Abstract
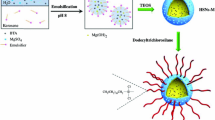
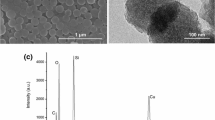
Recent developments in surface science and technology open up new opportunities for the development of smart pigments through the integration of nanoscale containers loaded with active components into coatings. Regarding the external factor to trigger the inhibitor release, a change in pH is a very interesting stimulus since corrosion activity leads to local changes in pH. Although several types of nanocontainers and encapsulation approaches have been proposed and studied to meet this goal, mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) are especially interesting as they retain their solid properties as long as pH of the surrounding medium does not exceed ~11. On the other hand, the use of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles (HMSNs) with a large cavity inside each original mesoporous silica nanoparticle has recently gained increasing interest due to the higher loading capacity. In the present work, an environmentally friendly corrosion inhibitor with good anticorrosive behavior when applied on steel substrates, sodium phosphomolybdate, has been successfully loaded and encapsulated on HMSNs. The pH-dependent release of the corrosion inhibitor from the loaded/encapsulated HMSNs has been confirmed. In addition, an improved anticorrosive behavior of the coatings formulated with loaded/encapsulated HMSNs has been observed by Scanning Kelvin Probe (SKP).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, H, Presuel, F, Kelly, RG, “Computational Modelling of Inhibitor Release and Transport from Multifunctional Organic Coatings.” Electrochim. Acta, 49 (2) 239–255 (2004)
Katz, SA, Salem, H, “The Toxicology of Chromium with Respect to Its Chemical Speciation: A Review.” J. Appl. Toxicol., 13 217–224 (1993)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration U.S. Department of Labor, “Small Entity Compliance Guide for the Hexavalent Chromium Standards”, OSHA 3320-10N (2006)
Andreeva, DV, Shchukin, G, “Smart Self-repairing Protective Coatings.” Mater. Today, 11 (10) 24–30 (2008)
Slowing, II, Trewyn, BG, Giri, S, Lin, VSY, “Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery and Biosensing Applications.” Adv. Funct. Mater., 17 (8) 1225–1236 (2007)
Kapoor, MP, Vinu, A, Fujii, W, Kimura, T, Yang, Q, Kasama, Y, Yanagi, M, Juneja, LR, “Self-assembly of Mesoporous Silicas Hollow Microspheres Via Food Grade Emulsifiers for Delivery Systems.” Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 128 187–193 (2010)
Zhao, Y, Zhang, J, Li, W, Zhang, C, Han, B, “Synthesis of Uniform Hollow Silica Spheres with Ordered Mesoporous Shells in a CO2 Induced Nanoemulsion.” Chem. Commun., 2009 (17) 2365–2367 (2009)
Yeh, YQ, Chen, BC, Lin, HP, Tang, CY, “Synthesis of Hollow Silica Spheres with Mesostructured Shell Using Cationic–Anionic–Neutral Block Copolymer Ternary Surfactants.” Langmuir, 22 (1) 6–9 (2006)
Botterhuis, NE, Sun, Q, Magusin, PCMM, van Santen, RA, Sommerdijk, NAJM, “Hollow Silica Spheres with an Ordered Pore Structure and Their Application in Controlled Release Studies.” Chem. Eur. J., 12 1448–1456 (2006)
Slowing, II, Trewyn, BG, Lin, VS, “Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Intracellular Delivery of Membrane-Impermeable Proteins.” J. Am. Chem. Soc., 129 8845–8849 (2007)
Zhao, W, Chen, H, Li, Y, Li, L, Lang, M, Shi, J, “Uniform Rattle-Type Hollow Magnetic Mesoporous Spheres as Drug Delivery Carriers and Their Sustained-Release Property.” Adv. Funct. Mater., 18 (18) 2780–2788 (2008)
Zhu, YF, Kockrick, E, Ikoma, T, Hanagata, N, Kaskel, S, “An Efficient Route to Rattle-Type Fe3O4@SiO2 Hollow Mesoporous Spheres Using Colloidal Carbon Spheres Templates.” Chem. Mater., 21 (12) 2547–2553 (2009)
