Abstract
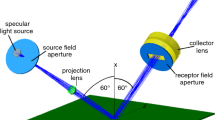
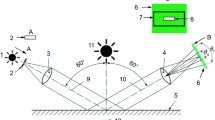
In order to numerically quantify and to ensure consistency of the visual appearance of the end product, many industries perform color and gloss measurements, through the results of which they define maximum tolerances during quality control. For this, they may primarily rely on precision data for repeatability and reproducibility as reported by instrument manufacturers, who develop their instruments according to standardized measurement geometries defined in international standards. This paper reports on an investigation of the inter-instrument agreement between specular gloss meters which conform to universally adopted gloss standards. Six commercially available instruments, manufactured by three different companies, and twenty-five gloss artifacts, with specular gloss values ranging between 2 and 110 gloss units (60° geometry), were selected for use in the study. The repeatability and reproducibility of the instruments were assessed according to the criteria described in ASTM D523-14 and ISO 2813:2014, and to the specifications reported by the instrument manufacturers. Ray tracing simulations were performed by use of the bidirectional reflectance distribution function measurement data of two samples, and based on the standardized optical design of the specular gloss meter, in order to get a better insight on the expected tolerances of the gloss readings from a theoretical point of view. On average, the practical results indicate that both the repeatability and reproducibility values are higher than those specified in the recommendations and by the manufacturers. Ray tracing simulations confirm this finding. While specified repeatability and reproducibility thresholds are based on ideal standards, in practice, there are parameters that can lead to significant higher deviations. Care should therefore be taken when analyzing measurement results obtained from different instruments, and when defining tolerances for evaluation of gloss measurements.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
ASTM recommends assessing the reproducibility from two results which are the mean of 3 readings instead of 5.
References
CIE Publication 175:2006, “A Framework for the Measurement of Visual Appearance.” CIE, Vienna (2006)
CIE Publication S 017/E:2011, “International Lighting Vocabulary.” CIE, Vienna (2011)
ASTM Standard D 523-14, “Standard Test Method for Specular Gloss.” In: Annual Book of ASTM Standards, vol. 06.01. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA (2015)
ISO Standard 2813:2014, “Paints and varnishes – Determination of gloss values at 20 degrees, 60 degrees and 85 degrees.” International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland (2014)
Cook, MP, Thomas, K, “Evaluation of Gloss Meters for Measurement of Moulded Plastics.” Polym. Test., 9 (4) 233–244 (1990)
Sève, R, “Problems Connected with the Concept of Gloss.” Color Res. Appl., 18 (4) 241–252 (1993)
Arney, JS, Ye, L, Banach, S, “Interpretation of Gloss Meter Measurements.” J. Imaging Sci. Technol., 50 (6) 567–571 (2006)
TAPPI Test Method T 480, “Specular Gloss of Paper and Paperboard at 75 Degrees.” TAPPI, Peachtree Corners, GA (2009)
Leyre, S, Ryckaert, J, Acuña, P, Audenaert, J, Meuret, Y, Durinck, G, Hofkens, J, Deconinck, G, Hanselaer, P, “A Hybrid Tool for Spectral Ray Tracing Simulations of Luminescent Cascade Systems.” Opt. Express, 22 (20) 24582–24593 (2014)
Veach, E, “Robust Monte Carlo Methods for Light Transport Simulation.” Doctoral Dissertation. Stanford University, Stanford, CA (1998)
Dutré, P, Bala, K, Bekaert, P, Advanced Global Illumination, 2nd ed. A K Peters Ltd, Wellesley, MA (2006)
Nicodemus, FE, Richmond, JC, Hsia, JJ, Ginsberg, IW, Limperis, T, “Geometric Considerations and Nomenclature for Reflectance.” National Bureau of Standards, Monograph 160 (1977)
Leloup, FB, Forment, S, Dutré, P, Pointer, MR, Hanselaer, P, “Design of an Instrument for Measuring the Spectral Bidirectional Scatter Distribution Function.” Appl. Opt., 47 (29) 5454–5467 (2008)
Obein, G, Audenaert, J, Ged, G, Leloup, FB, “Metrological Issues Related to BRDF Measurements Around the Specular Direction in the Particular Case of Glossy Surfaces.” Proc. SPIE, 9398, 93980D, San Francisco, March 2015
Hammond, HK, III, Nimeroff, I, “Measurement of Sixty-Degree Specular Gloss.” J. Res. NBS, 44 585–598 (1950)
Nadal, ME, Thompson, EA, “NIST Reference Goniophotometer for Specular Gloss Measurements.” J. Coat. Technol., 73 (917) 73–80 (2001)
Nadal, ME, Thompson, EA, “New Primary Standard for Specular Gloss Measurements.” J. Coat. Technol., 72 (911) 61–66 (2000)
Nadal, ME, Zwinckels, JC, Nöel, M, “Specular Gloss Scales Comparison Between the National Institute of Standards and Technology and the National Research Council of Canada.” J. Coat. Technol., 75 (943) 45–51 (2003)
Acknowledgments
This work has been partially funded by the European Metrology Research Programme (EMRP). The EMRP is jointly funded by the European Commission and participating countries within the European Association of National Metrology Institutes (EURAMET).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leloup, F.B., Audenaert, J., Obein, G. et al. Repeatability and reproducibility of specular gloss meters in theory and practice. J Coat Technol Res 13, 941–951 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-016-9813-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-016-9813-5