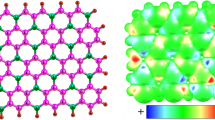
Abstract
Because nanomaterials are highly reactive and electronically sensitive towards a variety of drug molecules, they are thought of as efficient drug sensors. In the present research study, an aluminum carbide (C3Al) monolayer is employed and its interaction is examined with cyclophosphamide (CP) by performing DFT computations. The C3Al monolayer is highly reactive and sensitive towards CP according to the computations. CP interacts with the C3Al monolayer with the adsorption energy of −31.39 kcal/mol. A considerable charge transfer (CT) indicates an enhancement in the conductivity. Also, the charge density is explained based on the electron density differences (EDD). The decrease in CP/C3Al energy gap (Eg) by approximately 52.91% is due to the remarkable effect of adsorption on the LUMO and the HOMO levels. Therefore, due to the decrease in Eg which can generate an electrical signal, the electrical conductivity is considerably increased. These results suggest that the C3Al monolayer can be employed as a proper electronic drug sensor for CP. Also, the recovery time for the desorption process of CP form the surface of C3Al is 351 s at 598 K.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Confirmed.
References
Bray, F., Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Siegel, R. L., Torre, L. A., & Jemal, A. (2018). Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. C Ca: A Cancer Journal For Clinicians, 68, 394–424.
Arruebo, M., Vilaboa, N., Sáez-Gutierrez, B., Lambea, J., Tres, A., Valladares, M., et al. (2011). Assessment of the evolution of cancer treatment therapies. Cancers (Basel), 3, 3279–3330.
Queirós, V., Azeiteiro, U. M., Soares, A. M., & Freitas, R. (2021). The antineoplastic drugs cyclophosphamide and cisplatin in the aquatic environment–Review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 412, 125028.
Gómez-Canela, C., Santos, M. S., Franquet-Griell, H., Alves, A., Ventura, F., & Lacorte, S. (2020). Predicted environmental concentrations: A useful tool to evaluate the presence of cytostatics in surface waters. Fate and Effects of Anticancer Drugs in the Environment (pp. 27–54). Springer.
Grisolia, C. K. (2002). A comparison between mouse and fish micronucleus test using cyclophosphamide, mitomycin C and various pesticides. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 518, 145–150.
Chorvatovičová, D., Machová, E., & Šandula, J. (1996). Effect of ultrasonicated carboxymethylglucan on cyclophosphamide induced mutagenicity. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology, 371, 115–120.
Zhang, L., Hu, Z., Huang, J., Chen, Z., Li, X., Feng, Z., et al. (2022). Experimental and DFT studies of flower-like Ni-doped Mo2C on carbon fiber paper: A highly efficient and robust HER electrocatalyst modulated by Ni (NO3) 2 concentration. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 11, 1294–1306.
Sun, X., Li, J., Sun, X., Zheng, J., Wu, Z., Liu, W., et al. (2021). Efficient stabilization of arsenic in the arsenic-bearing lime-ferrate sludge by zero valent iron-enhanced hydrothermal treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 421, 129683.
Lin, H. H. H., & Lin, A. Y. C. (2014). Photocatalytic oxidation of 5-fluorouracil and cyclophosphamide via UV/TiO2 in an aqueous environment. Water research, 48, 559–568.
Isidori, M., Lavorgna, M., Russo, C., Kundi, M., Žegura, B., Novak, M., et al. (2016). Chemical and toxicological characterisation of anticancer drugs in hospital and municipal wastewaters from Slovenia and Spain. Environmental Pollution, 219, 275–287.
Lai, W. F., & Wong, W. T. (2021). Property-tuneable microgels fabricated by using flow-focusing microfluidic geometry for bioactive agent delivery. Pharmaceutics, 13, 787.
Yang, M., Li, C., Zhang, Y., Jia, D., Zhang, X., Hou, Y., et al. (2017). Maximum undeformed equivalent chip thickness for ductile-brittle transition of zirconia ceramics under different lubrication conditions. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 122, 55–65.
