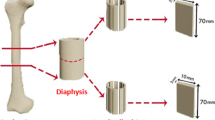
Abstract
Gamma radiation is widely used to sterilize bone allografts but may impair their strength. While radioprotectant use may reduce radiation damage they may compromise sterility by protecting pathogens. We assessed the radioprotective potential of various agents (L-cysteine, N-acetyl-L-cysteine, L-cysteine-ethyl-ester and L-cysteine-methyl-ester) to identify those which do not protect spores of Bacillus subtilis. We hypothesized charge of these agents will affect their ability to radioprotect spores. We also determined ability of these radioprotectants and a radiosensitizer (nitroimidazole-linked phenanthridinium) to selectively sensitize spores to radiation damage by intercalating into the nucleic acid of spores. Spores were treated either directly in solutions of these agents or treated after being embedded and sealed in bone to assess the ability of these agents to diffuse into bone. L-cysteine and L-cysteine-ethyl-ester did not provide radioprotection. Positively charged L-cysteine-methyl-ester protected the spores, whereas positively charged L-cysteine-ethyl-ester did not, indicating charge does not determine the extent of radioprotection. The spores were sensitized to radiation damage when irradiated in nitroimidazole-linked phenanthridinium solution and sensitization disappeared after rinsing, suggesting nitroimidazole-linked phenanthridinium was unable to intercalate into the nucleic acid of the spores. Some cysteine-derived radioprotectants do not shield bacterial spores against gamma radiation and may be suitable for curbing the radiation damage to bone grafts while achieving sterility.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
AAMI Technical Information Report. AAMI TIR33:2005 – Sterilization of Health Care Products - Radiation - Substantiation of a Selected Sterilization Dose - Method VDmax. Arlington, VA: Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation; 2006.
Akkus O, Belaney RM. Sterilization by gamma radiation impairs the tensile fatigue life of cortical bone by two orders of magnitude. J Orthop Res. 2005;23:1054–1058.
Akkus O, Belaney RM, Das P. Free radical scavenging alleviates the biomechanical impairment of gamma radiation sterilized bone tissue. J Orthop Res. 2005;23:838–845.
Akkus O, Rimnac CM. Fracture resistance of gamma radiation sterilized cortical bone allografts. J Orthop Res. 2001;19:927–934.
Anderson MJ, Keyak JH, Skinner HB. Compressive mechanical properties of human cancellous bone after gamma irradiation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74:747–752.
Asselmeier MA, Caspari RB, Bottenfield S. A review of allograft processing and sterilization techniques and their role in transmission of the human immunodeficiency virus. Am J Sports Med. 1993;21:170–175.
Braams R. Rate constants of hydrated electron reactions with amino acids. Radiat Res. 1966;27:319–329.
Bright RW, Burchardt H. The biomechanical properties of preserved bone grafts. In: Friedlander GE, Mankin HJ, Sell KW, eds. Osteochondral Allografts: Biology, Banking and Clinical Applications. Boston, MA: Little, Brown; 1984:241–247.
Bright RW, Smarsh JD, Gambill VM. Sterilization of human bone by irradiation. In: Friedlander GE, Mankin HJ, Sell KW, eds. Osteochondral Allografts: Biology, Banking and Clinical Applications. Boston, MA: Little, Brown; 1984:223–232.
Buck BE, Resnick L, Shah SM, Malinin TI. Human immunodeficiency virus cultured from bone. Implications for transplantation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;251:249–253.
Campbell DG, Li P, Stephenson AJ, Oakeshott RD. Sterilization of HIV by gamma irradiation. A bone allograft model. Int Orthop. 1994;18:172–176.
CDC: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hepatitis C virus transmission from an antibody-negative organ and tissue donor- United States, 2000–2002. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2003;52:273–276.
CDC: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Invasive streptococcus pyogenes after allograft implantation-Colorado, 2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2003;52:1173–1176.
CDC: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Septic arthritis following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using tendon allografts — Florida and Louisiana, 2000. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2001;50:1081–1083.
CDC: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Transmission of HIV through bone transplantation: case report and public health recommendations. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1988;37:597–599.
CDC: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Unexplained deaths following knee surgery - Minnesota, 2001. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2001;50:1080.
CDC: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Update: allograft associated bacterial infections-United States 2002. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2002;51:207–210.
Chan P, Milosevic M, Fyles A, Carson J, Pintilie M, Rauth M, Thomas G. A phase III randomized study of misonidazole plus radiation vs. radiation alone for cervix cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2004;70:295–299.
Committee on Research: Science and Therapy of the American Academy of Periodontology. Tissue banking of bone allografts used in periodontal regeneration. J Periodontol. 2001;72:834–838.
Conrad EU, Gretch DR, Obermeyer KR, Moogk MS, Sayers M, Wilson JJ, Strong DM. Transmission of the hepatitis C virus by tissue transplantation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77:214–224.
Cowan DS, Kanagasabapathy VM, McClelland RA, Rauth AM. Mechanistic studies of enhanced in vitro radiosensitization and hypoxic cell cytotoxicity by targeting radiosensitizers to DNA via intercalation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992;22:541–544.
Cowan DS, Matejovic JF, McClelland RA, Rauth AM. DNA-targeted 2-nitroimidazoles: in vitro and in vivo studies. Br J Cancer. 1994;70:1067–1074.
Cowan DS, Matejovic JF, Wardman P, McClelland RA, Rauth AM. Radiosensitizing and cytotoxic properties of DNA targeted phenanthridine-linked nitroheterocycles of varying electron affinities. Int J Radiat Biol. 1994;66:729–738.
Cowan DS, Panicucci R, McClelland RA, Rauth AM. Targeting radiosensitizers to DNA by attachment of an intercalating group: nitroimidazole-linked phenanthridines. Radiat Res. 1991;127:81–89.
