Abstract
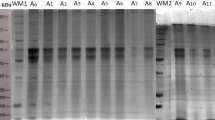
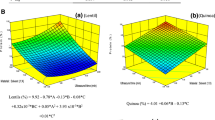
The effect of microwaves (MWs) and/or ultrasound (US) to assist alkaline extraction of peanut proteins was evaluated. Isolate extraction yields and purities were obtained as well as functional properties (water solubility and retention, fat absorption, nitrogen solubility, emulsifying activity, and foam activity and stability), in vitro digestibility, free amino nitrogen (FAN), microstructure and secondary structure. In MW-assisted treatments, power (145, 290, 435, 580, and 725 W) and time (2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 min) were evaluated, whereas in US-assisted assays, amplitude (20/100%) and time (15/40 min) were varied. For MW-assisted extraction, 725 W and 8 min yielded an extraction of 55% (100% purity), i.e., 77% more protein when compared with the control, while for US, an increase of 136% and purity of 86% was reached (100% amplitude and 15 min). The sequential use of both technologies was also evaluated, but a synergistic effect in protein extraction was not observed. In terms of functional properties, fat absorption index remained the same for both treatments whereas water absorption, foam activity, emulsifying activity (for MW), and in vitro digestibility (for MW only) improved. In the case of free amino nitrogen, a reduction of 50% for assisted peanut protein isolates was observed. Microstructure was not different among treatments, but secondary structure did change: β-sheet and nonordered structures were higher for experimental treatments compared with the traditional alkaline isolate (up to 8 and 4%, respectively). The use of MW and US favored peanut protein extraction for production of high purity isolates.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AACC:
-
American Association of Cereal Chemists
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- AOAC:
-
Association of Official Analytical Chemists
- CW:
-
Cell wall
- EA:
-
Emulsifying activity
- FA:
-
Foam activity
- FAI:
-
Fat absorption index
- FAN:
-
Free amino nitrogen
- FAO:
-
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
- FS:
-
Foam stability
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- MW:
-
Microwave
- NSI:
-
Nitrogen solubility index
- PB:
-
Protein body
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- US:
-
Ultrasound
- WAI:
-
Water absorption index
- WSI:
-
Water solubility index
References
AACC. (2000). Approved methods of the AACC. (A. A. Of & C. Chemists, Eds.) (10th ed.). St. Paul, MN.
Ahn, H. J., Kim, J. H., & Ng, P. K. W. (2005). Functional and thermal properties of wheat, barley, and soy flours and their blends treated with a microbial transglutaminase. Journal of Food Science, 70(6), c380–c386. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.2005.tb11433.x.
American Oil Chemist’s Society (AOCS). (2006). Official and tentative methods of the American Oil Chemist’s Society. (AOCS, Ed.). Urbana, IL, USA: AOCS.
AOAC. (1992). AOAC Official Methods. (A. International, Ed.). Washington, DC.
Awad, T. S., Moharram, H. A., Shaltout, O. E., Asker, D., & Youssef, M. M. (2012). Applications of ultrasound in analysis, processing and quality control of food: a review. Food Research International, 48(2), 410–427. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2012.05.004.
Beuchat, L. R., Cherry, J. P., & Quinn, M. R. (1975). Physicochemical properties of peanut flour as affected by proteolysis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 23(4), 616–620. doi:10.1021/jf60200a045.
Bylund, G. (2015). Dairy processing handbook (Third Edit.). Lund Sweden: Tetra Pak Processing Systems AB.
Caballero de la Peña, K. (2015). Análisis del valor nutrimental de una bebida a base de pulpa de fruta suplementada con proteína vegetal in vitro y en un modelo murino. Tesis de Maestría en Biotecnología. Tecnologico de Monterrey.
Cheewapramong, P., Riaz, M. N., Rooney, L. W., & Lusas, E. W. (2002). Use of partially defatted peanut flour in breakfast cereal flakes. Cereal Chemistry, 79(4), 586–592. doi:10.1094/CCHEM.2002.79.4.586.
Cheftel, J. ., Cuq, J. ., & Lorient, D. (1989). Propiedades Funcionales de las Proteínas. In Proteínas Alimentarias. España: Acribia.
Chel-Guerrero, L., Corzo-Ríos, L., & Betancur-Ancona, D. (2003). Estructura y propiedades funcionales de proteínas de leguminosas. Revista de la Universidad Autónoma de Yucatán, 227, 34–43.
Choi, I., Cho, S. J., Chun, J. K., & Moon, T. W. (2006). Extraction yield of soluble protein and microstructure of soybean affected by microwave heating. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 30(4), 407–419. doi:10.1111/j.1745-4549.2006.00075.x.
Colombo, A., Ribotta, P. D., & León, A. E. (2010). Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) studies on the thermal properties of peanut proteins. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58(7), 4434–4439. doi:10.1021/jf903426f.