Grung, M., Källqvist, T., Sakshaug, S., Skurtveit, S., & Thomas, K. V. (2008). Environmental assessment of norwegian priority pharmaceuticals based on the EMEA guideline. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 71, 328–340.
Durán-Alvarez, J. C., Becerril-Bravo, E., Castro, V. S., Jiménez, B., & Gibson, R. (2009). The analysis of a group of acidic pharmaceuticals, carbamazepine, and potential endocrine disrupting compounds in wastewater irrigated soils by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Talanta, 78, 1159–1166.
Mcdowell, D. C., Huber, M. M., Wagner, M., Von Gunten, U., & Ternes, T. A. (2005). Ozonation of carbamazepine in drinking water: Identification and kinetic study of major oxidation products (39 vol., pp. 8014–8022). Environmental Science & Technology.
Thelusmond, J. R., Strathmann, T. J., & Cupples, A. M. (2016). The identification of carbamazepine biodegrading phylotypes and phylotypes sensitive to carbamazepine exposure in two soil microbial communities. Science of the Total Environment, 571, 1241–1252.
Onmaz, D. E., Abusoglu, S., Ozturk, B., Abusoglu, G., Yerlikaya, F. H., & Unlu, A. (2021). Determination of serum carbamazepine and its metabolite by validated tandem mass spectrometric method and the effect of carbamazepine on various hematological and biochemical parameters. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 205, 114299.
Pargolghasemi, P., Hoseininezhad-Namin, S., & Jadid, M. P. (2017). Prediction of activities of BRAF (V600E) inhibitors by SW-MLR and GA-MLR methods. Current Computer-Aided Drug Design, 13, 249–261.
Trojanowicz, M. (2002). Determination of pesticides using electrochemical enzymatic biosensors. Electroanalysis: An International Journal Devoted to Fundamental and Practical Aspects of Electroanalysis, 14, 1311–1328.
Potyrailo, R. A. (2006). Polymeric sensor materials: Toward an alliance of combinatorial and rational design tools? Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 45, 702–723.
Rad, A. S. (2018). Comparison of X 1 2 Y 1 2 (X = Al, B and Y = N, P) fullerene-like nanoclusters toward adsorption of dimethyl ether. Journal of Theoretical and Computational Chemistry, 17, 1850013.
Shokuhi Rad, A., Zareyee, D., Pouralijan Foukolaei, V., Moghadas, K., & Peyravi, B. (2016). Study on the electronic structure of Al12N12 and Al12P12 fullerene-like nano-clusters upon adsorption of CH3F and CH3Cl. Molecular Physics, 114, 3143–3149.
Peyghan, A. A., Rastegar, S. F., & Hadipour, N. L. (2014). DFT study of NH3 adsorption on pristine, Ni-and Si-doped graphynes. Physics Letters A, 378, 2184–2190.
Abbaspour-Gilandeh, E., Aghaei-Hashjin, M., Jahanshahi, P., & Hoseininezhad-Namin, M. S. (2017). One-pot synthesis of pyrano [3, 2-c] quinoline-2, 5-dione derivatives by Fe3O4@ SiO2-SO3H as an efficient and reusable solid acid catalyst. Monatshefte für Chemie-Chemical Monthly, 148, 731–738.
Rad, A. S., Aghaei, S. M., Aali, E., & Peyravi, M. (2017). Study on the electronic structure of Cr-and Ni-doped fullerenes upon adsorption of adenine: A comprehensive DFT calculation. Diamond and Related Materials, 77, 116–121.
Wu, H., Zhang, F., & Zhang, Z. (2021). Droplet breakup and coalescence of an internal-mixing twin-fluid spray. Physics of Fluids, 33, 013317.
Li, B., Li, C., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Jia, D., Yang, M., et al. (2017). Heat transfer performance of MQL grinding with different nanofluids for Ni-based alloys using vegetable oil. Journal of Cleaner Production, 154, 1–11.
