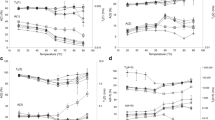
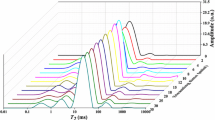
Abstract
Wheat starch-based model systems and wheat flour dough with the same water content (close to 45 %) were investigated upon heating (20–90 °C) using time-domain 1H NMR spectroscopy with the aim of assigning each spin–spin relaxation time (T 2) measured to a specific proton fraction. On the basis of the signal evolution according to Curie’s law for pure starch and pure water, temperature-associated changes for each T 2 value and their mass intensity were interpreted and assigned to water and/or biopolymer proton fractions related to the reversible swelling of starch or its gelatinization. The addition of 2 % (w/w) salt to model samples and dough induced few changes during the reversible swelling process but impacted on the measurements performed above 60 °C. Finally, studies performed on starch-based model systems improved understanding of the complex thermal processing of starch in dough by taking into account phenomena other than the starch swelling and gelatinization, such as gluten denaturation and changes in water–biopolymer interactions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ablett, S., Barnes, D. J., Davies, A. P., Ingman, S. J., & Patient, D. W. (1988). C-13 and pulse nuclear magnetic-resonance spectroscopy of wheat proteins. Journal of Cereal Science, 7(1), 11–20.
Assifaoui, A., Champion, D., Chiotelli, E., & Verel, A. (2006). Characterization of water mobility in biscuit dough using a low-field H-1 NMR technique. Carbohydrate Polymers, 64(2), 197–204. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2005.11.020.
Balla, A., Razafindralambo, H., Blecker, C., & Paquot, M. (1998). Interfacial properties of gluten monolayers spread on various chloride salt solutions. Effects of electrolytes, salt concentrations, and temperature. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 46(9), 3535–3539. doi:10.1021/jf971006j.
Biliaderis, C. G. (1992). Structures and phase-transitions of starch in food systems. Food Technology, 46(6), 98–109.
Bosmans, G. M., Lagrain, B., Deleu, L. J., Fierens, E., Hills, B. P., & Delcour, J. A. (2012). Assignments of proton populations in dough and bread using NMR relaxometry of starch, gluten, and flour model systems. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 60(21), 5461–5470. doi:10.1021/jf3008508.
Bosmans, G. M., Lagrain, B., Ooms, N., Fierens, E., & Delcour, J. A. (2013). Biopolymer interactions, water dynamics, and bread crumb firming. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61(19), 4646–4654. doi:10.1021/jf4010466.
Bosmans, G. M., Lagrain, B., Ooms, N., Fierens, E., & Delcour, J. A. (2014). Storage of parbaked bread affects shelf life of fully baked end product: a H-1 NMR study. Food Chemistry, 165, 149–156. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.05.056.
Chiotelli, E., Pilosio, G., & Le Meste, M. (2002). Effect of sodium chloride on the gelatinization of starch: a multi measurement study. Biopolymers, 63(1), 41–58. doi:10.1002/bip.1061.
Choi, S. G., & Kerr, W. L. (2003a). Effect of chemical modification of wheat starch on molecular mobility as studied by pulsed 1H NMR. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft Und-Technologie-Food Science and Technology, 36, 105–112. doi:10.1094/cchem.2003.80.3.290.
Choi, S. G., & Kerr, W. L. (2003b). H-1 NMR studies of molecular mobility in wheat starch. Food Research International, 36(4), 341–348. doi:10.1016/s0963-9969(02)00225-9.
Choi, S. G., & Kerr, W. L. (2004). Swelling characteristics of native and chemically modified wheat starches as a function of heating temperature and time. Starch-Starke, 56(5), 181–189. doi:10.1002/star.200300233.
Curti, E., Bubici, S., Carini, E., Baroni, S., & Vittadini, E. (2011). Water molecular dynamics during bread staling by nuclear magnetic resonance. LWT--Food Science and Technology, 44(4), 854–859. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2010.11.021.
Curti, E., Carini, E., Tribuzio, G., & Vittadini, E. (2014). Bread staling: effect of gluten on physico-chemical properties and molecular mobility. LWT--Food Science and Technology, 59(1), 418–425. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2014.04.057.
