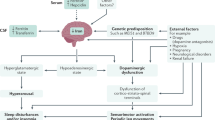
Opinion statement
In the past 10 years, restless legs syndrome (RLS) has gained recognition as a common sleep disorder. There are several therapeutic options in treating patients with RLS. RLS causes significant sleep disturbance and negatively impacts on patient quality of life. Pharmacologic treatment can result in improved sleep and quality of life issues. RLS patients should be evaluated for iron deficiency anemia; iron replacement in deficient patients may lead to a resolution of symptoms or may reduce the severity of their symptoms. For patients with daily symptoms, the initial therapy is dopamine agonists. Low doses given in the evening or 2 hours before bed provide adequate relief of symptoms for many RLS patients. Augmentation can be seen with all dopamine agents, but is most prevalent with levodopa. Levodopa therapy is best used for milder intermittent symptoms or in aggravating situations, such as long car rides. Opiates and antiepileptics remain a beneficial therapy for RLS and are useful in patients who experience pain as part of their RLS. Newer anticonvulsants may provide additional treatment options, but they have yet to undergo clinical trials. Intravenous iron also may provide relief of RLS symptoms; however, dosing and safety issues have not been fully evaluated in a RLS population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Ekbom KA: Restless legs syndrome. Neurology 1960, 10:868873.
Allen R, Hening W, Montplaisir J, et al.: Restless legs syndrome: diagnostic criteria, special considerations, and epidemiology. A report from the restless legs syndrome diagnosis and epidemiology workshop at the National Institute of Health. Sleep Med 2003, 4:101119. This paper provides an up-to-date review regarding diagnostic criteria, including criteria for children.
Saletu M, Anderer P, Saletu B, et al.: EEG mapping in patients with restless legs syndrome as compared with normal controls. Psychiatry Res 2002, 115:4961. One of many studies demonstrating that RLS significantly impacts quality of life.
Earley CJ: Clinical practice: restless legs syndrome. N Engl J Med 2003, 348:21032109. This paper is an excellent review of the disorder and treatment.
Thorpe M: Periodic limb movement disorder and restless leg syndrome. In The International Classification of Sleep Disorders Diagnostic and Coding Manual. Edited by Thorpe M. Lawrence: Allen Press; 1990:6571.
Bonati MT, Ferini-Strambi L, Aridon P, et al.: Autosomal dominant restless legs syndrome maps on chromosome 14q. Brain 2003, 126:14851492.
Desautels A, Turecki G, Montplaisir J, et al.: Identification of a major susceptibility locus for restless legs syndrome on chromosome 12q. Am J Hum Genet 2001, 69:12661270.
Tan EK, Seah A, See SJ, et al.: Restless legs syndrome in an Asian population: a study in Singapore. Mov Disord 2001, 16:577579.
Lavigne GJ, Montplaisir JY: Restless legs syndrome and sleep bruxism: prevalence and association among Canadians. Sleep 1994, 17:739743.
Winkelman JW, Chertow GM, Lazarus JM: Restless legs syndrome in end-stage renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis 1996, 28:372378.
Hui D, Wong T, Li T, et al.: Prevalence of sleep disturbances in Chinese patients with end stage renal failure on maintenance hemodialysis. Med Sci Monit 2002, 8:331336.
Winkelmann J, Stautner A, Samtleben W, Trenkwalder C: Long-term course of restless legs syndrome in dialysis patients after kidney transplantation. Mov Disord 2002, 17:10721076.
Manconi M, Govoni V, Cesnik E, et al.: Epidemiology of restless legs syndrome in a population of 606 pregnant women. Sleep 2003, 26:A330331.
Lee KA, Zaffke ME, Baratte-Beebe K: Restless legs syndrome and sleep disturbance during pregnancy: the role of folate and iron. J Womens Health Gend Based Med 2001, 10:335341.
O’Keeffe ST, Gavin K, Lavan JN: Iron status and restless legs syndrome in the elderly. Age Ageing 1994, 23:200203.
Sun ER, Chen CA, Ho G, et al.: Iron and the restless legs syndrome. Sleep 1998, 21:371377.
Comella CL: Restless legs syndrome: treatment with dopaminergic agents. Neurology 2002, 58:S87S92.
Silber MH, Shepard JW, Jr., Wisbey JA: Pergolide in the management of restless legs syndrome: an extended study. Sleep 1997, 20:878882.
Silber M, Girish M, Izurieta R: Pramipexole in the management of restless legs syndrome: an extended study. Sleep 2003, 26:819821. This study is just one of a few to provide long-term follow-up on treatment with evidence for augmentation; long-term studies will be essential.
Allen RP, Earley CJ: Augmentation of the restless legs syndrome with carbidopa/levodopa. Sleep 1996, 19:205213.
Hening W, Allen R, Earley C, et al.: The treatment of restless legs syndrome and periodic limb movement disorder: an American Academy of Sleep Medicine review. Sleep 1999, 22:970999. This review article provides an excellent overview of the clinical treatment studies done in RLS.