Perego, P., Giarola, M., Righetti, S. C., Supino, R., Caserini, C., Delia, D., et al. (1996). Association between cisplatin resistance and mutation of p53 gene and reduced bax expression in ovarian carcinoma cell systems. Cancer research, 56, 556–562.
Molina, M., Asadian-Birjand, M., Balach, J., Bergueiro, J., & Miceli, E. (2015). Calderón, M. Stimuli-responsive nanogel composites and their application in nanomedicine. Chemical Society Reviews, 44, 6161–6186.
Singh, B., Khurana, R. K., Garg, B., Saini, S., & Kaur, R. (2017). Stimuli-responsive systems with diverse drug delivery and biomedical applications: Recent updates and mechanistic pathways. Critical Reviews™ in Therapeutic Drug Carrier Systems, 34.
Li, B., Li, C., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Jia, D., & Yang, M. (2016). Grinding temperature and energy ratio coefficient in MQL grinding of high-temperature nickel-base alloy by using different vegetable oils as base oil. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 29, 1084–1095.
Li, H., Zhang, Y., Li, C., Zhou, Z., Nie, X., Chen, Y., et al. (2022). Extreme pressure and antiwear additives for lubricant: Academic insights and perspectives. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 120, 1–27.
Wang, X., Li, C., Zhang, Y., Said, Z., Debnath, S., Sharma, S., et al. (2022). Influence of texture shape and arrangement on nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication turning. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 119, 631–646.
Liu, Y., Shivananju, B. N., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Yu, W., Xiao, S., et al. (2017). Highly efficient and air-stable infrared photodetector based on 2D layered graphene–black phosphorus heterostructure. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 9, 36137–36145.
Li, R., Du, Z., Qian, X., Li, Y., Martinez-Camarillo, J. C., Jiang, L., et al. (2021). High resolution optical coherence elastography of retina under prosthetic electrode. Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery, 11, 918–927.
Kim, K. S., Zhao, Y., Jang, H., Lee, S. Y., Kim, J. M., Kim, K. S., et al. (2009). Large-scale pattern growth of graphene films for stretchable transparent electrodes. nature, 457, 706–710.
Ahn, J. H., & Hong, B. H. (2014). Graphene for displays that bend. Nature nanotechnology, 9, 737–738.
Cui, X., Li, C., Zhang, Y., Ding, W., An, Q., Liu, B., et al. (2022). A comparative assessment of force, temperature and wheel wear in sustainable grinding aerospace alloy using bio-lubricant. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering.
Duan, Z., Li, C., Zhang, Y., Yang, M., Gao, T., Liu, X., et al. (2022). Mechanical behavior and semiempirical force model of aerospace aluminum alloy milling using nano biological lubricant. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering.
Yang, Y., Gong, Y., Li, C., Wen, X., & Sun, J. (2021). Mechanical performance of 316 L stainless steel by hybrid directed energy deposition and thermal milling process. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 291, 117023.
Large, M. J., Ogilvie, S. P., King, A. A., & Dalton, A. B. (2017). Understanding solvent spreading for Langmuir deposition of nanomaterial films: A Hansen solubility parameter approach. Langmuir, 33, 14766–14771.
Hosseini, M. R., Esfandiarpour, R., Taghipour, S., & Badalkhani-Khamseh, F. (2020). Theoretical study on the Al-doped biphenylene nanosheets as NO sensors. Chemical Physics Letters, 754, 137712.
Shivananju, B., Hoh, H. Y., Yu, W., & Bao, Q. (2019). Optical biochemical sensors based on 2D materials. Fundamentals and sensing applications of 2D materials (pp. 379–406). Elsevier.
Choi, C., Choi, M. K., Liu, S., Kim, M. S., Park, O. K., Im, C., et al. (2017). Human eye-inspired soft optoelectronic device using high-density MoS2-graphene curved image sensor array. Nature Communications, 8, 1–11.
