Abstract
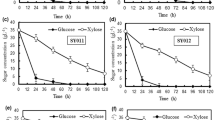
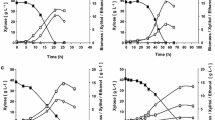
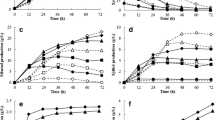
Efficient use of xylose along with glucose is necessary for the economic production of lignocellulosic based biofuels. Xylose transporters play an important role in the microorganisms for efficient utilization of xylose. In the present study, a novel method has been developed for a rapid assay of xylose transport activity in the xylose-utilizing isolates and other known yeasts. An assay was conducted to compare the activity of β-xylosidase using p-nitrophenyl-β-d-xylopyranoside (pNPX) in the intact, intracellular, and extracellular yeasts cells showing xylose transporter. Saccharomyces cerevisiae (MTCC 170) showed no xylosidase activity, while little growth was observed in the xylose-containing medium. Although other yeasts, i.e., Kluyveromyces marxianus NIRE-K1 (MTCC 5933), K. marxianus NIRE-K3 (MTCC 5934), and Candida tropicalis (MTCC 230), showed xylosidase activity in intact, intracellular, and extracellular culture. The xylosidase activity in intact cell was higher than that of extracellular and intracellular activity in all the yeast cells. The enzyme activity was higher in case of K. marxianus NIRE-K1 and K. marxianus NIRE-K3 rather than the C. tropicalis. Further, better xylosidase activity was observed in adapted K. marxianus cells which were 2.79–28.46 % higher than that of native (non-adapted) strains, which indicates the significant improvement in xylose transportation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behera, S., Mohanty, R. C., & Ray, R. C. (2011). Ethanol production from mahula (Madhuca latifolia L.) flowers with immobilized cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in Luffa cylindrica L. sponge discs. Appled Energy, 88, 212–215.
Arora, R., Behera, S., & Kumar, S. (2015). Bioprospecting thermophillic/thermotolerant microbes for production of lignocellulosic ethanol: a future perspective. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 51, 699–717.
Behera, S., Mohanty, R. C., & Ray, R. C. (2015). Batch ethanol production from cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz.) flour using Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells immobilized in calcium alginate. Annals of Microbiology, 65, 779–783.
Kumar, S., Singh, S. P., Mishra, I. M., & Adhikari, D. K. (2009). Recent advances in production of bioethanol from lignocellulosic biomass. Chemical Engineering and Technology, 32, 517–526.
Kumar, S., Singh, S. P., Mishra, I. M., & Adhikari, D. K. (2010). Feasibility of ethanol production with enhanced sugar concentration in bagasse hydrolysate at high temperature using Kluyveromyces sp. IIPE453. Biofuels, 1, 697–704.
Arora, R., Behera, S., Sharma, N. K., Singh, R., Yadav, Y. K., & Kumar, S. (2014). Biochemical conversion of rice straw (Oryza sativa L.) to bioethanol using thermotolerant isolate K. marxianus NIRE-K3. In N. R. Sharma, R. C. Thakur, M. Sharma, L. Parihar, & G. Kumar (Eds.), Exploring & basic sciences for next generation frontiers (pp. 143–146). New Delhi: Elsevier.
Behera, S., Arora, R., Nandhagopal, N., & Kumar, S. (2014). Importance of chemical pretreatment for bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 36, 91–106.
Behera, S., Arora, R., Sharma, N. K., & Kumar, S. (2014). Fermentation of glucose and xylose sugar for the production of ethanol and xylitol by the newly isolated NIRE-GX1 yeast. In S. Kumar, A. K. Sarma, S. K. Tyagi, & Y. K. Yadav (Eds.), Recent advances in bio-energy research (Vol. 3, pp. 175–182). SSS-NIRE: Kapurthala.