Cvetanović, A., Švarc-Gajić, J., Mašković, P., Savić, S., & Nikolić, L. (2015). Antioxidant and biological activity of chamomile extracts obtained by different techniques: perspective of using superheated water for isolation of biologically active compounds. Industrial Crops and Products, 65, 582–591. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.09.044.
Desai, B. B., Kotecha, P. M., & Salunkhe, D. K. (1999). Composition and nutritional quality. In Introduction science and technology of groundnut: biology, production, processing and utilization (pp. 185–199). New Delhi: Naya Prokash Publ.
Desai, M., Parikh, J., & Parikh, P. (2010). Extraction of natural products using microwaves as a heat source. Separation & Purification Reviews, 39(1–2), 1–32. doi:10.1080/15422111003662320.
Deshpande, S. S., & Damodaran, S. (1989). Structure-digestibility relationship of legume 7S proteins. Journal of Food Science, 54(1), 108–113. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1989.tb08579.x.
Fang, Y., Rogers, S., Selomulya, C., & Chen, X. D. (2012). Functionality of milk protein concentrate: effect of spray drying temperature. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 62, 101–105. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2011.05.007.
Ferhat, M. A., Meklati, B. Y., & Chemat, F. (2007). Comparison of different isolation methods of essential oil fromCitrus fruits: cold pressing, hydrodistillation and microwave “dry” distillation. Flavour and Fragrance Journal, 22(6), 494–504. doi:10.1002/ffj.1829.
Ferreyra, J. C., Kuskoski, E. M., Bordignon, M. T., Barrera, D., & Fett, R. (2007). Propiedades emulsificantes y espumantes de las proteínas de harina de cacahuate ( Arachis hypogaea Lineau ). Grasas y Aceites, 58(3), 264–269.
Gallegos-Hoyos, F. (2016). Informe de la evaluación técnica y comercial de tecnología para incrementar rendimientos en la elaboración de aislados de proteínas vegetales. Oficina de Transferencia de Tecnología. Tecnológico de Monterey. Monterrey, N.L. México.
Garidel, P., & Schott, H. (2006). Fourier-transform midinfrared spectroscopy for analysis and screening of liquid protein formulations part 2: details analysis and applications. Bioprocess International, 1, 48–55.
Haque, Z., & Kito, M. (1983). Lipophilization of .alpha.s1-casein. 2. Conformational and functional effects. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 31(6), 1231–1237. doi:10.1021/jf00120a022.
Hervera, M., Baucells, M. D., González, G., Pérez, E., & Castrillo, C. (2009). Prediction of digestible protein content of dry extruded dog foods: comparison of methods. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 93(3), 366–372. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0396.2008.00870.x.
Hsu, H. W., Vavak, D. L., Satterlee, L. D., & Miller, G. A. (1977). A multienzyme technique for estimating protein digestibility. Journal of Food Science, 42(5), 1269–1273. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1977.tb14476.x.
Jideani, V. a. (2011). Functional properties of soybean food ingredients in food systems (pp. 345–364). Chemistry and Physiology: Soybean - Biochemistry. doi:10.5772/1952.
Johnson, L. A., Farnsworth, J. T., Garland, R. J., & Lusas, E. W. (1979). Removal of raw peanut flavor and odor in peanut flour processed by direct solvent extraction. Peanut Science, 6(1), 43–45. doi:10.3146/i0095-3679-6-1-8.
Kain, R. J., Chen, Z., Sonda, T. S., & Abu-Kpawoh, J. (2009). Study on the effect of control variables on the extraction of peanut protein isolates from peanut meal (Arachis hypogaea L.). American Journal of Food Technology, 4, 47–55.
Karki, B. (2009). Use of high-power ultrasound during soy protein production and study of its effect on functional properties of soy protein isolate. PhD Dissertation. Graduate Theses and Dissertations. Paper 11055. Iowa State University.
Karki, B., Lamsal, B., Grewell, D., Pometto, A. L., Van Leeuwen, J., Khanal, S. K., & Jung, S. (2009). Functional properties of soy protein isolates produced from ultrasonicated defatted soy flakes. JAOCS, Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 86(10), 1021–1028. doi:10.1007/s11746-009-1433-0.
Kinsella, J. E. (1979). Functional properties of soy proteins. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 56(3), 242–258. doi:10.1007/BF02671468.
Lam, R. S. H., & Nickerson, M. T. (2013). Food proteins: a review on their emulsifying properties using a structure-function approach. Food Chemistry, 141(2), 975–984. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.04.038.
Liu, Y., Zhao, G., Ren, J., Zhao, M., & Yang, B. (2011). Effect of denaturation during extraction on the conformational and functional properties of peanut protein isolate. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 12(3), 375–380. doi:10.1016/j.ifset.2011.01.012.
Lupano, C. E. (2013). Modificaciones de componentes de los alimentos: cambios químicos y bioquímicos por procesamiento y almacenamiento. Editorial de la Universidad de la Plata.