Garcia-Borreguero D, Larrosa O, de la Llave Y, et al.: Treatment of restless legs syndrome with gabapentin: a double-blind, crossover study. Neurology 2002, 59:15731579. Although gabapentin had been used for RLS, this provides clinical evidence for its efficacy.
Chervin RD, Archbold KH, Dillon JE, et al.: Associations between symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, restless legs, and periodic leg movements. Sleep 2002, 25:213218.
Kryger MH, Otake K, Foerster J: Low body stores of iron and restless legs syndrome: a correctable cause of insomnia in adolescents and teenagers. Sleep Med 2002, 3:127132.
Walters AS, Mandelbaum DE, Lewin DS, et al.: Dopaminergic therapy in children with restless legs/ periodic limb movements in sleep and ADHD. Dopaminergic Therapy Study Group. Pediatr Neurol 2000, 22:182186.
Phillips B, Young T, Finn L, et al.: Epidemiology of restless legs symptoms in adults. Arch Intern Med 2000, 160:21372141.
Ohayon MM, Roth T: Prevalence of restless legs syndrome and periodic limb movement disorder in the general population. J Psychosom Res 2002, 53:547554.
Earley CJ, Yaffee JB, Allen RP: Randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled trial of pergolide in restless legs syndrome. Neurology 1998, 51:15991602.
Telstad W, Sorensen O, Larsen S, et al.: Treatment of the restless legs syndrome with carbamazepine: a double blind study. BMJ 1984, 288:444446.
von Scheele C, Kempi V: Long-term effect of dopaminergic drugs in restless legs: a 2-year follow-up. Arch Neurol 1990, 47:12231224.
Benes H, Kurella B, Kummer J, et al.: Rapid onset of action of levodopa in restless legs syndrome: a double-blind, randomized, multicenter, crossover trial. Sleep 1999, 22:10731081.
Kaplan PW, Allen RP, Buchholz DW, Walters JK: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the treatment of periodic limb movements in sleep using carbidopa/ levodopa and propoxyphene. Sleep 1993, 16:717723.
Trenkwalder C, Collado Seidel V, Kazenwadel J, et al.: One-year treatment with standard and sustained-release levodopa: appropriate long-term treatment of restless legs syndrome? Mov Disord 2003, 18:11841189.
Wetter TC, Trenkwalder C, Stiasny K, et al.: [Treatment of idiopathic and uremic restless legs syndrome with L-dopa—a double-blind cross-over study]. Wien Med Wochenschr 1995, 145:525527.
Saletu M, Anderer P, Hogl B, et al.: Acute double-blind, placebo-controlled sleep laboratory and clinical follow-up studies with a combination treatment of rr-L-dopa and sr-L-dopa in restless legs syndrome. J Neural Transm 2003, 110:611626.
Wetter TC, Stiasny K, Winkelmann J, et al.: A randomized controlled study of pergolide in patients with restless legs syndrome. Neurology 1999, 52:944950.
Pieta J, Millar T, Zacharias J, et al.: Effect of pergolide on restless legs and leg movements in sleep in uremic patients. Sleep 1998, 21:617622.
Stiasny K, Wetter TC, Winkelmann J, et al.: Long-term effects of pergolide in the treatment of restless legs syndrome. Neurology 2001, 56:13991402.
Montplaisir J, Nicolas A, Denesle R, Gomez-Mancilla B: Restless legs syndrome improved by pramipexole: a double-blind randomized trial. Neurology 1999, 52:938943.
Happe S, Sauter C, Klosch G, et al.: Gabapentin versus ropinirole in the treatment of idiopathic restless legs syndrome. Neuropsychobiology 2003, 48:8286.
Ondo W: Ropinirole for restless legs syndrome. Mov Disord 1999, 14:138140.
Thorp ML, Morris CD, Bagby SP: A crossover study of gabapentin in treatment of restless legs syndrome among hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 2001, 38:104108.
Schenck CH, Mahowald MW: Long-term, nightly benzodiazepine treatment of injurious parasomnias and other disorders of disrupted nocturnal sleep in 170 adults. Am J Med 1996, 100:333337.
Bezerra ML, Martinez JV: Zolpidem in restless legs syndrome. Eur Neurol 2002, 48:180181.
Walters AS, Wagner ML, Hening WA, et al.: Successful treatment of the idiopathic restless legs syndrome in a randomized double-blind trial of oxycodone versus placebo. Sleep 1993, 16:327332.
Walters AS, Winkelmann J, Trenkwalder C, et al.: Longterm follow-up on restless legs syndrome patients treated with opioids. Mov Disord 2001, 16:11051109.
Earley CJ, Heckler D, Allen RP: IV iron treatment for the restless legs syndrome (RLS). Sleep 2001, 24:A359.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lesage, S., Earley, C.J. Restless legs syndrome. Curr Treat Options Neurol 6, 209–219 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-004-0013-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-004-0013-8