Kumar, S., Dheeran, P., Singh, S. P., Mishra, I. M., & Adhikari, D. K. (2015). Bioprocessing of bagasse hydrolysate for ethanol and xylitol production using thermotolerant yeast. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 38, 39–47.
Dien, B. S., Cotta, M. A., & Jeffries, T. W. (2003). Bacteria engineered for fuel ethanol production: current status. Appled Microbiology and Biotechnology, 63, 258–266.
Jeffries, T. W. (2006). Engineering yeasts for xylose metabolism. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 17, 320–326.
Katahira, S., Mizuike, A., Fukuda, H., & Kondo, A. (2006). Ethanol fermentation from lignocellulosic hydrolysate by a recombinant xylose- and cellooligosaccharides assimilating yeast strain. Appled Microbiology and Biotechnology, 72, 1136–1143.
Kumar, S., Singh, S. P., Mishra, I. M., & Adhikari, D. K. (2009). Ethanol and xylitol production from glucose and xylose at high temperature by Kluyveromyces sp. IIPE453. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 36, 1483–1489.
Runquist, D., Hahn-Hagerdal, B., & Radström, P. (2010). Comparison of heterologous xylose transporters in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 3, 1–7.
Bhalla, A., Bischoff, K. M., & Sani, R. K. (2014). Highly thermostable GH39 β-xylosidase from a Geobacillus sp. strain WSUCF1. BMC Biotechnology, 14, 1–10.
Lagaert, S., Pollet, A., Courtin, C. M., & Volckaert, G. (2014). β-xylosidases and α-L-arabinofuranosidases: accessory enzymes for arabinoxylan degradation. Biotechnology Advances, 32, 316–332.
Basaran, P., & Ozcan, M. (2008). Characterization of b-xylosidase enzyme from a Pichia stipitis mutant. Bioresource Technology, 99, 38–43.
Shi, H., Li, X., Gu, H., Zhang, Y., Huang, Y., Wang, L., & Wang, F. (2013). Biochemical properties of a novel thermostable and highly xylose-tolerant β-xylosidase/α-arabinosidase from Thermotoga thermarum. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 6, 1–10.
Bosetto, A., Justo, P. I., Zanardi, B., Venzon, S. P., Graciano, L., Santos, E. L., & Simao, R. C. G. (2016). Research project concerning fungal and bacterial β-xylosidases. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 178, 766–795.
Knob, A., Terrasan, C. R. F., & Carmona, E. C. (2010). β-Xylosidases from filamentous fungi: an overview. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 26, 389–407.
Thakur, I. S., & Nakagoshi, N. (2011). Production of biofuels from lignocellulosic biomass in pulp and paper mill effluents for low carbon society. Journal of International Development Cooperation, 18, 1–12.
Linden, T., & Hahn-Hagerdal, B. (1989). Fermentation of lignocelluloses hydrolysates with yeasts and xylose isomerase. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 11, 583–589.
Manzanares, P., Ramon, D., & Querol, A. (1999). Screening of non-Saccharomyces wine yeasts for the production of b-D-xylosidase activity. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 46, 105–112.
Shao, W., Xue, Y., Wu, A., Kataeva, I., Pei, J., Wu, H., & Wiegel, J. (2011). Characterization of a novel beta-xylosidase, XylC, from Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum JW/SL-YS485. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77, 719–726.
Anand, A., Kumar, V., & Satyanarayana, T. (2013). Characteristics of thermostable endoxylanase and β-xylosidase of the extremely thermophilic bacterium Geobacillus thermodenitrificans TSAA1 and its applicability in generating xylooligosaccharides and xylose from agro-residues. Extremophiles, 17, 357–366.
Huang, Z., Liu, X., Zhang, S., & Liu, Z. (2014). GH52 xylosidase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus: characterization and introduction of xylanase activity by site-directed mutagenesis of Tyr509. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 41, 65–74.
Leandro, M. J., Goncalves, P., & Spencer-Martins, I. (2006). Two glucose/xylose transporter genes from the yeast Candida intermedia: first molecular characterization of a yeast xylose-H+ symporter. Biochemical Journal, 395, 543–549.
