Abstract
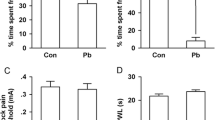
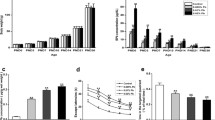
With the increasing applications of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) in industry and daily life, an increasing number of studies showed that TiO2 NPs may have negative effects on the respiratory or metabolic circle systems of organisms, while very few studies focused on the brain central nervous system (CNS). Synaptic plasticity in hippocampus is believed to be associated with certain high functions of CNS, such as learning and memory. Thus, in this study, we investigated the effects of developmental exposure to TiO2 NPs on synaptic plasticity in rats’ hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG) area using in vivo electrophysiological recordings. The input/output (I/O) functions, paired-pulse reaction (PPR), field excitatory postsynaptic potential, and population spike amplitude were measured. The results showed that the I/O functions, PPR, and long-term potentiation were all attenuated in lactation TiO2 NPs-exposed offspring rats compared with those in the control group. However, in the pregnancy TiO2 NPs exposure group, only PPR was attenuated significantly. These findings suggest that developmental exposure to TiO2 NPs could affect synaptic plasticity in offspring’s hippocampal DG area in vivo, which indicates that developmental brains, especially in lactation, are susceptible to TiO2 NPs exposure. This study reveals the potential toxicity of TiO2 NPs in CNS. It may give some hints on the security of TiO2 NPs production and application and shed light on its future toxicological studies.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oberdörster G, Maynard A, Donaldson K, Castranova V, Fitzpatrick J, Ausman K, Carter J, Karn B, Kreyling W, Lai D, Olin S, Monteiro-Riviere N, Warheit D, Yang H (2005) Principles for characterizing the potential human health effects from exposure to nanomaterials: elements of a screening strategy. Part Fibre Toxicol 2:8
Oberdörster G, Oberdörster E, Oberdörster J (2005) Nanotoxicology: an emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ Health Perspect 113:823–839
Colvin VL (2003) The potential environmental impact of engineered nanomaterials. Nat Biotechnol 21:1166–1170
Hoet PHM, Nemmar A, Nemery B (2004) Health impact of nanomaterials? Nat Biotechnol 22:19
Grassian VH, O’Shaughnessy PT, Adamcakova-Dodd A, Pettibone JM, Thorne PS (2007) Inhalation exposure study of titanium dioxide nanoparticles with a primary particle size of 2 to 5 nm. Environ Health Persp 115:397–402
Wang JX, Zhou GQ, Chen CY, Yu HW, Wang TC, Ma YM, Jia G, Gao YX, Li B, Sun J, Li YF, Jiao F, Zhao YL, Chai ZF (2007) Acute toxicity and biodistribution of different sized titanium dioxide particles in mice after oral administration. Toxicol Lett 168:176–185
Fabian E, Landsiedel R, Ma-Hock L, Wiench K, Wohlleben W, van Ravenzwaay B (2008) Tissue distribution and toxicity of intravenously administered titanium dioxide nanoparticles in rats. Arch Toxicol 82:151–157
Wang J, Zheng L, Wang S, Wang Y, Zhao X, Duan Y, Cui Y, Zhou M, Cai J, Gong S, Wang H, Hong F (2010) P38-Nrf-2 signaling pathway of oxidative stress in mice caused by nanoparticulate TiO2. Biol Trace Elem Res. doi:10.1007/s12011-010-8663-8
Cui YL, Liu HT, Zhou M, Duan YM, Li N, Gong XL, Hu RP, Hong MM, Hong FS (2011) Signaling pathway of inflammatory responses in the mouse liver caused by TiO2 nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res A 96A:221–229
