Abstract
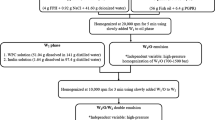
This work aims at studying the effects of whey protein concentrate (WP) and egg white powder (EW) as structuring agents in double emulsions (W1/O/W2). A D-optimal design was developed considering the following factors: type (WP, EW) and concentration (0, 5, 10 g/100 mL) of protein used to gel the inner water phase (W1), W1 volume percentage (20%, 30%, and 40%) in primary emulsion (W1/O), and W1/O volume percentage (40, 50, 60%) in W1/O/W2. The 21 samples were investigated by FT-IR spectroscopy, which revealed different protein conformations depending on W1 and W1/O fractions, and a better interaction with oil of WP rather than EW. Highly significant (p < 0.001) multivariate models were computed for yield, rheological properties, and creaming stability of W1/O/W2, being W1 and W1/O the most influent factors. Protein type significantly affected W1/O/W2 rheology, revealing a better structuring ability of EW with respect to WP, resulting in higher apparent viscosity and consistency coefficient values. A W1/O/W2 optimized for maximum values of apparent viscosity, yield, and creaming stability was developed, composed of 10 g/100 mL EW in W1, 29% W1, and 60% W1/O, with an oil content of 42.6 mL/100 mL. The optimized emulsion gave results in good agreement with the predicted values, thus confirming the validity of the developed multivariate models for the design of double emulsions with desired features.

Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alamprese, C., Datei, L., & Semeraro, Q. (2007). Optimization of processing parameters of a ball mill refiner for chocolate. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 67, 60–66.
Artiga-Artigas, M., Molet-Rodríguez, A., Salvia-Trujillo, L., & Martín-Belloso, O. (2019). Formation of double (W1/O/W2) emulsions as carriers of hydrophilic and lipophilic active compounds. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 12(3), 422–435.
Balcaen, M., Vermeir, L., Declerck, A., & Van der Meeren, P. (2016). Influence of internal water phase gelation on the shear- and osmotic sensitivity of W/O/W-type double emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids, 58, 356–363.
Bock, J. E., & Damodaran, S. (2013). Bran-induced changes in water structure and gluten conformation in model gluten dough studied by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Food Hydrocolloids, 31(2), 146–155.
Cheong, K. W., Mirhosseini, H., Leong, W. F., Hamid, N. S. A., Osman, A., Basri, M., & Tan, C. P. (2015). Rheological properties of modified starch–whey protein isolate stabilized soursop beverage emulsion systems. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8(6), 1281–1294.
Cofrades, S., Antoniou, I., Solas, M. T., Herrero, A. M., & Jiménez-Colmenero, F. (2013). Preparation and impact of multiple (water-in-oil-in-water) emulsions in meat systems. Food Chemistry, 141(1), 338–346.
Demetriades, K., Coupland, J. N., & McClements, D. J. (1997). Physical properties of whey protein stabilized emulsions as related to pH and NaCl. Journal of Food Science, 62(2), 342–347.
Erçelebi, E. A., & Ibanoğlu, E. (2009). Rheological properties of whey protein isolate stabilized emulsions with pectin and guar gum. European Food Research and Technology, 229(2), 281–286.
Freire, M., Bou, R., Cofrades, S., Solas, M. T., & Jiménez-Colmenero, F. (2016). Double emulsions to improve frankfurter lipid content: impact of perilla oil and pork backfat. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 96(3), 900–908.
Guo, Y., Huang, W.-C., Wu, Y., Qi, X., & Mao, X. (2019). Conformational changes of proteins and oil molecules in fish oil/water interfaces of fish oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by bovine serum albumin. Food Chemistry, 274, 402–406.
Hesso, N., Marti, A., Le-Bail, P., Loisel, C., Chevallier, S., Le-Bail, A., & Seetharaman, K. (2015). Conformational changes of polymers in model batter systems. Food Hydrocolloids, 51, 101–107.
Karaca, A. C., Low, N., & Nickerson, M. (2011). Emulsifying properties of chickpea, faba bean, lentil and pea proteins produced by isoelectric precipitation and salt extraction. Food Research International, 44(9), 2742–2750.
Kong, J., & Yu, S. (2007). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis of protein secondary structures. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica, 39(8), 549–559.
Kuropatwa, M., Tolkach, A., & Kulozik, U. (2009). Impact of pH on the interactions between whey and egg white proteins as assessed by the foamability of their mixtures. Food Hydrocolloids, 23(8), 2174–2181.
Lamba, H., Sathish, K., & Sabikhi, L. (2015). Double emulsions: emerging delivery system for plant bioactives. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8(4), 709–728.
Leong, T. S. H., Zhou, M., Kukan, N., Ashokkumar, M., & Martin, G. J. O. (2017). Preparation of water-in-oil-in-water emulsions by low frequency ultrasound using skim milk and sunflower oil. Food Hydrocolloids, 63, 685–695.
