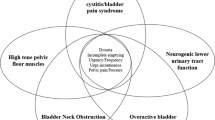
Abstract
Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS) is a prevalent chronic condition that can be challenging not only to diagnose but also to treat. We review recent diagnostic markers and therapies for IC/BPS from non-medication-based therapies, oral therapies, intravesical therapies, and surgical treatments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Parson JK, Parsons CL. The historical origins of interstitial cystitis. J Urol. 2004;171:20–2.
Skene AJC. Disease of the bladder and urethra in women. New York: Wm Wood; 1887. p. 167.
Hunner GL. A rare type of bladder ulcer in women: report of cases. Boston Med Surg J. 1915;172:660–4.
Hand JR. Interstitial cystitis: report of 223 cases (204 women and 19 men). J Urol. 1949;61:291–309.
Chrysanthopoulou EL, Doumouchtsis SK. Challenges and current evidence on the management of bladder pain syndrome. Neurourol Urodyn. 2013. doi:10.1002/nau.22475. Provides current evidence on the management of IC/BPS and provides definitions of IC/BPS according to different organization.
Hanno PM, Allen D, Burks JQ, Roger C, et al. AUA guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. J Urol. 2011;185:2162–70. AUA guidelines provide overall management strategy for IC/BPS based upon a systematic review of the literature.
Hanno P, Dmochowski R. Status of international consensus on interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome/painful bladder syndrome: 2008 snapshot. Neurourol Urodyn. 2009;28:274.
Braunstein R, Shapiro K, Kaye J, et al. The role of cystoscopy in the diagnosis of Hunner’s ulcer disease. J Urol. 2008;180:1383–6.
Koziol JA, Adams HP, Frutas A. Discrimination between the ulcerous and the nonulcerous forms of interstitial cystitis by non-invasive findings. J Urol. 1996;155:87–90.
Tomaszewski JE, Landi JR, Russack V, et al. Biopsy features are associated with primary symptoms in interstitial cystitis: results from the interstitial cystitis database study. Urology. 2001;57:67–81.
Peeker R, Fall M. Toward a precise definition of interstitial cystitis: further evidence of differences in classic and nonulcer disease. J Urol. 2002;167:2470–2.
Peeker R, Aldenborg F, Fall M. The treatment of interstitial cystitis with supratrigonal cystectomy and ileocystoplasty: difference in outcome between classic and nonulcer disease. J Urol. 1998;159:1479–82.
Warren JW, Wesselmann U, Morozov V, et al. Numbers and types of nonbladder syndromes as risk factors for interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Urology. 2011;77:313–9.
Clemens JQ, Meenan RT, O’Keefe-Rosetti MC, et al. Case-control study of medical comorbidities in women with interstitial cystitis. J Urol. 2008;179:2222–5.
Rodriguez MA, Afari N, Buchwald DS. Evidence for overlap between urological and nonurological unexplained clinical conditions. J Urol. 2013;189:S66–74.
Warren JW, van de Merwe JP, Nickel JC. Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and nonbladder syndromes: facts and hypotheses. Urology. 2011;78:727–32.
Chelimsky G, Heller E, Buffington CA, et al. Co-morbidities of interstitial cystitis. Front Neurosci. 2012;6:114.
Lifford KL, Curhan GC. Prevalence of painful bladder syndrome in older women. J Urol. 2008;73:494.
Rosenberg MT, Hazzard M. Prevalence of interstitial cystitis symptoms in women: a population based study in the primary care office. J Urol. 2005;174:2231–4.
Clemens JQ, Meenan RT, O’Keefe, et al. Prevalence of interstitial cystitis symptoms in a managed care population. J Urol. 2005;174:576–80.
Hanno PM. Chapter 12: bladder pain syndrome (interstitial cystitis) and related disorders. In: Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters AC, editors. Campbell-Walsh urology. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders/Elsevier; 2011. p. 357–401.
Berry SH, Elliott MN, Suttorp M, et al. Prevalence of symptoms of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis among adult females in the United States. J Urol. 2011;186:540–4.
Warren JW, Langenberg P, Greenberg P, et al. Sites of pain from interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. J Urol. 2008;180:1373–7.
Tripp DA, Nickel JC, Wong J, et al. Mapping of pain phenotypes in female patients with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis and controls. Eur Urol. 2012;62:1188–94.
Van De Merwe J, Nordling J, Bouchelouche P, et al. Diagnostic criteria, classification, and nomenclature for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: an ESSIC proposal. Eur Urol. 2008;53:60–7. Important paper on how to properly use the term IC/BPS.
