009) Size-dependent toxicity of metal oxide particles—a comparison between nano-and micrometer size. Toxicol Lett 188(2):112–118
Zhao J, Wang Z, Liu X, Xie X, Zhang K, Xing B (2011) Distribution of CuO nanoparticles in juvenile carp (Cyprinus carpio) and their potential toxicity. J Hazard Mater 197:304–310
Acknowledgements
This study was extracted from Pharm.D. thesis of Mehdi Nazari.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the research council of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experimental procedures were conducted according to the ethical standards and protocols approved by the Committee of Animal Experimentation of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirshafa, A., Nazari, M., Jahani, D. et al. Size-Dependent Neurotoxicity of Aluminum Oxide Particles: a Comparison Between Nano- and Micrometer Size on the Basis of Mitochondrial Oxidative Damage. Biol Trace Elem Res 183, 261–269 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1142-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1142-8