Lu, S., Yin, Z., Liao, S., Yang, B., Liu, S., Liu, M., et al. (2022). An asymmetric encoder–decoder model for Zn-ion battery lifetime prediction. Energy Reports, 8, 33–50.
Cai, K., Jing, X., Zhang, Y., Li, L., & Lang, X. (2022). A novel reed-leaves like aluminum-doped manganese oxide presetting sodium-ion constructed by coprecipitation method for high electrochemical performance sodium-ion battery. International Journal of Energy Research, 46, 14570–14580.
Xiao, X., Mu, B., Cao, G., Yang, Y., & Wang, M. (2022). Flexible battery-free wireless electronic system for food monitoring. Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices, 7, 100430.
Li, L., Zhang, D., Deng, J., Gou, Y., Fang, J., Cui, H., et al. (2021). Carbon-based materials for fast charging lithium-ion batteries. Carbon, 183, 721–734.
Li, J., Wan, C., Wang, C., Zhang, H., & Chen (2020). X. 2D material chemistry: Graphdiyne-based biochemical sensing. Chemical Research in Chinese Universities, 36, 622–630.
Liu, X., Liu, J., Yang, H., Huang, B., & Zeng, G. (2022). Design of a high-performance graphene/SiO 2-Ag periodic grating/MoS 2 surface plasmon resonance sensor. Applied Optics, 61, 6752–6760.
Chen, W., Ouyang, J., Liu, H., Chen, M., Zeng, K., Sheng, J., et al. (2017). Black phosphorus nanosheet-based drug delivery system for synergistic photodynamic/photothermal/chemotherapy of cancer. Advanced Materials, 29, 1603864.
Rajaji, U., Ganesh, P. S., Kim, S. Y., Govindasamy, M., Alshgari, R. A., & Liu, T. Y. (2022). MoS2 sphere/2D S-Ti3C2 MXene nanocatalysts on laser-induced graphene electrodes for hazardous aristolochic acid and Roxarsone electrochemical detection. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 5, 3252–3264.
Rajaji, U., Govindasamy, M., Sha, R., Alshgari, R. A., Juang, R. S., & Liu, T. Y. (2022). Surface engineering of 3D spinel Zn3V2O8 wrapped on sulfur doped graphitic nitride composites: Investigation on the dual role of electrocatalyst for simultaneous detection of antibiotic drugs in biological fluids. Composites Part B: Engineering, 242, 110017.
Wang, J. (2005). Nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors. The Analyst, 130, 421–426.
Song, S., Shen, H., Wang, Y., Chu, X., Xie, J., Zhou, N., et al. (2020). Biomedical application of graphene: From drug delivery, tumor therapy, to theranostics. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 185, 110596.
Govindasamy, M., Wang, S. F., Almahri, A., & Rajaji, U. (2021). Effects of sonochemical approach and induced contraction of core–shell bismuth sulfide/graphitic carbon nitride as an efficient electrode materials for electrocatalytic detection of antibiotic drug in foodstuffs. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 72, 105445.
Govindasamy, M., Wang, S. F., Jothiramalingam, R., Noora Ibrahim, S., & Al-lohedan, H. A. (2019). A screen-printed electrode modified with tungsten disulfide nanosheets for nanomolar detection of the arsenic drug roxarsone. Microchimica Acta, 186, 420.
Vinoth, S., Govindasamy, M., Wang, S. F., Alothman, A. A., & Alshgari, R. A. (2021). Hydrothermally synthesized cubical zinc manganite nanostructure for electrocatalytic detection of sulfadiazine. Microchimica Acta, 188, 131.
Yang, Y., Yang, M., Li, C., Li, R., Said, Z., Ali, H. M., et al. (2022). Machinability of ultrasonic vibration assisted micro-grinding in biological bone using nanolubricant. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering.
Reina, G., González-Domínguez, J. M., Criado, A., Vázquez, E., Bianco, A., & Prato, M. (2017). Promises, facts and challenges for graphene in biomedical applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 46, 4400–4416.