Peters KM, Killinger KA, Carrico DJ, et al. Sexual function and sexual distress in women with interstitial cystitis: a case-control study. Urology. 2007;70:543–7.
Cole EE, Scarpero HM, Dmochowski RR. Are patient symptoms predictive of the diagnostic and/or therapeutic value of hydrodistention? Neurourol Urodyn. 2005;24:638–42.
Richter B, Hesse U, Hansen AB, et al. Bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis in a Danish population: a study using the 2008 criteria of the European society for the study of interstitial cystitis. BJU Int. 2010;105:660–7.
Keay S, Zhang C-O, Chai T, Warren J, Koch K, Grkovic D, et al. Antiproliferative factor, heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor, and epidermal growth factor in men with interstitial cystitis vs. chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Urology. 2004;63:22–6.
Erickson DR, Kunselman AR, Bentley CM, et al. Changes in urine markers and symptoms after bladder distention for interstitial cystitis. J Urol. 2007;177:556–60.
Chung SD, Liu HT, Lin H, et al. Elevation of serum C-reactive protein in patients with OAB and IC/BPS implies chronic inflammation in the urinary bladder. Neurourol Urodyn. 2011;30:417–20.
Kuo HC, Liu H, Tyagi P, Chancellor MB. Urinary nerve growth factor levels in urinary tract diseases with or without frequency urgency symptoms. LUTS. 2010;2:88–94.
Kuo HC. Potential urine and serum biomarkers for patients with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Int J Urol. 2014;21(1):34–41. Review of urine and serum biomarkers for IC/BPS.
Tyagi P, Killinger K, Tyagi V, et al. Urinary chemokines as noninvasive predictors of ulcerative interstitial cystitis. J Urol. 2012;187:2243–8.
Cervigni M, Natale F, Nasta L, Padoa A, Voi R, Porru D. A combined intravesical therapy with hyaluronic acid and chondroitin for refractory painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2008;19:943–7.
Giannantoni A, Bini V, Dmochowski R, et al. Contemporary management of the painful bladder: a systematic review. Eur Urol. 2012;61:29–53.
Shorter B, Lesser M, Moldwin R, et al. Effect of comestibles on symptoms of interstitial cystitis. J Urol. 2007;178:145–52.
Fisher BP, Bavendam TG, Roberts BW, et al. Blinded placebo controlled evaluation on the ingestion of acidic foods and their effect on urinary pH and the symptomatology of interstitial cystitis. Orlando: FL, NIDDK; 1993. p. 53.
Bassaly R, Downes K, Hart S. Dietary consumption triggers in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2011;17(1):36–9.
Peters DM, Carrico DJ, Kalinowski SE, et al. Prevalence of pelvic floor dysfunction in patients with interstitial cystitis. Urology. 2007;70:16.
Simons DG, Travell JG, Simons LS. Travell and Simons myofascial pain and dysfunction: the trigger point manual, vol. 1. 2nd ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins; 1999.
Fitzgerald MP, Anderson RU, Potts J, et al. Randomized multicenter feasibility trial of myofascial physical therapy for the treatment of urological chronic pelvic pain syndromes. J Urol. 2009;182:570.
Weiss JM. Pelvic floor myofascial trigger points: manual therapy for interstitial cystitis and the urgency-frequency syndrome. J Urol. 2001;166:2226–31.
Oyama IA, Rejba A, Lukban JC, et al. Modified Thiele massage as therapeutic intervention for female patients with interstitial cystitis and high-tone pelvic floor dysfunction. Urology. 2004;64:862.
Fitzgerald MP, Payne CK, Lukacz ES, et al. Randomized multicenter clinical trial of myofascial physical therapy in women with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome and pelvic floor tenderness. J Urol. 2012;187:2113–8. Demonstrated efficacy of myofascial physical therapy compared to therapeutic massage in relieving IC/BPS.
Van Ophoven A, Pokupic S, Heinecke A, et al. A prospective, randomized, placebo controlled, double blind study of amitriptyline for the treatment of interstitial cystitis. J Urol. 2004;172:533.
Foster Jr HE, Hanno PM, Nickel JC, et al. Effect of amitriptyline on symptoms in treatment naïve patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. J Urol. 2010;183:1853–8.
Lee JW, Han DY, Jeong HJ. Bladder pain syndrome treated with triple therapy with gabapentin, amitriptyline, and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Int Neurourol J. 2010;14:256–60.
