Abstract
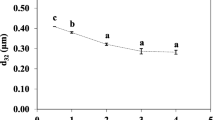
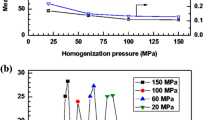
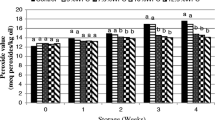
W/O/W emulsion is an emerging system in developing new functional and low-calorie food products. The aim of this study is to produce food-grade monodisperse water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) emulsions loaded with a hydrophilic bioactive oleuropein. W/O/W emulsions were prepared via high-pressure homogenization and subsequent microchannel (MC) emulsification. The internal aqueous phase was a 5-mM sodium phosphate buffer containing d(+)-glucose (5 wt.%) and oleuropein (0.1–0.7 wt.%). The oil phase consisted of soybean oil and tetraglycerin monolaurate condensed ricinoleic acid esters (TGCR; 3–8 wt.%). The external aqueous phase was a 5-mM sodium phosphate buffer containing d(+)-glucose (5 wt.%) and decaglycerol monolaurate (1 wt.%). Oleuropein-loaded submicron W/O emulsions with average droplet diameters as small as 0.15 μm and monomodal droplet size distributions were prepared by high-pressure homogenization when applying high TGCR concentrations of 5–8 wt.% and low oleuropein concentrations of 0.1–0.3 wt.%. Monodisperse oleuropein-loaded W/O/W emulsions with average W/O droplet diameters of around 27 μm and coefficients of variation of below 5 % were successfully prepared when using a silicon MC array plate with wide channels of 5-μm depth and 18-μm width. The monodisperse W/O/W emulsions prepared at high TGCR concentrations and low oleuropein concentrations were the most stable during 40 days of storage. The adsorption behavior of oleuropein at the internal aqueous–oil interface was relevant to W/O/W emulsions microstructure and stability. The results are believed to provide useful information for successfully preparing stable monodisperse W/O/W emulsions loaded with hydrophilic functional compounds. The surface activity of the loaded material seems to be a key parameter in optimizing the formulation of W/O/W food emulsion.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreadou, I., Iliodromitis, E. K., Mikros, E., Constantinou, M., Agalias, A., Magiatis, P., et al. (2006). The olive constituent oleuropein exhibits anti-ischemic, antioxidative, and hypolipidemic effects in anesthetized rabbits. The Journal of Nutrition, 136(8), 2213–2219.
Benavente-Garcı́a, O., Castillo, J., Lorente, J., Ortuño, A., & Del Rio, J. A. (2000). Antioxidant activity of phenolics extracted from Oleaeuropaea L. leaves. Food Chemistry, 68(4), 457–462.
Benichou, A., Aserin, A., & Garti, N. (2004). Double emulsions stabilized with hybrids of natural polymers for entrapment and slow release of active matters. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 20(108–109), 29–41.
Bonnet, M., Cansell, M., Berkaoui, A., Ropers, M. H., Anton, M., & Leal-Calderon, F. (2009). Release rate profiles of magnesium from multiple W/O/W emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids, 23(1), 92–101.
Charrouf, Z., & Guillaume, D. (2007). Phenols and polyphenols from Argania spinosa. American Journal of Food Technology, 2, 679–683.
Chu, B. S., Ichikawa, S., Kanafusa, S., & Nakajima, M. (2007). Preparation and characterization of β-carotene nanodispersions prepared by solvent displacement technique. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 55(16), 6754–6760.
Chuah, A. M., Kuroiwa, T., Kobayashi, I., & Nakajima, M. (2009). Effect of chitosan on the stability and properties of modified lecithin stabilized oil-in-water monodisperse emulsion prepared by microchannel emulsification. Food Hydrocolloid, 23(3), 600–610.
Dickinson, E. (2011). Double emulsions stabilized by food Biopolymers. Food Biophysics, 6(1), 1–11.
Durlu-Ozkaya, F., & Ozkaya, M. T. (2011). Oleuropein using as an additive for feed and products used for humans. Journal of Food Processing and Technology, 2(3), 113.
Han, J., Talorete, T., Yamada, P., & Isoda, H. (2009). Anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects of oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol on human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Cytotechnology, 59, 45–53.
Hemar, Y., Cheng, L. J., Oliver, C. M., Sanguansri, L., & Augustin, M. (2010). Encapsulation of resveratrol using water-in-oil-in-water double emulsions. Food Biophysics, 5(2), 120–127.
Iancu, M. N., Chevalie, Y., Popa, M., & Hamaide, T. (2009). Internally gelled W/O and W/O/W double emulsions. e-Polymers, 1(no. 099), 1–13.
Jager-Lezer, N., Terrisse, I., Bruneau, F., Tokgoz, S., Ferreira, L., Clausse, D., et al. (1997). Influence of lipophilic surfactant on the release kinetics of water-soluble molecules entrapped in a W/O/W multiple emulsions. Journal of Controllled Release, 45(1), 1–13.
Jemai, H., El Feki, A., & Sayadi, S. (2009). Antidiabetic and antioxidant effects of hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein from olive leaves in alloxan-diabetic rats. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 57(19), 8798–8804.
Kawakatsu, T., Tragardh, G., & Tragardh, C. (2001). Production of W/O/W emulsions and S/O/W pectin microcapsules by microchannel emulsification. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 189(1–3), 257–264.
Kumar, R., Kumar, M. S., & Mahdevan, N. (2012). Multiple emulsions: a review. International Journal of Recent Advances in Pharmaceutical Research, 2(1), 9–19.
