Abstract
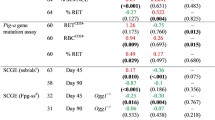
The aim of the present study is to evaluate the radioprotective effect of low-dose selenium supplementation (multiple administrations) on radiation toxicities and mortality induced by lethal dose of whole-body irradiation (WBI). For this, BALB/c mice received sodium selenite (4 μg/kg body wt) intraperitoneally for five consecutive days and subjected to WBI at an absorbed dose of 8 Gy (60Co, 1 Gy/min). Administration of sodium selenite was continued even during the post irradiation days three times a week till the end of the experiment. The radioprotective effect was evaluated in terms of the improvement in 30 days post irradiation survival, protection from DNA damage, and biochemical and histological changes in radiosensitive organs. The results indicated that low-dose sodium selenite administration did not protect the mice from radiation-induced hematopoietic and gastrointestinal injuries and subsequent mortality. However, it significantly prevented the radiation-induced genotoxicity or DNA damage in peripheral leukocytes. Further sodium selenite administration modulated the messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of GPx1, GPx2, and GPx4 in the spleen and intestine differentially and led to a significant increase in GPx activity (∼1.5 to 2-folds) in these organs. In line with this observation, sodium selenite administration reduced the level of lipid peroxidation in the intestine. In conclusion, our study shows that low-dose sodium selenite supplementation can be an effective strategy to prevent WBI-induced genotoxicity but may not have an advantage against mortality sustained during nuclear emergencies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fairweather-Tait SJ, Bao Y, Broadley MR, Collings R, Ford D, Hesketh JE, Hurst R (2011) Selenium in human health and disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 7:1337–1383
Rosenfield I, Beath OA (1964) Selenium: genotoxicity, biochemistry, toxicity and nutrition. Academic Press, New York
Brenneisen P, Steinbrenner H, Sies H (2005) Selenium, oxidative stress, and health aspects. Mol Asp Med 26:256–267
Rayman MP (2000) The importance of selenium to human health. Lancet 356:233–241
Papp LV, Lu J, Holmgren A, Khanna KK (2007) From selenium to selenoproteins: synthesis, identity, and their role in human health. Antioxid Redox Signal 9:775–806
Lu J, Jiang C (2005) Selenium and cancer chemoprevention: hypotheses integrating the actions of selenoproteins and selenium metabolites in epithelial and non-epithelial target cells. Antioxid Redox Signal 7:1715–1727
Brozmanova J, Manikova D, Vlckova V, Chovanec M (2010) Selenium: a double-edged sword for defense and offence in cancer. Arch Toxicol 84:919–938
Puspitasari IM, Abdulah R, Yamazaki C, Kameo S, Nakano T, Koyama H (2014) Updates on clinical studies of selenium supplementation in radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol 9:125
Micke O, Schomburg L, Buentzel J, Kisters K, Muecke R (2009) Selenium in oncology: from chemistry to clinics. Molecules 14:3975–3988
Sanmartin C, Plano D, Font M, Palop JA (2011) Selenium and clinical trials: new therapeutic evidence for multiple diseases. Curr Med Chem 18:4635–4650
Weiss JF, Landauer MR (2003) Protection against ionizing radiation by antioxidant nutrients and phytochemicals. Toxicology 189:1–20
Weiss JF, Srinivasan V, Kumar KS, Landauer MR, Patchen ML (1994) Radioprotection by selenium compounds. In: Trace elements and free radicals in oxidative diseases, AOCS Press, Champaign, pp 211–222
Hurt HD, Cary EE, Allaway WH, Visek WJ (1971) Effect of dietary selenium on the survival of rats exposed to chronic whole body irradiation. J Nutr 101:363–366
Hollo MA, Zlatarov S (1960) Prevention of deaths by means of selenium salts administered after roentgen irradiation. Borgy Venerol Szemle 36:204–207
Sieber F, Muira SA, Cohen EP, North PE, Fish BL, Irving AA, Mader M, Moulder JE (2009) High-dose selenium for the mitigation of radiation injury: a pilot study in a rat model. Radiat Res 171:368–373
Sieber F, Muir SA, Cohen EP, Fish BL, Mader M, Schock AM, Althouse BJ, Moulder JE (2011) Dietary selenium for the mitigation of radiation injury: effects of selenium dose escalation and timing of supplementation. Radiat Res 176:366–374
Olson OE (1986) Selenium toxicity in animals with emphasis on man. Int J Toxicol 5:45–70
Sagowski C, Wenzel S, Jenicke L, Metternich FU, Jaehne M (2005) Sodium selenite is a potent radioprotector of the salivary glands of the rat: acute effects on the morphology and parenchymal function during fractioned irradiation. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 6:459–464
Gehringer MM, Downs KS, Downing TG, Naudé RJ, Shephard EG (2003) An investigation into the effect of selenium supplementation on microcystin hepatotoxicity. Toxicon 41:451–458
Rosa DE V, Erkeko LUP, Forestier A, Favier A, Hinchal F, Diamond AM, Rachidi W (2012) Low doses of selenium specifically stimulate the repair of oxidative DNA damage in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Free Radic Res 46:105–116
Charab MA, Abouzeinab NS, Moustafa ME (2016) The protective effect of selenium on oxidative stress induced by waterpipe (Narghile) smoke in lungs and liver of mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 174:392–401