Currey JD, Foreman J, Laketic I, Mitchell J. Effects of ionizing radiation on the mechanical properties of human bone. J Orthop Res. 1997;15:111–117.
DeLara J, Fernandez PS, Periago PM. Irradiation of spores of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus subtilis with electron beams. Innovat Food Sci EmergTechnol. 2002;3:379–384.
Denny WA, Roberts PB, Anderson RF, Brown JM, Phil D, Wilson WR. NLA-1: a 2-nitroimidazole radiosensitizer targeted to DNA by intercalation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992;22:553–556.
Enescu M, Cardey B. Mechanism of cysteine oxidation by a hydroxyl radical: A theoretical study. Chemphyschem. 2006;7:912–919.
Grieb TA, Forng RY, Bogdansky S, Ronholdt C, Parks B, Drohan WN, Burgess WH, Lin J. High-dose gamma irradiation for soft tissue allografts: High margin of safety with biomechanical integrity. J Orthop Res. 2006;24:1011–1018.
Grieb TA, Forng RY, Stafford RE, Lin J, Almeida J, Bogdansky S, Ronholdt C, Drohan WN, Burgess WH. Effective use of optimized, high-dose (50 kGy) gamma irradiation for pathogen inactivation of human bone allografts. Biomaterial. 2005;26:2033–2042.
Halliwel B, Gutteridge JMC. Free Radicals in Biology, Medicine. Oxford UK: Clarendon Press; 1989.
Hamer AJ, Stockley I, Elson RA. Changes in allograft bone irradiated at different temperatures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81:342–344.
Hamer AJ, Strachan JR, Black MM, Ibbotson CJ, Stockley I, Elson RA. Biomechanical properties of cortical allograft bone using a new method of bone strength measurement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996;78:363–368.
Hawkins CL, Davies MJ. Oxidative damage to collagen and related substrates by metal ion/hydrogen peroxide systems: random attack or site-specific damage? Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1997;1360:84–96.
Kitchen AD, Mann GF, Harrison JF, Zuckerman AJ. Effect of gamma irradiation on the human immunodeficiency virus and human coagulation proteins. Vox Sang. 1989;56:223–229.
Lietman SA, Tomford WW, Gebhardt MC, Springfield DS, Mankin HJ. Complications of irradiated allografts in orthopaedic tumor surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000:214–217.
Marciniec B, Ogrodowczyk M, Ambroz H, Przybytniak G. The effect of gamma-radiation on nitroimidazole derivatives. Acta Pol Pharm. 2000;57:95–99.
Miekka SI, Forng RY, Rohwer RG, MacAuley C, Stafford RE, Flack SL, MacPhee M, Kent RS, Drohan WN. Inactivation of viral and prion pathogens by gamma-irradiation under conditions that maintain the integrity of human albumin. Vox Sang. 2003;84:36–44.
Mitchell EJ, Stawarz AM, Kayacan R, Rimnac CM. The effect of gamma radiation sterilization on the fatigue crack propagation resistance of human cortical bone. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:2648–2657.
Nguyen H, Morgan DA, Forwood MR. Sterilization of allograft bone: is 25 kGy the gold standard for gamma irradiation? Cell Tissue Bank. 2007;8:81–91.
Nucifora G, Smaller B, Avery EC, Remko R. Transient radicals of DNA bases by pulse radiolysis - effects of cysteine and cysteamine as radioprotectors. Radiat Res. 1972;49:96–111.
Ohan MP, Dunn MG. Glucose stabilizes collagen sterilized with gamma irradiation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003;67:1188–1195.
Panicucci R, Heal R, Laderoute K, Cowan D, McClelland RA, Rauth AM. NLP-1: a DNA intercalating hypoxic cell radiosensitizer and cytotoxin. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989;16:1039–1043.
Rougee M, Bensasson RV, Land EJ, Pariente R. Deactivation of singlet molecular-oxygen by thiols and related compounds, possible protectors against skin photosensitivity. Photochem Photobiol. 1988;47:485–489.
Simonds RJ, Holmberg SD, Hurwitz RL, Coleman TR, Bottenfield S, Conley LJ, Kohlenberg SH, Castro KG, Dahan BA, Schable CA. Transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from a seronegative organ and tissue donor. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:726–732.
Stadtman ER. Oxidation of free amino acids and aminoacid residues by radiolysis and by metal-catalyzed reactions. Ann Rev Biochem. 1993;62:797–821.
Tami AE, Schaffler MB, Knothe Tate ML. Probing the tissue to subcellular level structure underlying bone’s molecular sieving function. Biorheology. 2003;40:577–590.
Tomford WW, Mankin HJ, Friedlaender GE, Doppelt SH, Gebhardt MC. Methods of banking bone and cartilage for allograft transplantation. Orthop Clin North Am. 1987;18:241–247.
Varmenot N, Remita S, Abedinzadeh Z, Wisniowski P. Strzelczak G. Bobrowski K. Oxidation processes of N,S-diacetyl-L-cysteine ethyl ester: Influence of S-acetylation. J Phys Chem. 2001;105:6867–6875.
Ward JF. The yield of DNA double strand breaks produce intracellularly by ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Biol. 1990;57:1141–1150.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Musculoskeletal Transplant Foundation for providing human femurs. We also thank Arun Mohan for assistance in preparing bone samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
One or more of the authors (OA, JS, SAK) has received funding from a research grant from the Musculoskeletal Transplant Foundation.
About this article
Cite this article
Kattaya, S.A., Akkus, O. & Slama, J. Radioprotectant and Radiosensitizer Effects on Sterility of γ-irradiated Bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466, 1796–1803 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0283-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0283-7