Abstract
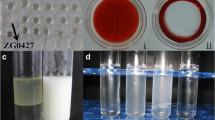
The indigenous microbial community utilizing aliphatic, aromatic, and polar components from the oily sludge as sole source of carbon and energy was selected from the soil samples of Ankleshwar, India for biosurfactant production. Evaluation of biosurfactant production was done using screening assays such as surface tension reduction, hemolytic activity, emulsification activity, drop-collapse assay, and cell surface hydrophobicity studies. Maximum biosurfactant (6.9 g/l) production was achieved after 5 days of growth from Bacillus subtilis DSVP23 which was identified by 16S RNA technique (NCBI GenBank accession no. EU679368). Composition of biosurfactant showed it to be lipopeptide in nature with 15.2% protein content and 18.0% lipid content. Functional group analysis was also done by using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy which showed it to be a protein-bound lipid thereby imparting them special properties. Analysis by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometric and nuclear magnetic resonance revealed that the major constituents of lipopeptide are leucine and isoleucine. Gas chromatographic analysis data indicated that oily sludge components of chain length C12–C30 and aromatic hydrocarbons were degraded effectively by B. subtilis DSVP23 after 5 days of incubation. These results collectively points toward the importance of B. subtilis DSVP23 as a potential candidate for bioremediation studies.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abouseouda, M., Maachi, R., Amranec, A., Boudergua, S., & Nabia, A. (2008). Desalination, 223, 143–151.
Das, K., & Mukherjee, A. K. (2007). Process Biochemistry, 42, 1191–1199.
Cunha, C. D., Rosario, M., Rosado, A. S., & Leite, S. G. F. (2004). Process Biochemistry, 39, 2277–2282.
Desai, J. D., & Banat, I. M. (1997). Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 61, 47–64.
Joshi, S. J., & Desai, A. J. (2010). Advances in experimental medicine and biology. In R. Sen (Ed.), Biosurfactants (Vol. 672, p. 222). New York: Springer.
Lima, A. S., & Alegre, R. M. (2009). Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology, 52, 285–290.
Rocha, C. A., Pedregosa, A. M., & Laborda, F. (2011). AMB Express, 1, 9.
Das, K., & Mukherjee, A. K. (2007). Bioresource Technology, 98, 1339–1345.
Abalos, A., Vinas, M., & Sabate, J. (2004). Biodegradation, 15, 249–260.
Cubitto, M. A., Moran, A. C., Commendatore, M., Chiarello, M. N., Baldini, M. D., & Sineriz, F. (2004). Biodegradation, 15, 281–287.
Pruthi, V., & Cameotra, S. S. (2003). Journal of Surfactants and Detergents, 6, S12971–S12974.
Lal, B., & Khanna, S. (1996). Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 81, 355–362.
Dhote, M., Juwarkar, A., Kumar, A., Kanade, G. S., & Chakrabarti, T. (2010). World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 26, 329–335.
Bodour, A. A., & Miller-Maier, M. R. (1998). Journal of Microbiological Methods, 32, 273–280.
Noudeh, G. D., Noodeh, A. D., Moshafi, M. H., Behravan, E., Afzadi, M. A., & Sodagar, M. (2010). African Journal of Microbiology Research, 4, 1814–1822.
Pruthi, V., & Cameotra, S. S. (1997). Biotechnology Techniques, 11, 671–674.
Rosenberg, M., Gutnick, D., & Rosenberg, E. (1980). FEMS Microbiology Letters, 9, 29–33.
Sneath, P. H. A., Mair, N. S., & Sharpe, M. E. (1986). Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology (Vol. 2, pp. 999–1436). Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins.
De Clerck, E., Rodrıguez-Dıaz, M., Vanhoutte, T., Heyrman, J., Logan, N. A., & De Vos, P. (2004). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 54, 941–946.
Pitcher, D. G., Saunders, N. A., & Owen, R. J. (1989). Letters in Applied Microbiology, 8, 151–156.
Kumar, S., Tamura, K., & Nei, M. (2004). Brief Bioinformatics, 5, 150–163.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrought, N. J., Farr, A., & Randall, R. J. (1951). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 139, 265–274.
Okoh, A. I., & Trejo-Hernandez, M. R. (2006). African Journal of Biotechnology, 5, 2520–2525.
Emtiazi, G., & Shakarami, H. (2004). African Journal of Biotechnology, 4, 172–176.
Kasai, Y., Kishira, H., Sasaki, T., Syutsubo, K., Watanabe, K., & Harayama, S. (2002). Environmental Microbiology, 4, 141–147.
Okerentugba, P., & Ezeronye, O. (2003). African Journal of Biotechnology, 2, 288–292.
Batista, S. B., Mounteer, A. H., Amorim, F. R., & Tótola, M. R. (2006). Bioresource Technology, 97, 868–875.
Bodour, A. A., Guerrero-Barajas, C., Jiorle, B. V., Malcomson, M. E., Paull, A. K., Somogyi, A., Trinh, L. N., Bates, R. B., & Maier, R. M. (2004). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 114–120.
Youssef, N., Duncan, K., & Nagle, D. (2004). Journal of Microbiological Methods, 56, 339–347.
Ouoba, L. I., Thorsen, L., & Varnham, A. H. (2008). International Journal of Food Microbiology, 124, 224–230.
Yakimov, M. M., Timmis, K. N., Wray, V., & Fredrickson, H. L. (1995). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 61, 1706–1713.
Nitschke, M., & Pastore, G. (2003). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 108, 295–301.
Vater, J., Kablitz, B., Wilde, C., Franke, P., Mehta, N., & Cameotra, S. S. (2002). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 6210–6219.
Makkar, R. S., & Cameotra, S. S. (1999). Journal of Surfactants and Detergents, 2, 237–241.
Joshi, S., Bharucha, C., Jha, S., Yadav, S., Nerurkar, A., & Desai, A. J. (2008). Bioresource Technology, 99, 195–199.
Makkar, R. S., & Cameotra, S. S. (1997). Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 18, 37–42.
Mahanty, B., Pakshirajan, K., & Dasu, V. V. (2006). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 134, 129–141.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pemmaraju, S.C., Sharma, D., Singh, N. et al. Production of Microbial Surfactants from Oily Sludge-Contaminated Soil by Bacillus subtilis DSVP23. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167, 1119–1131 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9613-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9613-z