Chen, F, Hong, H, Shi, S, Goel, S, Valdovinos, HF, Hernandez, R, Theuer, CP, Barnhart, TE, Cai, W, “Engineering of Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Remarkably Enhanced Tumor Active Targeting Efficacy.” Sci. Rep., 4 5080 (2014)
Yang, Y, Chen, F, Shi, S, Graves, S, Nickles, R, Cai, W, “In Vivo Tumor Targeting of CD146 with Antibody-Conjugated Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles.” J. Nucl. Med., 56 (3) 117 (2015)
Jiao, J, Li, X, Zhang, S, Liu, J, Di, D, Zhang, Y, Zhao, O, Wang, S, “Redox and pH Dual-Responsive PEG and Chitosan-Conjugated Hollow Mesoporous Silica for Controlled Drug Release.” Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl., 67 26–33 (2016)
Suarez, FJ, Sevilla, M, Alvarez, S, Valdes-Solis, T, Fuertes, AB, “Synthesis of Highly Uniform Mesoporous Sub-Micrometric Capsules of Silicon Oxycarbide and Silica.” Chem. Mater., 19 3096–3098 (2007)
Fowler, CE, Khushalani, D, Mann, S, “Interfacial Synthesis of Hollow Microspheres of Mesostructured Silica.” Chem. Commun., 2001 2028–2029 (2001)
Wang, JG, Li, F, Zhou, HJ, Sun, PC, Ding, DT, Chen, TH, “Silica Hollow Spheres with Ordered and Radially Oriented Amino-Functionalized Mesochannels.” Chem. Mater., 21 612–620 (2009)
Tan, B, Lehmler, HJ, Vyas, SM, Knutson, BL, Rankin, SE, “Fluorinated-Surfactant-Templated Synthesis of Hollow Silica Particles with a Single Layer of Mesopores in Their Shells.” Adv. Mater., 17 (19) 2368–2371 (2005)
Rana, RK, Mastai, Y, Gedanken, A, “Acoustic Cavitation Leading to the Morphosynthesis of Mesoporous Silica Vesicles.” Adv. Mater., 14 (19) 1414–1418 (2002)
Guo, X, Deng, Y, Tu, B, Zhao, D, “Facile Synthesis of Hierarchically Mesoporous Silica Particles with Controllable Cavity in Their Surfaces.” Langmuir, 26 (2) 702–708 (2010)
Danumah, C, Vaudreuil, S, Bonneviot, L, Bousmina, M, Giasson, S, Kaliaguine, S, “Synthesis of Macrostructured MCM-48 Molecular Sieves.” Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 44 (1) 241–247 (2001)
Blas, H, Save, M, Pasetto, P, Boissiere, C, Sanchez, C, Charleux, B, “Elaboration of Monodisperse Spherical Hollow Particles with Ordered Mesoporous Silica Shells Via Dual Latex/Surfactant Templating: Radial Orientation of Mesopore Channels.” Langmuir, 24 (22) 13132–13137 (2008)
Guo, X, Kim, YS, Kim, GJ, “Fabrication of SiO2, Al2O3, and TiO2 Microcapsules with Hollow Core and Mesoporous Shell Structure.” J. Phys. Chem. C, 113 (19) 8313–8319 (2009)
Zhao, Y, Wang, H, Liu, Y, Ye, J, Shen, S, “Hollow MCM-41 Microspheres Derived from P(St-MMA)/MCM-41 Core/Shell Composite Particles.” Mater. Lett., 62 (27) 4254–4256 (2008)
Tartaj, P, Gonzalez-Carreno, T, Serna, CJ, “Single-Step Nanoengineering of Silica Coated Maghemite Hollow Spheres with Tunable Magnetic Properties.” Adv. Mater., 13 (21) 1620–1624 (2001)
Hah, HJ, Kim, JS, Jeon, BJ, Koo, SM, Lee, YE, “Simple Preparation of Monodisperse Hollow Silica Particles Without Using Templates.” Chem. Commun., 2003 1712–1713 (2003)
Wang, Q, Liu, Y, Yan, H, “Mechanism of a Self-Templating Synthesis of Monodispersed Hollow Silica Nanospheres with Tunable Size and Shell Thickness.” Chem. Commun., 2007 2339–2341 (2007)
Zhang, T, Zhang, Q, Ge, J, Goebl, J, Sun, M, Tan, Y, Liu, Y, Chang, C, Guo, J, Yin, Y, “A Self-templated Route to Hollow Silica Microspheres.” J. Phys. Chem. C, 113 (8) 3168–3175 (2009)
Hao, N, Jayawardana, KW, Chen, X, Yan, M, “One-Step Synthesis of Amine-Functionalized Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Efficient Antibacterial and Anticancer Materials.” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 7 (2) 1040–1045 (2015)
Zuo, S, Liu, W, Yao, C, Li, X, Luo, S, Wu, F, Kong, Y, Liu, X, “One-Pot Template-Free Fabrication of Hollow Mesoporous Sodalite Nanospheres for Drug Release.” Appl. Clay Sci., 119 (Part 1) 170–174 (2016)