Kobayashi, I., Lou, X., Mukataka, S., & Nakajima, M. (2005). Preparation of monodisperse aqueous-in-oil-in-aqueous emulsions using microfluidization and straight through microchannel emulsification. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society, 82(1), 65–71.
Kobayashi, I., Neves, M. A., Wada, Y., Uemura, K., & Nakajima, M. (2012). Large microchannel emulsification device for mass producing uniformly sized droplets on a liter per hour scale. Journal of Green Processing and Synthesis, 1, 353–362.
Kobayashi, I., Wada, Y., Uemura, K., & Nakajima, M. (2010). Microchannel emulsification for mass production of uniform fine droplets: integration of microchannel arrays on a chip. Microfluid Nanofluid, 8, 255–262.
Lutz, R., Aserin, A., Wicker, L., & Garti, N. (2009). Release of electrolytes from W/O/W double emulsions stabilized by a soluble complex of modified pectin and whey protein isolate. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 74(1), 178–185.
Markopoulos, C., Vertzoni, M., Agalias, A., Magiatis, P., & Reppas, C. (2009). Stability of oleuropein in the human proximal gut. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 61(2), 143–149.
Mataumoto, S., & Kang, W. W. (1989). Formation and applications of multiple emulsions. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 10(4–5), 455–482.
McClements DJ. (2005) Food emulsions principles, practices, and techniques (second edition). Boca Raton, CRC Press. p. 609.
Muschiolik, G. (2007). Multiple emulsions for food use. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 12(4–5), 213–220.
Mun, S., Choi, Y., Rho, S. J., Kang, C. G., Park, C. H., & Kim, Y. R. (2010). Preparation and characterization of water/oil/water emulsions stabilized by polyglycerol polyricinoleate and whey protein isolate. Journal of Food Science, 75(2), 116–125.
Nakashima, T., Shimizu, M., & Kukizaki, M. (2000). Particle control of emulsion by membrane emulsification and its applications. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 45(1), 47–56.
Okushima, S., Nisisako, T., Torii, T., & Higuchi, T. (2004). Controlled production of monodisperse double emulsions by two-step droplet breakup in microfluidic devices. Langmuir, 20(23), 9905–9908.
Richard, K., Apenten, O., & Zhu, Q. H. (1996). Interfacial parameters for spans and tweens in relation to aqueous-in-oil-in-aqueous multiple emulsion stability. Food Hydrocolloids, 10(2), 245–250.
Rodis, P. S., Karathanos, V. T., & Mantzavinou, A. (2002). Partitioning of olive oil antioxidants between oil and water phases. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 50(3), 596–601.
Saija, A., Trombetta, D., Tomaino, A., Cascio, R. L., Princi, P., Uccella, N., et al. (1998). `In vitro' evaluation of the antioxidant activity and biomembrane interaction of the plant phenols oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 166(2), 123–133.
Scherze, I., Knöfel, R., & Muschiolik, G. (2005). Automated image analysis as a control tool for multiple emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids, 19(3), 617–624.
Su, J., Flanagan, J., & Singh, H. (2008). Improving encapsulation efficiency and stability of water-in-oil-in-water emulsions using a modified gum arabic (Acacia (sen) SUPER GUM™). Food Hydrocolloids, 22(1), 112–120.
Sugiura, S., Nakajima, M., Ushijima, H., Yamamoto, K., & Seki, M. (2001). Preparation charachteristics of monodispersed water-in-oil emulsions using microchannel emulsification. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 34(6), 757–765.
Sugiura, S., Nakajima, M., & Seki, M. (2002). Effect of channel structure on microchannel emulsification. Langmuir, 18(15), 5708–5712.
Sugiura, S., Nakajima, M., Yamamoto, K., Iwamoto, S., Oda, T., Satake, M., et al. (2004). Preparation characteristics of water-in-oil-in-water multiple emulsions using microchannel emulsification. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 270(1), 221–228.
Van der Graaf, S., Schroën, C. G. P. H., & Boom, R. M. (2005). Preparation of double emulsions by membrane emulsification—a review. Journal of Membrane Science, 251(1–2), 7–15.
Villa, C. H., Lawson, L. B., Li, Y., & Papadopoulos, K. D. (2003). Internal coalescence as a mechanism of instability in water-in-oil-in-water double-emulsion globules. Langmuir, 19(2), 244–249.
Vladisavljević, G. T., & Williams, R. A. (2007). Multiple emulsions: technology and applications chapter 6. Recent developments in manufacturing particulate products from Double-emulsion templates using membrane and microfluidic devices. In A. Aserin (Ed.), Multiple emulsions. Technology and applications (pp. 121–164). New York: Wiley.
Vladisavljević, G. T., Shimizu, M., & Nakashima, T. (2006). Production of multiple emulsions for drug delivery systems by repeated SPG membrane homogenization: Influence of mean pore size, interfacial tension and continuous phase viscosity. Journal of Membrane Science, 284(1–2), 373–383.
Wang, Z., Neves, M. A., Yin, L.-J., Kobayashi, I., Uemura, K., & Nakajima, M. (2012). In vitro gastrointestinal digestibility of soybean oil–water emulsion droplets stabilized by polyglycerol esters of fatty acid. Food Science and Technology Research, 18(2), 149–156.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development (SATREPS) Project, financially supported by JICA and JST, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Souilem, S., Kobayashi, I., Neves, M.A. et al. Preparation of Monodisperse Food-Grade Oleuropein-Loaded W/O/W Emulsions Using Microchannel Emulsification and Evaluation of Their Storage Stability. Food Bioprocess Technol 7, 2014–2027 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-013-1182-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-013-1182-9