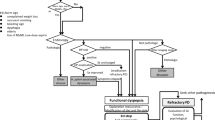
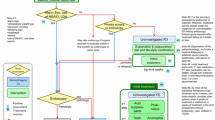
Opinion statement
Functional dyspepsia (FD) is a common reason a patient presents with upper gastrointestinal symptoms for medical care. Although treatment of FD remains expensive, the agents are rarely used in a systematic manner; the majority of treatments are empirical and the results short lived once therapy is ceased. This is partly due to the lack of consistent pathophysiologic markers in FD, so therapy is symptom driven. This review appraises the best evidence on available interventions. A structured scheme for deciding on appropriate therapies is to consider the possible putative pathophysiologic mechanisms. Eradicating Helicobacter pylori, if present, is a first-line strategy. In patients who have symptoms suggesting excessive gastric acid secretion, particularly epigastric pain, antisecretory agents are recommended. Prokinetics may confer benefits on symptoms suggestive of upper gastrointestinal dysmotility, like fullness or early satiety. However, their use is limited due to availability issues. The expanding field of psychologic therapies provides a promising avenue of treatment. Complementary medicines are now widely use and their benefits have been suggested in recent controlled trials. Emerging treatments include cholecystokinin 1 blockers, opioid receptor agonists, and serotonergic agents, although their application in FD is in the preliminary stages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Locke GR, 3rd: The epidemiology of functional gastrointestinal disorders in North America. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 1996, 25: 1–19.
Nyren O, Lindberg G, Lindstrom E, et al.: Economic costs of functional dyspepsia. Pharmacoeconomics 1992, 1: 312–324.
Moayyedi P, Mason J: Clinical and economic consequences of dyspepsia in the community. Gut 2002, 50(Suppl 4):iv10-iv12.
Stanghellini V, Tosetti C, Paternic A, et al.: Risk indicators of delayed gastric emptying of solids in patients with functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 1996, 110: 1036–1042.
Tack J, Caenepeel P, Fischler B, et al.: Symptoms associated with hypersensitivity to gastric distention in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 2001, 121: 526–535.
Samsom M, Verhagen MA, van Berge Henegouwen GP, et al.: Abnormal clearance of exogenous acid and increased acid sensitivity of the proximal duodenum in dyspeptic patients. Gastroenterology 1999, 116: 515–520.
Holtmann G, Siffert W, Haag S, et al.: G-protein beta 3 subunit 825 CC genotype is associated with unexplained (functional) dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 2004, 126: 971–979.
Talley NJ, Silverstein MD, Agreus L, et al.: AGA technical review: evaluation of dyspepsia. American Gastroenterological Association. Gastroenterology 1998, 114: 582–595.
Talley NJ, Quan C: Review article: Helicobacter pylori and nonulcer dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002, 16(Suppl 1):58–65.
MoayyediP, Soo S, Deeks J, et al.: Eradication of Helicobacter pylori for non-ulcer dyspepsia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005, 1: CD002096. The most comprehensive systematic review on this controversial subject. Updated regularly.
Chiba N, Van Zanten SJ, Sinclair P, et al.: Treating Helicobacter pylori infection in primary care patients with uninvestigated dyspepsia: the Canadian adult dyspepsia empiric treatment-Helicobacter pylori positive (CADET-Hp) randomised controlled trial.[see comment]. BMJ 2002, 324: 1012–1016.
Farkkila M, Sarna S, Valtonen V, et al.: Does the ‘test-and-treat’ strategy work in primary health care for management of uninvestigated dyspepsia? A prospective two-year follow-up study of 1552 patients. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 2004, 39: 327–335.
Moayyedi P, Delaney BC, Vakil N, et al.: The efficacy of proton pump inhibitors in nonulcer dyspepsia: A systematic review and economic analysis. Gastroenterology 2004, 127: 1329–1337.
Moayyedi P, Soo S, Deeks J, et al.: Systematic review: Antacids, H2-receptor antagonists, prokinetics, bismuth and sucralfate therapy for non-ulcer dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003, 17: 1215–1227. Useful overview of the merits of current pharmacological treatments for dyspepsia. Treatments are evaluated in comparison to each other as well as placebo.