Day, L., Fayet, C., & Homer, S. (2013). Effect of NaCl on the thermal behaviour of wheat starch in excess and limited water. Carbohydrate Polymers, 94(1), 31–37. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.12.063.
Donald, A. M. (2004). Understanding starch structure and functionality. In A.-C. Eliasson (Ed.), Starch in food: structure, function and applications (CRC press LLC ed (pp. 171–199). Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing Limited.
Doona, C. J., & Baik, M. Y. (2007). Molecular mobility in model dough systems studied by time-domain nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Journal of Cereal Science, 45(3), 257–262. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2006.07.015.
Eliasson, A. C. (1983). Differential scanning calorimetry studies on wheat starch-gluten mixtures. I. Effect of gluten on the gelatinization of wheat starch. Journal of Cereal Science, 1, 199–205.
Engelsen, S. B., Jensen, M. K., Pedersen, H. T., Norgaard, L., & Munck, L. (2001). NMR-baking and multivariate prediction of instrumental texture parameters in bread. Journal of Cereal Science, 33(1), 59–69. doi:10.1006/jcrs.2000.0343.
Fan, D. M., Ma, S. Y., Wang, L. Y., Zhao, H. F., Zhao, J. X., Zhang, H., et al. (2013). H-1 NMR studies of starch-water interactions during microwave heating. Carbohydrate Polymers, 97(2), 406–412. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.05.021.
Gallant, D. J., Bouchet, B., & Baldwin, P. M. (1997). Microscopy of starch: evidence of a new level of granule organization. Carbohydrate Polymers, 32(3–4), 177–191. doi:10.1016/s0144-8617(97)00008-8.
Hills, B., Costa, A., Marigheto, N., & Wright, K. (2005). T-1-T-2 NMR correlation studies of high-pressure-processed starch and potato tissue. Applied Magnetic Resonance, 28(1–2), 13–27.
Hoseney, R. C. (1994). Back to the basics—bread baking. Cereal Foods World, 39(3), 180–183.
Jenkins, P. J., & Donald, A. M. (1995). The influence of amylose on starch granule structure. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 17(6), 315–321. doi:10.1016/0141-8130(96)81838-1.
Jenkins, P. J., & Donald, A. M. (1998). Gelatinisation of starch: a combined SAXS/WAXS/DSC and SANS study. Carbohydrate Research, 308(1–2), 133–147. doi:10.1016/s0008-6215(98)00079-2.
Kontogiorgos, V. (2011). Microstructure of hydrated gluten network. Food Research International, 44(9), 2582–2586. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2011.06.021.
Le Botlan, D., Rugraff, Y., Martin, C., & Colonna, P. (1998). Quantitative determination of bound water in wheat starch by time domain NMR spectroscopy. Carbohydrate Research, 308(1–2), 29–36. doi:10.1016/s0008-6215(98)00068-8.
Le Grand, F., Cambert, M., & Mariette, F. (2007). NMR signal analysis to characterize solid, aqueous, and lipid phases in baked cakes. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55(26), 10947–10952. doi:10.1021/jf071735r.
Leach, H., Cowen, L., & Schoch, T. (1961). Structure of the starch granule. II Action of various amylases on granular starches. Cereal Chemistry, 36, 534–544.
Leon, A., Rosell, C. M., & de Barber, C. B. (2003). A differential scanning calorimetry study of wheat proteins. European Food Research and Technology, 217(1), 13–16. doi:10.1007/s00217-003-0699-y.
Luyts, A., Wilderjans, E., Waterschoot, J., Van Haesendonck, I., Brijs, K., Courtin, C. M., et al. (2013). Low resolution H-1 NMR assignment of proton populations in pound cake and its polymeric ingredients. Food Chemistry, 139(1–4), 120–128. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.01.062.
MacRitchie, F. (1976). The liquid-phase of dough and its role in baking. Cereal Chemistry, 53(3), 318–326.