Yourdkhani, S., Korona, T., & Hadipour, N. L. (2015). Structure and energetics of complexes of B12N12 with Hydrogen Halides SAPT (DFT) and MP2 study. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 119, 6446–6467.
Karjabad, K. D., Mohajeri, S., Shamel, A., Khodadadi-Moghaddam, M., & Rajaei, G. E. (2020). Boron nitride nanoclusters as a sensor for cyclosarin nerve agent: DFT and thermodynamics studies. SN Applied Sciences, 2, 1–8.
Liu, W., Chen, G., Huang, X., & Wu, D. (2012). Yu, Y.-p. DFT studies on the interaction of an open-ended single-walled aluminum nitride nanotube (AlNNT) with gas molecules. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 116, 4957–4964.
Ma, Y., Huo, K., Wu, Q., Lu, Y., Hu, Y., Hu, Z., et al. (2006). Self-templated synthesis of polycrystalline hollow aluminium nitride nanospheres. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 16, 2834–2838.
Wang, J., Ai, K., & Lu, L. (2019). Flame-retardant porous hexagonal boron nitride for safe and effective radioactive iodine capture. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 7, 16850–16858.
Wang, M., Jiang, C., Zhang, S., Song, X., Tang, Y., & Cheng, H. M. (2018). Reversible calcium alloying enables a practical room-temperature rechargeable calcium-ion battery with a high discharge voltage. Nature Chemistry, 10, 667–672.
Tong, X., Zhang, F., Ji, B., Sheng, M., & Tang, Y. (2016). Carbon-coated porous aluminum foil anode for high‐rate, long‐term cycling stability, and high energy density dual‐ion batteries. Advanced Materials, 28, 9979–9985.
Zhang, J., Li, C., Zhang, Y., Yang, M., Jia, D., Liu, G., et al. (2018). Experimental assessment of an environmentally friendly grinding process using nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication with cryogenic air. Journal of Cleaner Production, 193, 236–248.
Dai, J., Yuan, J., & Giannozzi, P. (2009). Gas adsorption on graphene doped with B, N, Al, and S: A theoretical study. Applied Physics Letters, 95, 232105.
Ren, K., Sun, M., Luo, Y., Wang, S., Yu, J., & Tang, W. (2019). First-principle study of electronic and optical properties of two-dimensional materials-based heterostructures based on transition metal dichalcogenides and boron phosphide. Applied Surface Science, 476, 70–75.
Ao, Z., Yang, J., Li, S., & Jiang, Q. (2008). Enhancement of CO detection in Al doped graphene. Chemical Physics Letters, 461, 276–279.
Chi, M., & Zhao, Y. P. (2009). Adsorption of formaldehyde molecule on the intrinsic and Al-doped graphene: A first principle study. Computational Materials Science, 46, 1085–1090.
Serinçay, N., & Fellah, M. F. (2020). Acetaldehyde adsorption and detection: A density functional theory study on Al-doped graphene. Vacuum, 175, 109279.
Ao, Z., & Peeters, F. (2010). High-capacity hydrogen storage in Al-adsorbed graphene. Physical Review B, 81, 205406.
Shahabi, D., & Tavakol, H. (2018). A DFT study on the catalytic ability of aluminum doped graphene for the initial steps of the conversion of methanol to gasoline. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 1127, 8–15.
Zhang, X., Tang, Y., Zhang, F., & Lee, C. S. (2016). A novel aluminum–graphite dual-ion battery. Advanced Energy Materials, 6, 1502588.
Ji, B., Zhang, F., Song, X., & Tang, Y. (2017). A novel potassium-ion‐based dual‐ion battery. Advanced Materials, 29, 1700519.
Mu, S., Liu, Q., Kidkhunthod, P., Zhou, X., Wang, W., & Tang, Y. (2021). Molecular grafting towards high-fraction active nanodots implanted in N-doped carbon for sodium dual-ion batteries. National Science Review, 8, nwaa178.