Tatsuta M, Iishi H, Nakaizumi A, et al.: Effect of treatment with cisapride alone or in combination with domperidone on gastric emptying and gastrointestinal symptoms in dyspeptic patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1992, 6: 221–228.
Corinaldesi R, Stanghellini V, Raiti C, et al.: Effect of chronic administration of cisapride on gastric emptying of a solid meal and on dyspeptic symptoms in patients with idiopathic gastroparesis. Gut 1987, 28: 300–305.
Kellow JE, Cowan H, Shuter B, et al.: Efficacy of cisapride therapy in functional dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1995, 9: 153–160.
TackJ, Bisschops R, Sarnelli G: Pathophysiology and treatment of functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 2004, 127(4):1239–1255. Excellent overview of the current theories behind the mechanisms of functional dyspepisa.
Gotthard R, Bodemar G, Brodin U, et al.: Treatment with cimetidine, antacid, or placebo in patients with dyspepsia of unknown origin. Scand J Gastroenterol 1988, 23: 7–18.
Nyren O, Adami HO, Bates S, et al.: Absence of therapeutic benefit from antacids or cimetidine in non-ulcer dyspepsia. N Engl J Med 1986, 314: 339–343.
Moayyedi P, Soo S, Deeks J, et al.: Pharmacological interventions for non-ulcer dyspepsia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2004:CD001960.
Haug TT, Svebak S, Wilhelmsen I, et al.: Psychological factors and somatic symptoms in functional dyspepsia. A comparison with duodenal ulcer and healthy controls. J Psychosom Res 1994, 38: 281–291.
Talley NJ, Fung LH, Gilligan IJ, et al.: Association of anxiety, neuroticism, and depression with dyspepsia of unknown cause. A case-control study. Gastroenterology 1986, 90: 886–892.
Haug TT, Svebak S, Hausken T, et al.: Low vagal activity as mediating mechanism for the relationship between personality factors and gastric symptoms in functional dyspepsia. Psychosom Med 1994, 56: 181–186.
Lorena SL, Tinois E, Brunetto SQ, et al.: Gastric emptying and intragastric distribution of a solid meal in functional dyspepsia: influence of gender and anxiety. J Clin Gastroenterol 2004, 38: 230–236.
Camilleri M, Malagelada JR, Kao PC, et al.: Gastric and autonomic responses to stress in functional dyspepsia. Dig Dis Sci 1986, 31: 1169–1177.
Soo S, Moayyedi P, Deeks J, et al.: Psychological interventions for non-ulcer dyspepsia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2004:CD002301.
Haug TT, Wilhelmsen I, Svebak S, et al.: Psychotherapy in functional dyspepsia. J Psychosom Res 1994, 38: 735–744.
Hamilton J, Guthrie E, Creed F, et al.: A randomized controlled trial of psychotherapy in patients with chronic functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 2000, 119: 661–669.
Calvert EL, Houghton LA, Cooper P, et al.: Long-term improvement in functional dyspepsia using hypnotherapy. Gastroenterology 2002, 123: 1778–1785.
Bates S, Sjoden PO, Nyren O: Behavioral treatment of non-ulcer dyspepsia. Scand J Behav Ther 1988, 17: 155–165.
Jackson JL, O’Malley PG, Tomkins G, et al.: Treatment of functional gastrointestinal disorders with antidepressant medications: a meta-analysis. Am J Med 2000, 108: 65–72.
Loldrup D, Langemark M, Hansen HJ, et al.: Clomipramine and mianserin in chronic idiopathic pain syndrome. A placebo controlled study. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1989, 99: 1–7.
Mertz H, Fass R, Kodner A, et al.: Effect of amitriptyline on symptoms, sleep, and visceral perception in patients with functional dyspepsia. Am J Gastroenterol 1998, 93(2):160–165.
Tack J, Broekaert D, Coulie B, et al.: Influence of the selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitor, paroxetine, on gastric sensorimotor function in humans. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003, 17: 603–608.
Tindle HA, Davis RB, Phillips RS, et al.: Trends in use of complementary and alternative medicine by US adults: 1997–2002. Altern Ther Health Med 2005, 11: 42–49.