Lobato-Calleros, C., Rodriguez, E., Sandoval-Castilla, O., Vernon-Carter, E. J., & Alvarez-Ramirez, J. (2006). Reduced-fat white fresh cheese-like products obtained from W1/O/W2 multiple emulsions: viscoelastic and high-resolution image analyses. Food Research International, 39(6), 678–685.
Lobato-Calleros, C., Sosa-Pérez, A., Rodríguez-Tafoya, J., Sandoval-Castilla, O., Pérez-Alonso, C., & Vernon-Carter, E. J. (2008). Structural and textural characteristics of reduced-fat cheese-like products made from W1/O/W2 emulsions and skim milk. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 41(10), 1847–1856.
Lobato-Calleros, C., Recillas-Mota, M. T., Espinosa-Solares, T., Alvarez-Ramirez, J., & Vernon-Carter, E. J. (2009). Low-fat stirred yoghurts made with skim milk and multiple emulsions. Journal of Texture Studies, 40(6), 657–675.
Márquez, A. L., & Wagner, J. R. (2010). Rheology of double (w/o/w) emulsions prepared with soybean milk and fortified with calcium. Journal of Texture Studies, 41(5), 651–671.
Márquez, A. L., Medrano, A., Panizzolo, L. A., & Wagner, J. R. (2010). Effect of calcium salts and surfactant concentration on the stability of water-in-oil (w/o) emulsions prepared with polyglycerol polyricinoleate. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 341(1), 101–108.
Matsumoto, S., & Kohda, M. (1980). The viscosity of W/O/W emulsions: an attempt to estimate the water permeation coefficient of the oil layer from the viscosity changes in diluted systems on aging under osmotic pressure gradients. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 73(1), 13–20.
McClements, D. J. (2016). Food emulsions. Principles, practices, and techniques (3rd ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press (Chapter 13).
Mohammadian, M., Salami, M., Emam-Djomeh, Z., Momen, S., & Moosavi-Movahedi, A. A. (2018). Gelation of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by heat-denatured and nanofibrillated whey proteins through ion bridging or citric acid-mediated cross-linking. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 120(Pt B), 2247–2258.
Momeny, E., Mirhosseini, H., & Sarker, M. Z. I. (2017). Effect of medium-high energy emulsification condition on physicochemical properties of β-sitosterol multiple emulsion. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 10(9), 1642–1654.
Montgomery, D. C. (2001). Design and analysis of experiments. New York: Wiley.
Muschiolik, G. (2007). Multiple emulsions for food use. Current Opinion in Colloid and Interface Sciences, 12(4–5), 213–220.
Muschiolik, G., & Dickinson, E. (2017). Double emulsions relevant to food systems: preparation, stability, and applications. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 16(3), 532–555.
Oppermann, A. K. L., Renssen, M., Schuch, A., Stieger, M., & Scholten, E. (2015). Effect of gelation of inner dispersed phase on stability of (W1/O/W2) multiple emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids, 48, 17–26.
Oppermann, A. K. L., Piqueras-Fiszman, B., de Graaf, C., Scholten, E., & Stieger, M. (2016). Descriptive sensory profiling of double emulsions with gelled and non-gelled inner water phase. Food Research International, 85, 215–223.
Panagopoulou, E., Evageliou, V., Kopsahelis, N., Ladakis, D., Koutinas, A., & Mandala, I. (2017). Stability of double emulsions with PGPR, bacterial cellulose and whey protein isolate. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 522, 445–452.
Perez-Moral, N., Watt, S., & Wilde, P. (2014). Comparative study of the stability of multiple emulsions containing a gelled or aqueous internal phase. Food Hydrocolloids, 42, 215–222.
Sağlam, D., Venema, P., de Vries, R., Sagis, L. M. C., & van der Linden, E. (2011). Preparation of high protein micro-particles using two-step emulsification. Food Hydrocolloids, 25(5), 1139–1148.
Steffe, J. F. (1996). Rheological methods in food process engineering (2nd ed.). East Lansing: Freeman Press.
Su, J., Flanagan, J., Hemar, Y., & Singh, H. (2006). Synergistic effects of polyglycerol ester of polyricinoleic acid and sodium caseinate on the stabilisation of water-oil-water emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids, 20(2–3 SPEC. ISS), 261–268.
Surh, J., Vladisavljević, G. T., Mun, S., & McClements, D. J. (2007). Preparation and characterization of water/oil and water/oil/water emulsions containing biopolymer-gelled water droplets. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55(1), 175–184.
Takahashi, Y., Aizawa, S., Tamai, S., Yoshida, T., & Takahashi, T. (1986). Process for preparation of dressings comprising W/O/W type multiple emulsions. US patent 4632840A.
van Aken, G. A., Vingerhoeds, M. H., & de Wijk, R. A. (2011). Textural perception of liquid emulsions: role of oil content, oil viscosity and emulsion viscosity. Food Hydrocolloids, 25(4), 789–796.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.E.M.: methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation. C.A.: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of Data and Material
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moriano, M.E., Alamprese, C. Whey Protein Concentrate and Egg White Powder as Structuring Agents of Double Emulsions for Food Applications. Food Bioprocess Technol 13, 1154–1165 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02467-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02467-0