Mariette, F., Davenel, A., Marchal, P., & Chaland, B. (1998). A study of water by NMR and MRI in dairy processes. Revue de l’Institut Francais du Petrole, 53(4), 521–525.
Marquardt, D.W. (1979). Algorithm for least-squares estimation of non-linear parameters. Current Contents/Engineering Technology & Applied Sciences (27), 14–14.
Meiboom, S., & Gill, D. (1958). Modified spin-echo method for measuring nuclear-relaxation times. Current Contents/Engineering Technology & Applied Sciences (38), 16–16.
Miller, R. A., & Hoseney, R. C. (2008). Role of salt in baking. Cereal Foods Word, 53(1), 4–6.
Ollett, A. L., Kirby, A. R., Clark, S. A., Parker, R., & Smith, A. C. (1993). The effect of water-content on the compaction behavior of potato starch. Starch-Starke, 45(2), 51–55. doi:10.1002/star.19930450205.
Ritota, M., Gianferri, R., Bucci, R., & Brosio, E. (2008). Proton NMR relaxation study of swelling and gelatinisation process in rice starch-water samples. Food Chemistry, 110(1), 14–22. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.01.048.
Roudaut, G., Farhat, I., Poirier-Brulez, F., & Champion, D. (2009). Influence of water, temperature and sucrose on dynamics in glassy starch-based products studied by low field H-1 NMR. Carbohydrate Polymers, 77(3), 489–495. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.01.029.
Rugraff, Y. L., Desbois, P., & LeBotlan, D. J. (1996). Quantitative analysis of wheat starch water suspensions by pulsed NMR spectroscopy measurements. Carbohydrate Research, 295, 185–194. doi:10.1016/s0008-6215(96)90140-8.
Steeneken, P. A. M. (1989). Rheological properties of aqueous suspensions of swollen starch granules. Carbohydrate Polymers, 11(1), 23–42. doi:10.1016/0144-8617(89)90041-6.
Tananuwong, K., & Reid, D. S. (2004). DSC and NMR relaxation studies of starch-water interactions during gelatinization. Carbohydrate Polymers, 58(3), 345–358. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2004.08.003.
Tang, H. R., Godward, J., & Hills, B. (2000). The distribution of water in native starch granules—a multinuclear NMR study. Carbohydrate Polymers, 43(4), 375–387. doi:10.1016/s0144-8617(00)00183-1.
Tang, H. R., Brun, A., & Hills, B. (2001). A proton NMR relaxation study of the gelatinisation and acid hydrolysis of native potato starch. Carbohydrate Polymers, 46(1), 7–18. doi:10.1016/s0144-8617(00)00265-4.
Uthayakumaran, S., Batey, I. L., Day, L., & Wrigley, C. W. (2011). Salt reduction in wheat-based foods—technical challenges and opportunities. Food Australia, 63(4), 137–140.
Wang, X., Choi, S. G., & Kerr, W. L. (2004). Water dynamics in white bread and starch gels as affected by water and gluten content. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft Und-Technologie-Food Science and Technology, 37(3), 377–384. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2003.10.008.
Wilhoft, E. M. (1973). Mechanism and theory of staling of bread and baked goods. And associated changes in textural properties. Journal of Texture Studies, 4, 292–322.
Zhu, W. X., Gayin, J., Chatel, F., Dewettinck, K., & Van der Meeren, P. (2009). Influence of electrolytes on the heat-induced swelling of aqueous dispersions of native wheat starch granules. Food Hydrocolloids, 23(8), 2204–2211. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2009.05.002.
Acknowledgments
This work was performed using the NMR facilities of the PRISM Research Platform (Rennes, France) which has been awarded an ISO 9001 certification for its activities related to research. The authors thank M. Pojic (FINS, Novi Sad, Serbia) for valuable comments concerning the starch impact on dough structure, as well as G. Collewet (Irstea, Rennes, France) for her help in performing ANOVA calculations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rondeau-Mouro, C., Cambert, M., Kovrlija, R. et al. Temperature-Associated Proton Dynamics in Wheat Starch-Based Model Systems and Wheat Flour Dough Evaluated by NMR. Food Bioprocess Technol 8, 777–790 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1445-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1445-0