Shin JA, Lee EJ, Seo SM, Kim HS, Kang JL, Park EM (2010) Nanosized titanium dioxide enhanced inflammatory responses in the septic brain of mouse. Neuroscience 165:445–454
Li N, Ma LL, Wang J, Zheng L, Liu J, Duan YM, Liu HT, Zhao XY, Wang SS, Wang H, Hong FS, Xie YN (2010) Interaction between nano-anatase TiO2 and liver DNA from mice in vivo. Nanoscale Res Lett 5:108–115
Bhattacharya K, Davoren M, Boertz J, Schins RPF, Hoffmann E, Dopp E (2009) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and DNA-adduct formation but not DNA-breakage in human lung cells. Part Fibre Toxicol 6:17
Cui YL, Gong XL, Duan YM, Li N, Hu RP, Liu HT, Hong MM, Zhou M, Wang L, Wang H, Hong FS (2010) Hepatocyte apoptosis and its molecular mechanisms in mice caused by titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 183:874–880
Lai JCK, Lai MB, Jandhyam S, Dukhande VV, Bhushan A, Daniels CK, Leung SW (2008) Exposure to titanium dioxide and other metallic oxide nanoparticles induces cytotoxicity on human neural cells and fibroblasts. Int J Nanomed 3:533–545
Liu HT, Ma LL, Zhao JF, Liu J, Yan JY, Ruan J, Hong FS (2009) Biochemical toxicity of nano-anatase TiO2 particles in mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 129:170–180
Kim HW, Ahn EK, Jee BK, Yoon HK, Lee KH, Lim Y (2009) Nanoparticulate-induced toxicity and related mechanism in vitro and in vivo. J Nanopart Res 11:55–65
Trouiller B, Reliene R, Westbrook A, Solaimani P, Schiestl RH (2009) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce DNA damage and genetic instability in vivo in mice. Cancer Res 69:8784–8789
Ma LL, Zhao JF, Wang J, Liu J, Duan YM, Liu HT, Li N, Yan JY, Ruan J, Wang H, Hong FS (2009) The acute liver injury in mice caused by nano-anatase TiO2. Nanoscale Res Lett 4:1275–1285
Li N, Duan YM, Hong MM, Zheng L, Fei M, Zhao XY, Wang J, Cui YL, Liu HT, Cai JW, Gong SJ, Wang H, Hong FS (2010) Spleen injury and apoptotic pathway in mice caused by titanium dioxide nanoparticules. Toxicol Lett 195:161–168
Duan YM, Liu J, Ma LL, Li N, Liu HT, Wang J, Zheng L, Liu C, Wang XF, Zhao XY, Yan JY, Wang SS, Wang H, Zhang XG, Hong FS (2010) Toxicological characteristics of nanoparticulate anatase titanium dioxide in mice. Biomaterials 31:894–899
Long TC, Saleh N, Tilton RD, Lowry GV, Veronesi B (2006) Titanium dioxide (P25) produces reactive oxygen species in immortalized brain microglia (BV2): implications for nanoparticle neurotoxicity. Environ Sci Technol 40:4346–4352
Long TC, Tajuba J, Sama P, Saleh N, Swartz C, Parker J, Hester S, Lowry GV, Veronesi B (2007) Nanosize titanium dioxide stimulates reactive oxygen species in brain microglia and damages neurons in vitro. Environ Health Persp 115:1631–1637
Wang JX, Liu Y, Jiao F, Lao F, Li W, Gu YQ, Li YF, Ge CC, Zhou GQ, Li B, Zhao YL, Chai ZF, Chen CY (2008) Time-dependent translocation and potential impairment on central nervous system by intranasally instilled TiO2 nanoparticles. Toxicology 254:82–90
Wang JX, Chen CY, Liu Y, Jiao F, Li W, Lao F, Li YF, Li B, Ge CC, Zhou GQ, Gao YX, Zhao YL, Chai ZF (2008) Potential neurological lesion after nasal instillation of TiO2 nanoparticles in the anatase and rutile crystal phases. Toxicol Lett 183:72–80
Ma L, Liu J, Li N, Wang J, Duan Y, Yan J, Liu H, Wang H, Hong F (2010) Oxidative stress in the brain of mice caused by translocated nanoparticulate TiO2 delivered to the abdominal cavity. Biomaterials 31:99–105
Yang Z, Liu ZW, Allaker RP, Reip P, Oxford J, Ahmad Z, Ren G (2010) A review of nanoparticle functionality and toxicity on the central nervous system. J R Soc Interface 7:S411–S422