Hector, R., Qureshi, N., Hughes, S., & Cotta, M. (2008). Expression of a heterologous xylose transporter in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain engineered to utilize xylose improves aerobic xylose consumption. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 80, 675–684.
Runquist, D., Fonseca, C., Radstrom, P., Spencer-Martins, I., & Hahn-Hagerdal, B. (2009). Expression of the Gxf1 transporter from Candida intermedia improves fermentation performance in recombinant xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 82, 123–130.
Chen, T., Zhang, J., Liang, L., Yang, R., & Lin, Z. (2009). An in vivo, label-free quick assay for xylose transport in Escherichia coli. Analytical Biochemistry, 390, 63–67.
Wang, C., Shen, Y., Hou, J., Suo, F., & Bao, X. (2013). An assay for functional xylose transporters in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Analytical Biochemistry, 442, 241–248.
Ren, C., Chen, T., Zhang, J., Liang, L., & Lin, Z. (2009). An evolved xylose transporter from Zymomonas mobilis enhances sugar transport in Escherichia coli. Microbal Cell Factories, 8, 1–9.
Lee, W. J., Kim, M. D., Ryu, Y. W., Bisson, L. F., & Seo, J. H. (2002). Kinetic studies on glucose and xylose transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 60, 186–191.
Stambuk, B. U., Franden, M. A., Singh, A., & Zhang, M. (2003). D-Xylose transport by Candida succiphila and Kluyveromyces marxianus. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 106, 255–265.
Arora, R., Behera, S., Sharma, N. K., & Kumar, S. (2015). A new search for thermotolerant yeasts, its characterization and optimization using response surface methodology for ethanol production. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6, 1–16.
Kumar, S. (2009). Bioethanol production from biomass. Ph.D thesis, IIT Roorkee .
Arora, R., Behera, S., & Kumar, S. (2014). Comparative study of fermentation efficiency for bio-ethanol production by isolates. In S. Kumar, A. K. Sarma, S. K. Tyagi, & Y. K. Yadav (Eds.), Recent advances in bio-energy research (pp. 149–155). Kapurthala: SSS-NIRE, III.
Young, E., Lee, S. M., & Alper, H. (2010). Optimizing pentose utilization in yeast: the need for novel tools and approaches. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 3, 1–12.
Subtil, T., & Boles, E. (2012). Competition between pentoses and glucose during uptake and catabolism in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 5, 1–12.
Lasrado, L. D., & Gudipati, M. (2013). Purification and characterization of β-D-xylosidase from Lactobacillus brevis grown on xylo-oligosaccharides. Carbohydrate Polymers, 92, 1978–1983.
Kuhad, R. C., Gupta, R., Khasa, Y. P., Singh, A., & Zhang, Y. H. P. (2011). Bioethanol production from pentose sugars: current status and future prospects. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Review, 15, 4950–4962.
Smith, J., Van Rensburg, E., & Gorgens, J. F. (2014). Simultaneously improving xylose fermentation and tolerance to lignocellulosic inhibitors through evolutionary engineering of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae harbouring xylose isomerase. BMC Biotechnology, 15, 14–41.
Vilela, L. F., De Araujo, V. P., Paredes, R. S., Bon, E. P., Torres, F. A., Neves, B. C., & Eleutherio, E. C. (2015). Enhanced xylose fermentation and ethanol production by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. AMB Express, 26, 5–16.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, Govt. of India for providing funds to carry out the research activities. We thank Prof. Y. K. Yadav, Director General, SSS-NIBE, Kapurthala, India for his valuable suggestions and encouragement for the completion of this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Behera, S., Sharma, N.K., Arora, R. et al. Effect of Evolutionary Adaption on Xylosidase Activity in Thermotolerant Yeast Isolates Kluyveromyces marxianus NIRE-K1 and NIRE-K3. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 179, 1143–1154 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2055-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2055-2