Yang, M., Li, C., Zhang, Y., Jia, D., Li, R., Hou, Y., et al. (2019). Predictive model for minimum chip thickness and size effect in single diamond grain grinding of zirconia ceramics under different lubricating conditions. Ceramics International, 45, 14908–14920.
Goenka, S., Sant, V., & Sant, S. (2014). Graphene-based nanomaterials for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Journal of Controlled Release, 173, 75–88.
Molaei, M. J. (2021). Two-dimensional (2D) materials beyond graphene in cancer drug delivery, photothermal and photodynamic therapy, recent advances and challenges ahead: A review. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 61, 101830.
Li, Z., & Cheng, F. (2022). C3Al: A tunable bandgap semiconductor with high electron mobility and negative Poisson’s ratio. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 138, 115082.
Wang, J., Yang, Y., Liu, H., Dong, H., Ding, L., & Li, Y. (2022). Adsorption of metal atoms on two-dimensional BC3 and AlC3 nanosheets: Computational studies. Chemical Physics Letters, 792, 139403.
Bao, Q., Zhang, H., Ni, Z., Wang, Y., Polavarapu, L., Shen, Z., et al. (2011). Monolayer graphene as a saturable absorber in a mode-locked laser. Nano Research, 4, 297–307.
Huang, W., Xie, Z., Fan, T., Li, J., Wang, Y., Wu, L., et al. (2018). Black-phosphorus-analogue tin monosulfide: An emerging optoelectronic two-dimensional material for high-performance photodetection with improved stability under ambient/harsh conditions. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 6, 9582–9593.
Jiang, Y., Miao, L., Jiang, G., Chen, Y., Qi, X., Jiang, X., et al. (2015). Broadband and enhanced nonlinear optical response of MoS2/graphene nanocomposites for ultrafast photonics applications. Scientific Reports, 5, 1–12.
Huang, Z., Han, W., Tang, H., Ren, L., Chander, D. S., Qi, X., et al. (2015). Photoelectrochemical-type sunlight photodetector based on MoS2/graphene heterostructure. 2D Materials, 2, 035011.
Ahmadi Peyghan, A., Hadipour, N. L., & Bagheri, Z. (2013). Effects of Al doping and double-antisite defect on the adsorption of HCN on a BC2N nanotube: Density functional theory studies. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 117, 2427–2432.
Hossain, M. R., Hasan, M. M., Rahman, H., Rahman, M. S., Ahmed, F., Ferdous, T., et al. (2021). Adsorption behaviour of metronidazole drug molecule on the surface of hydrogenated graphene, boron nitride and boron carbide nanosheets in gaseous and aqueous medium: A comparative DFT and QTAIM insight. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 126, 114483.
Vatanparast, M., & Shariatinia, Z. (2018). AlN and AlP doped graphene quantum dots as novel drug delivery systems for 5-fluorouracil drug: Theoretical studies. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 211, 81–93.
Min Lee, J., & Lim, H. (2013). Thermally activated magnetization switching in a nanostructured synthetic ferrimagnet. Journal of Applied Physics, 113, 063914.
Yang, H., Wang, Z., Ye, H., Zhang, K., Chen, X., & Zhang, G. (2018). Promoting sensitivity and selectivity of HCHO sensor based on strained InP3 monolayer: A DFT study. Applied Surface Science, 459, 554–561.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M. M. Kadhim: Conceptualization, methodology, software, writing, conceptualization, methodology, management, and responsibility for the research activity planning and execution; A. M. Rheima, S. K. Hachim, S. A. H. Abdullaha: methodology, software, writing—review and editing; Z. T. Taban, S. A. Malik: writing—original draft, methodology, software, review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not required
Consent to Participate
Confirmed
Consent for Publication
Confirmed
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kadhim, M.M., Rheima, A.M., Hachim, S.K. et al. Theoretical Sensing Performance for Detection of Cyclophosphamide Drug by Using Aluminum Carbide (C3Al) Monolayer: a DFT Study. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 4164–4176 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04305-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04305-9