Kwon WA, Ahn SH, Oh TA. Effect of low-dose triple therapy using gabapentin, amitriptyline, and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug for overactive bladder symptoms in patients with bladder pain syndrome. Int Neurourol J. 2013;17:78–82.
Thilagarajah R, Witherow RO, Walker MM. Oral cimetidine gives effective symptom relief in painful bladder disease: a prospective, randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled trial. BJU Int. 2001;87:207–12.
Seshadri P, Emerson L, Moarles A. Cimetidine in the treatment of interstitial cystitis. Urology. 1994;44:614–6.
Dasgupta P, Sharma SD, Womack C, et al. Cimetidine in painful bladder syndrome: a histopathological study. BJU Int. 2001;88:183–6.
Davis EL, El Khoudary SR, Talbott EO, et al. Safety and efficacy of the use of intravesical and oral pentosan polysulfate sodium for interstitial cystitis: a randomized double-blind clinical trial. J Urol. 2008;179(1):177–85.
Nickel JC, Barkin J, Forrest J, et al. Randomized, double-blind, dose-ranging study of pentosan polysulfate sodium for interstitial cystitis. Urology. 2005;65:654–8.
Sant GR, Propert KJ, Hanno PM, et al. A pilot clinical trial of oral pentosan polysulfate and oral hydroxyzine in patients with interstitial cystitis. J Urol. 2003;170:810–5.
Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development, L.L.C. Effectiveness and safety study of pentosan polysulfate sodium for the treatment of interstitial cystitis. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00086684.
Minogiannis P, El-Mansoury M, Betances JA, et al. Hydroxyzine inhibits neurogenic bladder mast cell activation. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1998;20:553–63.
Theoharides TC. Hydroxyzine in the treatment of interstitial cystitis. Urol Clin N Am. 1994;21:113–9.
Theoharides TC, Sant GR. Hydroxyzine therapy for interstitial cystitis. Urology. 1997;49:108.
Sairanen J, Forsell T, Ruutu M. Long-term outcome of patients with interstitial cystitis treated with low dose cyclosporine A. J Urol. 2004;171:2138–41.
Sairanen J, Tammela TL, Leppilahti M, et al. Cyclosporine A and pentosan polysulfate sodium for the treatment of interstitial cystitis: a randomized comparative study. J Urol. 2005;174:2235–8.
Forrest JB, Payne CK, Erickson DR. Cyclosporin A for refractory interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: experience of 3 tertiary centers. J Urol. 2012;188(4):1186–91.
Hefti FF, Rosenthal A, Walicke PA, et al. Novel class of pain drugs based on antagonism of NGF. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006;27:85.
Delafoy L, Taymond F, Doherty AM, et al. Role of nerve growth factor in the trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colonic hypersensitivity. Pain. 2003;105:489.
Lamb K, Kang YM, Gebhart GF, et al. Nerve growth factor and gastric hyperplasia in the rat. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2003;15:355.
Evans RJ, Moldwin RM, Cossons N, et al. Proof of concept trail of tanezumab for the treatment of symptoms associated with interstitial cystitis. J Urol. 2011;185(5):1716–21. Randomized, double blind study showing efficacy of tanezumab.
Teichman JM, Moldwin R. The role of the bladder surface in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Can J Urol. 2007;4:3599–607.
Parsons CL. The role of the urinary epithelium in the pathogenesis of interstitial cystitis/prostatitis/urethritis. Urology. 2007;69:9–16.
Parsons CL, Housley T, Schmidt JD, et al. Treatment of interstitial cystitis with intravesical heparin. Br J Urol. 1994;73:504–7.
Henry R, Patterson L, Avery N, et al. Absorption of alkalized intravesical lidocaine in normal and inflamed bladders: a simple method for improving bladder anesthesia. J Urol. 2001;165:1900–3.
Parsons CL. Successful downregulation of bladder sensory nerves with combination of heparin and alkalinized lidocaine in patients with interstitial cystitis. Urology. 2005;65(1):45–8.
Welk BK, Teichman JM. Dyspareunia response in patients with interstitial cystitis treated with intravesical lidocaine, bicarbonate, and heparin. Urology. 2008;71(1):67–70.
Nomiya A, Naruse T, Niimi A, et al. On- and post-treatment symptom relief by repeated instillations of heparin and alkalized lidocaine in interstitial cystitis. Int J Urol. 2013;20:1118–22.
Nickel JC, Egerdie RB, Steinhoff G, et al. A multi-center, randomized, double-blind, parallel group pilot evaluation of the efficacy and safety of intravesical sodium chondroitin sulfate versus vehicle control in patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Urol. 2010;76:804–9.