Holtmann G, Adam B, Haag S, et al.: Efficacy of artichoke leaf extract in the treatment of patients with functional dyspepsia: a six-week placebocontrolled, double-blind, multicentre trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003, 18: 1099–1105.
Thompson Coon J, Ernst E: Herbal medicinal products for non-ulcer dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002, 16: 1689–1699.
Melzer J, Rosch W, Reichling J, et al.: Meta-analysis: phytotherapy of functional dyspepsia with the herbal drug preparation STW 5 (Iberogast). Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004, 20: 1279–1287.
Tack J, Piessevaux H, Coulie B, et al.: Role of impaired gastric accommodation to a meal in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 1998, 115: 1346–1352.
Mertz H, Fullerton S, Naliboff B, et al.: Symptoms and visceral perception in severe functional and organic dyspepsia. Gut 1998, 42: 814–822.
Tack J, Coulie B, Wilmer A, et al.: Influence of sumatriptan on gastric fundus tone and on the perception of gastric distension in man. Gut 2000, 46: 468–473.
Tack J, Caenepeel P, Corsetti M, et al.: Role of tension receptors in dyspeptic patients with hypersensitivity to gastric distention. Gastroenterology 2004, 127: 1058–1066.
Camilleri M, Mayer EA, Drossman DA, et al.: Improvement in pain and bowel function in female irritable bowel patients with alosetron, a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1999, 13: 1149–1159.
Talley NJ, Van Zanten SV, Saez LR, et al.: A dose-ranging, placebo-controlled, randomized trial of alosetron in patients with functional dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2001, 15: 525–537.
Delvaux M, Louvel D, Lagier E, et al.: The kappa agonist fedotozine relieves hypersensitivity to colonic distention in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 1999, 116: 38–45.
Read NW, Abitbol JL, Bardhan KD, et al.: Efficacy and safety of the peripheral kappa agonist fedotozine versus placebo in the treatment of functional dyspepsia. Gut 1997, 41: 664–668.
Fraitag B, Homerin M, Hecketsweiler P: Double-blind dose-response multicenter comparison of fedotozine and placebo in treatment of nonulcer dyspepsia. Dig Dis Sci 1994, 39: 1072–1077.
Delgado-Aros S, Chial HJ, Cremonini F, et al.: Effects of asimadoline, a kappa-opioid agonist, on satiation and postprandial symptoms in health. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003, 18: 507–514.
Mansi C, Borro P, Giacomini M, et al.: Comparative effects of levosulpiride and cisapride on gastric emptying and symptoms in patients with functional dyspepsia and gastroparesis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000, 14: 561–569.
Distrutti E, Fiorucci S, Hauer SK, et al.: Effect of acute and chronic levosulpiride administration on gastric tone and perception in functional dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002, 16: 613–622.
Mearin F, Rodrigo L, Perez-Mota A, et al.: Levosulpiride and cisapride in the treatment of dysmotility-like functional dyspepsia: a randomized, double-masked trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004, 2: 301–308.
Tsubouchi T, Saito T, Mizutani F, et al.: Stimulatory action of itopride hydrochloride on colonic motor activity in vitro and in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2003, 306: 787–793. Epub 2003 Apr 30.
Holtmann G, Schnittker J, Boos G, et al.: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled dose finding study of Itopride for the treatment of patients with funcitonal dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 2004, 126: A-100.
Feinle C, Grundy D, Otto B, et al.: Relationship between increasing duodenal lipid doses, gastric perception, and plasma hormone levels in humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2000, 278: R1217-R1223.
Moran TH, Kinzig KP: Gastrointestinal satiety signals II. Cholecystokinin. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2004, 286: G183-G188.
Feinle C, Meier O, Otto B, et al.: Role of duodenal lipid and cholecystokinin A receptors in the pathophysiology of functional dyspepsia. Gut 2001, 48: 347–355.
Varga G: Dexloxiglumide Rotta Research Lab. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2002, 3: 621–626.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halder, S.L.S., Talley, N.J. Treatment of functional dyspepsia. Curr Treat Options Gastro 8, 325–336 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11938-005-0026-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11938-005-0026-8