Jerome-Morais A, Bera S, Rachidi W, Gann PH, Diamond AM (2013) The effects of selenium and the GPx-1 selenoprotein on the phosphorylation of H2AX. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830:3399–3406
Hatfield DL, Berry MJ, Gladyshev VN (2006) Selenium: its molecular biology and role in human health, 3rd edn. Springer, New York
Kunwar A, Bansal P, Kumar SJ, Bag PP, Paul P, Reddy N, Kumbhare LB, Jain VK, Chaubey RC, Unnikrishnan MK, Priyadarsini KI (2010) In vivo radioprotection studies of 3,3′-diselenodipropionic acid, a selenocystine derivative. Free Radic Biol Med 48:399–410
Kunwar A, Narang H, Priyadarsini KI, Krishna M, Pandey R, Sainis KB (2007) Delayed activation of PKCdelta and NFkappaB and higher radioprotection in splenic lymphocytes by copper (II)-curcumin (1:1) complex as compared to curcumin. J Cell Biochem 102:1214–1224
Kunwar A, Verma P, Bhilwade HN, Iwaoka M, Priyadarsini KI (2016) Dihydroxyselenolane (DHS) supplementation improves survival following whole-body irradiation (WBI) by suppressing tissue-specific inflammatory responses. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 807:33–46
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Sandhya T, Lathika KM, Pandey BN, Bhilwade HN, Chaubey RC, Priyadarsini KI, Mishra KP (2006) Protection against radiation oxidative damage in mice by Triphala. Mutat Res 609:17–25
Suryavanshi S, Sharma D, Checker R, Thoh M, Gota V, Sandur SK (2015) Amelioration of radiation-induced hematopoietic syndrome by an antioxidant chlorophyllin through increased stem cell activity and modulation of hematopoiesis. Free Radic Biol Med 85:56–70
Carsten AL (1984) Acute lethality: the hematopoietic syndrome in different species, In: Response of different species to total body irradiation, Springer, Netherlands, pp. 59–86
Kunwar A, Adhikary B, Jayakumar S, Barik A, Chattopadhyay S, Raghukumar S, Priyadarsini KI (2012) Melanin, a promising radioprotector: mechanisms of actions in a mice model. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 264:202–211
Mavragani IV, Laskaratou DA, Frey B, Candeias SM, Gaipl US, Lumniczky K, Georgakilas AG (2016) Key mechanisms involved in ionizing radiation-induced systemic effects: a current review. Toxicology Research 5:12–33
Carr KE, Hume SP, Ettarh R, Carr EA, McCollough S (1995) Radiation-induced changes to epithelial and non-epithelial tissue, In: Radiation and the Gastrointestinal Tract, Taylor and Francis, pp 113–128
Denham JW, Hauer-Jensen M (2002) The radiotherapeutic injury—a complex “wound”. Radiother Oncol 63:129–145
Seo YR, Sweeney C, Smith ML (2002) Selenomethionine induction of DNA repair response in human fibroblasts. Oncogene 21:3663–3669
Baliga MS, Wang H, Zhuo P, Schwartz JL, Diamond AM (2007) Selenium and GPx-1 overexpression protect mammalian cells against UV-induced DNA damage. Biol Trace Elem Res 115:227–242
Baliga MS, Diwadkar-Navsariwala V, Koh T, Fayad R, Fantuzzi G, Diamond AM (2008) Selenoprotein deficiency enhances radiation-induced micronuclei formation. Mol Nutr Food Res 52:1300–1304
Ferguson LR, Karunasinghe N, Zhu S, Wang AH (2012) Selenium and its role in the maintenance of genomic stability. Mutat Res 733:100–110
Bera S, De Rosa V, Rachidi W, Diamond AM (2013) Does a role for selenium in DNA damage repair explain apparent controversies in its use in chemoprevention? Mutagenesis 28:127–134
Weiss JF, Srinivasan V, Kumar KS, Landauer MR (1992) Radioprotection by metals: selenium. Adv Space Res 12:223–231
Diamond AM, Murray JL, Dale P, Tritz R, Grdina DJ (1995) The effects of selenium on glutathione peroxidase activity and radioprotection in mammalian cells. Radiat Oncol Investi 3:383–386
Flohe RB, Maiorino M (2013) Glutathione peroxidases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830:3289–3303
Bermingham EN, Hesketh JE, Sinclair BR, Koolaard JP, Roy NC (2014) Selenium-enriched foods are more effective at increasing glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activity compared with selenomethionine: a meta-analysis. Nutrients 6:4002–4031
Chittum HS, Hill KE, Carlson BA, Lee BJ, Burk RF, Hatfield DL (1997) Replenishment of selenium deficient rats with selenium results in redistribution of the selenocysteine tRNA population in a tissue specific manner. Biochim Biophys Acta 1359:25–34
Burk RF, Hill KE (2009) Selenoprotein P—expression, functions, and roles in mammals. Biochim Biophys Acta 1790:1441–1447
Eckers JC, Kalen AL, Xiao W, Sarsour EH, Goswami PC (2013) Selenoprotein P inhibits radiation-induced late reactive oxygen species accumulation and normal cell injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 87:619–625
Acknowledgments
Miss Prachi Verma acknowledges the Homi Bhabha National Institute for financial assistance in the form of senior research fellowship. The authors also wish to thank Dr. (Smt) S. Suvarna and Mr. G. Kiran Kumar of the Analytical Chemistry Division, Chemistry Group, BARC, for providing help in the selenium estimation in the mice chow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, P., Kunwar, A. & Indira Priyadarsini, K. Effect of Low-Dose Selenium Supplementation on the Genotoxicity, Tissue Injury and Survival of Mice Exposed to Acute Whole-Body Irradiation. Biol Trace Elem Res 179, 130–139 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-0955-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-0955-9