Nickel JC, Hanno P, Kumar K, et al. Second multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group evaluation of effectiveness and safety of intravesical chondroitin sulfate compared with inactive vehicle control in subjects with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Urology. 2012;79:1220–4.
Thakkinstian A, Nickel JC. Efficacy of intravesical chondroitin sulphate in treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS): individual patient data (IPD) meta-analytical approach.
Engelhardt PF, Morakis N, Daha LK, et al. Long-term results of intravesical hyaluronan therapy in bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Int Urogynecol J. 2011;22:401–5.
Interstitial Cystitis Association. Bioniche trial. 2003.
Reece JB, Urry L, Cain M, et al. Campbell biology (9th edition; international edition.). Harlow: Pearson Education; 2011.
Nickel JC et al. Intravesical alkalinized lidocaine (PSD597) offers sustained relief from symptoms of interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome. BJU Int. 2009;103:910–8. The major study in demonstrating the efficacy of intravesicular lidocaine.
Nickel JC, Jain P, Shore N, et al. Continuous intravesical lidocaine treatment for interstitial cystitis / bladder pain syndrome: safety and efficacy of a new drug delivery device. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:143ra100.
Nickel JC. Placebo controlled study of safety, tolerability, and efficacy of LiRIS in women with interstitial cystitis, followed by open label extension. IN: ClinicalTrails.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2000. Available from: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01475253. Cited 2014 Aug.
Lv YS, Zhou HL, Mao HP, et al. Intravesical hyaluronic acid, alkalinized lidocaine for the treatment of severe painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Int Urogynecol J. 2012;23:1715–20.
Jacob SW, Bischel M, Herschler RJ. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO): a new concept in pharmacotherapy. Curr Ther Res. 1964;6:134–5.
Perez-Marrero R, Emerson LE, Feltis JT. A controlled study of dimethyl sulfoxide in interstitial cystitis. J Urol. 1988;140:36–9.
Peeker R, Haghsheno MA, Holmang S, et al. Intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin and dimethyl sulfoxide for treatment of classic and nonulcer interstitial cystitis: a prospective, randomized double blind study. J Urol. 2000;164:1912–5.
Stav K, Beberashvili I, Lindner A, et al. Predictors of response to intravesical dimethyl-sulfoxide cocktail in patients with interstitial cystitis. Urology. 2012;80:61–5.
Hung MJ, Chet YT, Shen PS, et al. Risk factors that affect the treatment of interstitial cystitis using intravesical therapy with a dimethyl sulfoxide cocktail. Int Urogynecol J. 2012;23(11):1533–9.
Chuang YC, Tyagi P, Hunag CC, et al. Urodynamic and immunohistochemical evaluation of intravesical botulinum toxin A delivery using liposomes. J Urol. 2009;182:786–92.
Fraser MO, Chuang YC, Tyagi P, et al. Intravesical liposomes administration: a novel treatment for hyperactive bladder in the rat. Urology. 2003;61:656–63.
Chuang YC, Lee WC, Chiang PH. Intravesical liposome versus oral pentosan polysulfate for interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. J Urol. 2009;182:1393–400.
Lee WC, Chuang YC, Lee WC, et al. Safety and dose flexibility clinical evaluation of intravesical liposome in patients with interstitial cystitis or painful bladder syndrome. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2011;27:437–40.
Kaufman J, Lipella Pharmaceuticals Inc. Efficacy of Intravesical LP08 in patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. IN: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2000. Available from: http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01393223. NCT identifier: 01393223. Cited 2014 Aug.
Cruz F. Targets for botulinum toxin in the lower urinary tract. Neurourol Urodyn. 2014;33:31–8.
Rapp DE, Turk KW, Bales GT, et al. Botolinum toxin type a inhibits calcitonin gene-related peptide release from isolated rat bladder. J Urol. 2006;175:1138–42.
Kuo HC, Chancellor MB. Comparison of intravesical botulinum toxin A injections plus hydrodistention with hydrodistention alone for the treatment of refractory interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. BJU Int. 2009;1:1–5.
Kuo HC. Repeated onabotulinumtoxin-a injections provide better results than single injection in treatment of painful bladder syndrome. Pain Physician. 2013;16(1):15–23.
Pinto R, Lopes T, Silva J, et al. Persistent therapeutic effect of repeated injections of onabotulinum toxin a in refractory bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. J Urol. 2013;189:548–53.
