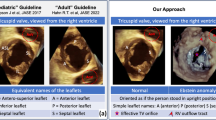
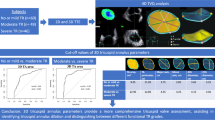
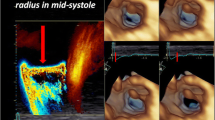
Abstract
Purpose of Review
This review article provides an overview of the various roles of 3-dimensional (3D) echocardiography in the evaluation of the tricuspid valve (TV) with specific focus on tricuspid regurgitation (TR) and its treatment.
Recent Findings
The prognostic implications of TR and the advent of new transcatheter therapies have underscored the need of accurate assessment of the TV.
Summary
3D echocardiography is key to assess the anatomy and function of TV and has provided new insights that have led to new classifications of the type of TR. Furthermore, 3D echocardiography is superior to 2-dimensional echocardiography to assess the right ventricle, an important parameter to select the patients with severe TR who may benefit from intervention. Finally, the use of 3D echocardiography during the guidance of transcatheter interventions is pivotal to ensure procedural success and minimize the complications. Three-dimensional echocardiography provides the soft tissue resolution that fluoroscopy does not provide.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Nath J, Foster E, Heidenreich PA. Impact of tricuspid regurgitation on long-term survival. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:405–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2003.09.036.
Hahn RT. State-of-the-art review of echocardiographic imaging in the evaluation and treatment of functional tricuspid regurgitation. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.116.005332.
Prihadi EA, van der Bijl P, Gursoy E, Abou R, Mara Vollema E, Hahn RT, et al. Development of significant tricuspid regurgitation over time and prognostic implications: new insights into natural history. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:3574–81. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehy3524.
Rodes-Cabau J, Taramasso M, O’Gara PT. Diagnosis and treatment of tricuspid valve disease: current and future perspectives. Lancet. 2016;388:2431–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00740-6.
Addetia K, Muraru D, Badano LP, Lang RM. New directions in right ventricular assessment using 3-dimensional echocardiography. JAMA Cardiol. 2019;4:936–44. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2019.2424.
•• Praz F, Muraru D, Kreidel F, Lurz P, Hahn RT, Delgado V, et al. Transcatheter treatment for tricuspid valve disease. EuroIntervention. 2021;17:791–808. https://doi.org/10.4244/EIJ-D-21-00695. Landmark review article highlighting the need for standardization in the assessment of the mechanisms of severe tricuspid regurgitation.
Muraru D, Hahn RT, Soliman OI, Faletra FF, Basso C, Badano LP. 3-Dimensional echocardiography in imaging the tricuspid valve. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019;12:500–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.10.035.
Peters AC, Gong FF, Rigolin VH. Three-dimensional echocardiography for the assessment of the tricuspid valve. Echocardiography. 2020;37:758–68. https://doi.org/10.1111/echo.14658.
Hahn RT, Weckbach LT, Noack T, Hamid N, Kitamura M, Bae R, et al. Proposal for a standard echocardiographic tricuspid valve nomenclature. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021;14:1299–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmg.2021.01.012.
Muraru D, Veronesi F, Maddalozzo A, Dequal D, Frajhof L, Rabischoffsky A, et al. 3D printing of normal and pathologic tricuspid valves from transthoracic 3D echocardiography data sets. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017;18:802–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjci/jew215.
Prihadi EA, Delgado V, Leon MB, Enriquez-Sarano M, Topilsky Y, Bax JJ. Morphologic types of tricuspid regurgitation: characteristics and prognostic implications. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019;12:491–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.09.027.
• Utsunomiya H, Harada Y, Susawa H, Takahari K, Ueda Y, Izumi K, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of tricuspid regurgitation location and severity using vena contracta analysis: a color Doppler three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiographic study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2019;32(1526–1537):e1522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.echo.2019.07.022. This article highlights the importance of using 3-dimensional echocardiography to assess the severity of tricuspid regurgitation in various clinical scenarios.
Lancellotti P, Pibarot P, Chambers J, La Canna G, Pepi M, Dulgheru R, et al. Multi-modality imaging assessment of native valvular regurgitation: an EACVI and ESC council of valvular heart disease position paper. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022;23:e171–232. https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjci/jeab253.
Velayudhan DE, Brown TM, Nanda NC, Patel V, Miller AP, Mehmood F, et al. Quantification of tricuspid regurgitation by live three-dimensional transthoracic echocardiographic measurements of vena contracta area. Echocardiography. 2006;23:793–800. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-8175.2006.00314.x.
Chen TE, Kwon SH, Enriquez-Sarano M, Wong BF, Mankad SV. Three-dimensional color Doppler echocardiographic quantification of tricuspid regurgitation orifice area: comparison with conventional two-dimensional measures. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2013;26:1143–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.echo.2013.07.020.
Chouchani M, Michaelsen J, Langenbrink L, Piatkowski M, Altiok E, Hoffmann R. Quantification of tricuspid regurgitation area by 3-dimensional color Doppler echocardiography considering different clinical settings. Echocardiography. 2020;37:1120–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/echo.14765.
Sheehan F, Redington A. The right ventricle: anatomy, physiology and clinical imaging. Heart. 2008;94:1510–5. https://doi.org/10.1136/hrt.2007.132779.
Muraru D, Spadotto V, Cecchetto A, Romeo G, Aruta P, Ermacora D, et al. New speckle-tracking algorithm for right ventricular volume analysis from three-dimensional echocardiographic data sets: validation with cardiac magnetic resonance and comparison with the previous analysis tool. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016;17:1279–89. https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjci/jev309.
Dahou A, Levin D, Reisman M, Hahn RT. Anatomy and physiology of the tricuspid valve. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019;12:458–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.07.032.
•• Fortuni F, Marques AI, Bax JJ, Ajmone Marsan N, Delgado V. Echocardiography-computed tomography fusion imaging for guidance of transcatheter tricuspid valve annuloplasty. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020;21:937–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjci/jeaa054. This article shows cutting-edge technology applied to computed tomography that permits live guidance of transcatheter interventions for tricuspid regurgitation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Victoria Delgado received speaker fees from Abbott Vascular, Edwards Lifesciences, GE Healthcare, Medtronic, Novartis, and MSD; consulting fees from Novo Nordisk and Edwards Lifesciences; and research grants from Abbott Vascular, Edwards Lifesciences, and GE Healthcare. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Echocardiography
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Escabia, C., Bayes-Genis, A. & Delgado, V. Three-Dimensional Echocardiography for Tricuspid Valve Assessment. Curr Cardiol Rep 24, 1611–1618 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11886-022-01780-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11886-022-01780-8