Li, ZZ, Wen, LX, Shao, L, Chen, JF, “Fabrication of Porous Hollow Silica Nanoparticles and Their Applications in Drug Release Control.” J. Control. Release, 98 (2) 245–254 (2004)
Chen, JF, Ding, HM, Wang, JX, Shao, L, “Preparation and Characterization of Porous Hollow Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Application.” Biomaterials, 25 (4) 723–727 (2004)
Sharma, RK, Das, S, Maitra, A, “Enzymes in the Cavity of Hollow Silica Nanoparticles.” J. Colloid Interface Sci., 284 (1) 358–361 (2005)
Wang, J, Ding, H, Tao, X, Chen, J, “Storage and Sustained Release of Volatile Substances from a Hollow Silica Matrix.” Nanotechnology, 18 (24) 245705 (2007)
Zhu, YF, Shi, JL, Chen, HR, Shen, WH, Dong, XP, “A Facile Method to Synthesize Novel Hollow Mesoporous Silica Spheres and Advanced Storage Property.” Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 84 (1–3) 218–222 (2005)
Li, ZZ, Xu, SA, Wen, LX, Liu, F, Liu, AQ, Wang, Q, Sun, HY, Yu, W, Chen, JF, “Controlled Release of Avermectin from Porous Hollow Silica Nanoparticles: Influence of Shell Thickness on Loading Efficiency, UV-Shielding Property and Release.” J. Controlled Release, 111 (1–2) 81–88 (2006)
Zhou, J, Wu, W, Caruntu, D, Yu, MH, Martin, A, Chen, JF, O’Connor, CJ, Zhou, WL, “Synthesis of Porous Magnetic Hollow Silica Nanospheres for Nanomedicine Application.” J. Phys. Chem. C, 111 (47) 17473–17477 (2007)
Chen, T, Fu, J, “pH-Responsive Nanovalves Based on Hollow Mesoporous Silica Spheres for Controlled Release of Corrosion Inhibitor.” Nanotechnology, 23 (23) 235605 (2012)
Ge, C, Zhang, D, Wang, A, Yin, H, Ren, M, Liu, Y, Jiang, T, Yu, L, “Synthesis of Porous Hollow Silica Spheres Using Polystyrene–Methyl Acrylic Acid Latex Template at Different Temperatures.” J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 70 (11) 1432–1437 (2009)
Agrawal, M, Pich, A, Gupta, S, Zafeiropoulos, NE, Simon, P, Stamm, M, “Synthesis of Novel Tantalum Oxide Sub-micrometer Hollow Spheres with Tailored Shell Thickness.” Langmuir, 24 (3) 1013–1018 (2008)
Zea, C, Barranco-García, R, Chico, B, Díaz, I, Morcillo, M, de la Fuente, D, “Smart Mesoporous Silica Nanocapsules as Environmentally Friendly Anticorrosive Pigments.” Int. J. Corros., 2015 426397 (2015)
Tumurova, LV, Kvashnina, EV, Mokhosoev, MV, “Passivation of a Corrosion-Resisting Chrome Steel in the Presence of a Mixture of Phosphate- and Molybdate-Ions.” Prot. Met. (Engl. Transl.), 26 347–349 (1990)
Kalendovà, A, Kalenda, P, Veselý, D, “Comparison of the Efficiency of Inorganic Nonmetal Pigments with Zinc Powder in Anticorrosion Paints.” Prog. Org. Coat., 57 (1) 1–10 (2006)
Karekar, SE, Bhanvase, BA, Sonawane, SH, Deosarkar, MP, Pinjari, DV, Pandit, AB, “Synthesis of Zinc Molybdate and Zinc Phosphomolybdate Nanopigments by an Ultrasound Assisted Route: Advantage Over Conventional Method.” Chem. Eng. Process., 87 51–59 (2015)
de Lima-Neto, P, de Araújo, AP, Araújo, WS, Correia, AN, “Study of the Anticorrosive Behaviour of Epoxy Binders Containing Non-toxic Inorganic Corrosion Inhibitor Pigments.” Prog. Org. Coat., 62 (3) 344–350 (2008)
Shchukin, DG, Möhwald, H, “Surface-Engineered Nanocontainers for Entrapment of Corrosion Inhibitors.” Adv. Funct. Mater., 17 1451–1458 (2007)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support for this work from the Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness of Spain (MAT 2011-28178 and MAT 2014-59752R).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zea, C., Barranco-García, R., Alcántara, J. et al. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with phosphomolybdate as smart anticorrosive pigment. J Coat Technol Res 14, 869–878 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-017-9924-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-017-9924-7