Manning J, Dywer P, Rosamilia A, et al. A multicentre, prospective, randomized, double-blind study to measure the treatment effectiveness of abobotulinum A (AboBTXA) among women with refractory interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Int Urogynecol J. 2014;25:593–9.
Ottem DP, Teichman JM. What is the value of cystoscopy with hydrodistention for interstitial cystitis? Urology. 2005;66:494–9.
Hillelsohn JH, Rais-Bahrami S, Friedlander JI, et al. Fulguration for Hunner ulcers: long-term clinical outcomes. J Urol. 2012;188(6):2238–41.
Roffiem O, Hom D, Freid RM, et al. Use of the neodymium:YAG laser for interstitial cystitis: a prospective study. J Urol. 2001;166(1):134–6.
Cox M, Klutke JJ, Klutke CG. Assessment of patient outcomes following submucosal injection of triamcinolone for treatment of Hunner’s ulcer subtype interstitial cystitis. Can J Urol. 2009;16(2):4536–40.
Weiss JP, Mattei DM, Neville EC, et al. Primary treatment of radiation-induced hemorrhagic cystitis with hyperbaric oxygen: 10-year experience. J Urol. 1994;151(6):1514–7.
Hader JE, Marzella L, Myers RA, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment for experimental cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis. J Urol. 1993;149(6):1617–21.
Tanaka T, Nitta Y, Morimoto K, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis resistant to conventional treatments: long-term results of a case series in Japan. BMC Urol. 2011;11:11.
Gallego-Vilar D, Garcia-Fadrique G, Povo-Martin I, et al. Maintenance of the response to dimethyl sulfoxide treatment using hyperbaric oxygen in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome: a prospective, randomized, comparative study. Urol Int. 2013;9:411–6.
Shaker H, Wang Y, Loung D, et al. Role of C-afferent fibres in the mechanism of action of sacral nerve root neuromodulation in the chronic spinal cord injury. BJU Int. 2000;85:905–10.
Gajewski JM, Al-Zahrani AA. The long-term efficacy of sacral neuromodulation in the management of intractable cases of bladder pain syndrome: 14 years of experience in one centre. BJU Int. 2011;107(8):1258–64.
Ghazwani YQ, Elkelini MS, Hassouna MM. Efficacy of sacral neuromodulation in treatment of bladder pain syndrome: long-term follow-up. Neurourol Urodyn. 2011;30(7):1271–5. Summarizes the experience of neuromodulation for pain in IC/BPS.
Peters KM, Fever KM, Bennett RC. A prospective, single-blind, randomized crossover trial of sacral vs pudendal nerve stimulation for interstitial cystitis. BJU Int. 2007;100:835–9.
Gokyildiz S, Kizilkaya Beji N, Yalcin O, et al. Effects of percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation therapy on chronic pelvic pain. Gynecol Obstet Investig. 2012;73(2):99–105.
Peters KM, Jaeger C, Killinger KA, et al. Cystectomy for ulcerative interstitial cystitis: sequelae and patients’ perceptions of improvement. J Urol. 2013;82:829–33.
Rossberger J, Fall M, Jonsson O, et al. Long-term results of reconstructive surgery in patients with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis: subtyping is imperative. Urology. 2007;70:638.
Elliott CS, Payne CK. Interstitial cystitis and the overlap with overactive bladder. Curr Urol Rep. 2012;13(5):319–26.
Acknowledgments
Support from the Ministrelli Program for Urology Research and Education—MPURE is gratefully acknowledged.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
ᅟ
Conflict of Interest
Avinash Chennamsetty, Kim Killinger, Michael Ehlert, and Kenneth Peters have no conflicts of interest relevant to this work.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Genitourinary Infections
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chennamsetty, A., Ehlert, M.J., Peters, K.M. et al. Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment of Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome. Curr Infect Dis Rep 17, 454 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11908-014-0454-5
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11908-014-0454-5
Keywords
- Interstitial cystitis
- Bladder pain syndrome
- Hunner’s ulcer
- Non-bladder syndromes
- Urine biomarkers
- Diet
- Pelvic floor physical therapy
- Amitriptyline
- Cimetidine
- Pentosan polysulfate
- Hydroxyzine
- Cyclosporine A
- Tanezumab
- Dimethylsulfoxide
- Heparin
- Glycosaminoglycans
- Lidocaine
- Liposomes
- Botulinum toxin
- Hydrodistention
- Fulguration
- Hyperbaric oxygen
- Neuromodulation
- Surgical reconstruction