Padilla, F. C., Guédez, T., Alfaro, M. J., Regnault, M., & Rincón, A. M. (2010). Fraccionamiento y caracterización de las proteínas solubles de la harina de nuez de Barinas (Caryodendron orinocense K.). Revista del Instituto Nacional de Higiene Rafael Rangel, 41(1), 38–42 Accessed 10 March 2016.
Pan, X., Niu, G., & Liu, H. (2003). Microwave-assisted extraction of tea polyphenols and tea caffeine from green tea leaves. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 42(2), 129–133. doi:10.1016/S0255-2701(02)00037-5.
Porzucek, H., Larsson-Raznikiewicz, M., & Klepacka, M. (1991). In vitro protein digestibility of flours and protein isolates from seeds of some leguminous plants. tp://agris.fao.org/agrissearch/
Rafiee, Z., Jafari, S., Alami, M., & Khomeiri, M. (2011). Microwave-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from olive leaves; a comparison with maceration. The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 4(21), 738–745.
Raso, J., Mañas, P., Pagán, R., & Sala, F. J. (1999). Influence of different factors on the output power transferred into medium by ultrasound. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 5(4), 157–162. doi:10.1016/S1350-4177(98)00042-X.
Salinas-Valdés, A., De la Rosa Millán, J., Serna-Saldívar, S. O., & Chuck-Hernández, C. (2015). Yield and textural characteristics of panela cheeses produced with dairy-vegetable protein (soybean or peanut) blends supplemented with transglutaminase. Journal of Food Science, 80(12), s2950–s2956. doi:10.1111/1750-3841.13126.
Singh, U., & Singh, B. (1991). Functional properties of sorghum-peanut composite flour. Cereal Chemistry, 68(5), 460–463.
Sorgentini, D. A., Wagner, J. R., & Anon, M. C. (1995). Effects of thermal treatment of soy protein isolate on the characteristics and structure-function relationship of soluble and insoluble fractions. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 43(9), 2471–2479. doi:10.1021/jf00057a029.
Soria-Hernández, C., Serna-Saldívar, S., & Chuck-Hernández, C. (2015). Physicochemical and functional properties of vegetable and cereal proteins as potential sources of novel food ingredients. Food Technology and Biotechnology, 53(3), 269–277. doi:10.17113/ftb.53.03.15.3920.
Vanga, S. K., Singh, A., Kalkan, F., Gariepy, Y., Orsat, V., & Raghavan, V. (2015). Effect of thermal and high electric fields on secondary structure of peanut protein. International Journal of Food Properties, 19(6), 1259–1271. doi:10.1080/10942912.2015.1071841.
Vilkhu, K., Mawson, R., Simons, L., & Bates, D. (2008). Applications and opportunities for ultrasound assisted extraction in the food industry—a review. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 9(2), 161–169. doi:10.1016/j.ifset.2007.04.014.
Whisstock, J. C., & Lesk, A. M. (2003). Prediction of protein function from protein sequence and structure. Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics, 36(03), 307–340.
Wu, H., Wang, Q., Ma, T., & Ren, J. (2009). Comparative studies on the functional properties of various protein concentrate preparations of peanut protein. Food Research International, 42(3), 343–348. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2008.12.006.
Yu, J., Ahmedna, M., & Goktepe, I. (2007). Peanut protein concentrate: production and functional properties as affected by processing. Food Chemistry, 103(1), 121–129. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.08.012.
Zhang, H., Tang, L., & Yang, Q. (2011). Optimization of the ultrasonic wave-assisted extraction condition of peanut protein isolate. Advanced Materials Research, 189-193, 3904–3911. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.189-193.3904.
Zhang, Q., Tu, Z., Xiao, H., Wang, H., Huang, X., Liu, G., et al. (2014). Influence of ultrasonic treatment on the structure and emulsifying properties of peanut protein isolate. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 92(1), 30–37. doi:10.1016/j.fbp.2013.07.006.
Zhao, G., Liu, Y., Ren, J., Zhao, M., & Yang, B. (2013). Effect of protease pretreatment on the functional properties of protein concentrate from defatted peanut flour. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 36(1), 9–17. doi:10.1111/j.1745-4530.2011.00646.x.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Nutriomics Research Group (School of Engineering and Sciences, Tecnologico de Monterrey-Campus Monterrey) and to the kind support of Consejo Nacional De Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT, Scientific Development Projects to Solve National Problems 2013). We express our gratitude to CONACyT and Tecnologico de Monterrey for Ariana Ochoa’s postgraduate scholarship and to the Center for Research and Protein Development’s staff (CIDPRO) for your kind and warm support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ochoa-Rivas, A., Nava-Valdez, Y., Serna-Saldívar, S.O. et al. Microwave and Ultrasound to Enhance Protein Extraction from Peanut Flour under Alkaline Conditions: Effects in Yield and Functional Properties of Protein Isolates. Food Bioprocess Technol 10, 543–555 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1838-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1838-3