Shimizu M, Tainaka H, Oba T, Mizuo K, Umezawa M, Takeda K (2009) Maternal exposure to nanoparticulate titanium dioxide during the prenatal period alters gene expression related to brain development in the mouse. Part Fibre Toxicol 6:20
Takeda K, Suzuki KI, Ishihara A, Kubo-Irie M, Fujimoto R, Tabata M, Oshio S, Nihei Y, Ihara T, Sugamata M (2009) Nanoparticles transferred from pregnant mice to their offspring can damage the genital and cranial nerve systems. J Health Sci 55:95–102
Bliss TV, Collingridge GL (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361:31–39
Lynch MA (2004) Long-term potentiation and memory. Physiol Rev 84:87–136
AT JRM (1993) NMDA receptors have a dominant role in population spike-paired pulse facilitation in the dentate gyrus of urethane-anesthetized rats. Brain Res 604:273–282
Lynch MA (1998) Age-related impairment in long-term potentiation in hippocampus: a role for the cytokine, interleukin-1 beta? Prog Neurobiol 56:571–589
Hougaard KS, Jackson P, Jensen KA, Sloth JJ, Loschner K, Larsen EH, Birkedal RK, Vibenholt A, Boisen AMZ, Wallin H, Vogel U (2010) Effects of prenatal exposure to surface-coated nanosized titanium dioxide (UV-Titan). A study in mice. Part Fibre Toxicol 7:16
Hu R, Gong X, Duan Y, Li N, Che Y, Cui Y, Zhou M, Liu C, Wang H, Hong F (2010) Neurotoxicological effects and the impairment of spatial recognition memory in mice caused by exposure to TiO2 nanoparticles. Biomaterials 31:8043–8050
Serrano F, Klann E (2004) Reactive oxygen species and synaptic plasticity in the aging hippocampus. Ageing Res Rev 3:431–443
Lynch MA (2002) Interleukin-1 beta exerts a myriad of effects in the brain and in particular in the hippocampus: analysis of some of these actions. Vitam Horm 64:185–219
Kelly A, Lynch A, Vereker E, Nolan Y, Queenan P, Whittaker E, O’Neill LA, Lynch MA (2001) The anti-inflammatory cytokine, interleukin (IL)-10, blocks the inhibitory effect of IL-1 beta on long term potentiation. A role for JNK. J Biol Chem 276:45564–45572
Murray CA, Lynch MA (1998) Evidence that increased hippocampal expression of the cytokine interleukin-1 beta is a common trigger for age- and stress-induced impairments in long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 18:2974–2981
Cunningham AJ, Murray CA, O’Neill LA, Lynch MA, O’Connor JJ (1996) Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) and tumour necrosis factor (TNF) inhibit long-term potentiation in the rat dentate gyrus in vitro. Neurosci Lett 203:17–20
Altman J, Bayer SA (1990) Migration and distribution of two populations of hippocampal granule cell precursors during the perinatal and postnatal periods. J Comp Neurol 301:365–381
Taupin P (2007) The hippocampus: neurotransmission and plasticity in the nervous system. Nova, New York, 94
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (WK2070000002, 2070000004, and 2070000008), The National Nature Science Foundations of China (30630057, 30670554/30670662, and 31070936). We confirm that we have no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, X., Yin, S., Tang, M. et al. Effects of Developmental Exposure to TiO2 Nanoparticles on Synaptic Plasticity in Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus Area: an In Vivo Study in Anesthetized Rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 143, 1616–1628 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-8990-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-8990-4