Abstract
Recent advances in genetics and technology have led to breakthroughs in understanding the genes that predispose individuals to autoimmune diseases. A common haplotype of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 (STAT4) gene has been shown to be associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and primary Sjögren’s syndrome. STAT4 is a transcription factor that transduces interleukin-12, interleukin-23, and type 1 interferon cytokine signals in T cells and monocytes, leading to T-helper type 1 and T-helper type 17 differentiation, monocyte activation, and interferon-γ production. Although the evidence for this association is very strong and well replicated, the exact mechanism by which polymorphisms in this gene lead to disease remains unknown. In concert with the identification of other disease-associated loci, elucidating how the variant form of STAT4 modulates immune function should lead to an improved understanding of the pathophysiology of autoimmunity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Vyse TJ, Todd JA: Genetic analysis of autoimmune disease. Cell 1996, 85:311–318.
Goronzy J, Weyand CM, Fathman CG: Shared T cell recognition sites on human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen class II molecules of patients with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest 1986, 77:1042–1049.
Harley JB, Kelly JA, Kaufman KM: Unraveling the genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus. Springer Semin Immunopathol 2006, 28:119–130.
Jawaheer D, Seldin MF, Amos CI, et al.: A genomewide screen in multiplex rheumatoid arthritis families suggests genetic overlap with other autoimmune diseases. Am J Hum Genet 2001, 68:927–936.
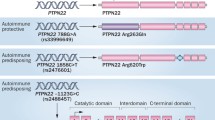
Bottini N, Musumeci L, Alonso A, et al.: A functional variant of lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase is associated with type I diabetes. Nat Genet 2004, 36:337–338.
Begovich AB, Carlton VE, Honigberg LA, et al.: A missense single-nucleotide polymorphism in a gene encoding a protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPN22) is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Hum Genet 2004, 75:330–337.
Vang T, Miletic AV, Bottini N, Mustelin T: Protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN22 in human autoimmunity. Autoimmunity 2007, 40:453–461.
Kyogoku C, Langefeld CD, Ortmann WA, et al.: Genetic association of the R620W polymorphism of protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN22 with human SLE. Am J Hum Genet 2004, 75:504–507.
Plenge RM, Seielstad M, Padyukov L, et al.: TRAF1-C5 as a risk locus for rheumatoid arthritis—a genomewide study. N Engl J Med 2007, 357:1199–1209.
Plenge RM, Cotsapas C, Davies L, et al.: Two independent alleles at 6q23 associated with risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet 2007, 39:1477–1482.
Thomson W, Barton A, Ke X, et al.: Rheumatoid arthritis association at 6q23. Nat Genet 2007, 39:1431–1433.
Harley JB, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Criswell LA, et al.: Genome-wide association scan in women with systemic lupus erythematosus identifies susceptibility variants in ITGAM, PXK, KIAA1542 and other loci. Nat Genet 2008, 40:204–210.
Hom G, Graham RR, Modrek B, et al.: Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with C8orf13-BLK and ITGAM-ITGAX. N Engl J Med 2008, 358:900–909.
Kozyrev SV, Abelson AK, Wojcik J, et al.: Functional variants in the B-cell gene BANK1 are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 2008, 40:211–216.
van Heel DA, Franke L, Hunt KA, et al.: A genome-wide association study for celiac disease identifies risk variants in the region harboring IL2 and IL21. Nat Genet 2007, 39:827–829.
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium: Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 2007, 447:661–678.
Zhernakova A, Alizadeh BZ, Bevova M, et al.: Novel association in chromosome 4q27 region with rheumatoid arthritis and confirmation of type 1 diabetes point to a general risk locus for autoimmune diseases. Am J Hum Genet 2007, 81:1284–1288.
Amos CI, Chen WV, Lee A, et al.: High-density SNP analysis of 642 Caucasian families with rheumatoid arthritis identifies two new linkage regions on 11p12 and 2q33. Genes Immun 2006, 7:277–286.
Remmers EF, Plenge RM, Lee AT, et al.: STAT4 and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 2007, 357:977–986.
Barton A, Thomson W, Ke X, et al.: Re-evaluation of putative rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility genes in the post-genome wide association study era and hypothesis of a key pathway underlying susceptibility. Hum Mol Genet 2008 Apr 22 (Epub ahead of print).
Kurreeman FA, Padyukov L, Marques RB, et al.: A candidate gene approach identifies the TRAF1/C5 region as a risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS Med 2007, 4:e278.
Kallberg H, Padyukov L, Plenge RM, et al.: Gene-gene and gene-environment interactions involving HLA-DRB1, PTPN22, and smoking in two subsets of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Hum Genet 2007, 80:867–875.
Lee HS, Remmers EF, Le JM, et al.: Association of STAT4 with rheumatoid arthritis in the Korean population. Mol Med 2007, 13:455–460.
Palomino-Morales RJ, Rojas-Villarraga A, Gonzalez CI, et al.: STAT4 but not TRAF1/C5 variants influence the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus in Colombians. Genes Immun 2008, 9:379–382.
Cantor RM, Yuan J, Napier S, et al.: Systemic lupus erythematosus genome scan: support for linkage at 1q23, 2q33, 16q12–13, and 17q21–23 and novel evidence at 3p24, 10q23–24, 13q32, and 18q22–23. Arthritis Rheum 2004, 50:3203–3210.
Taylor KE, Remmers E, Lee A, et al.: Specificity of the STAT4 genetics association with severe disease manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS Genet 2008, 4:e1000084.
Korman BD, Alba MI, Le JM, et al.: Variant form of STAT4 is associated with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Genes Immun 2008, 9:267–270.
Li Y, Wu B, Xiong H, et al.: Polymorphisms of STAT-6, STAT-4 and IFN-gamma genes and the risk of asthma in Chinese population. Respir Med 2007, 101:1977–1981.
Pykalainen M, Kinos R, Valkonen S, et al.: Association analysis of common variants of STAT6, GATA3, and STAT4 to asthma and high serum IgE phenotypes. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005, 115:80–87.
Park BL, Cheong HS, Kim LH, et al.: Association analysis of signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 (STAT4) polymorphisms with asthma. J Hum Genet 2005, 50:133–138.
Horvath CM: STAT proteins and transcriptional responses to extracellular signals. Trends Biochem Sci 2000, 25:496–502.
Watford WT, Hissong BD, Bream JH, et al.: Signaling by IL-12 and IL-23 and the immunoregulatory roles of STAT4. Immunol Rev 2004, 202:139–156.
Grusby MJ: Stat4-and Stat6-deficient mice as models for manipulating T helper cell responses. Biochem Soc Trans 1997, 25:359–360.
Jacob CO, Zang S, Li L, et al.: Pivotal role of Stat4 and Stat6 in the pathogenesis of the lupus-like disease in the New Zealand mixed 2328 mice. J Immunol 2003, 171:1564–1571.
Singh RR, Saxena V, Zang S, et al.: Differential contribution of IL-4 and STAT6 vs STAT4 to the development of lupus nephritis. J Immunol 2003, 170:4818–4825.
Finnegan A, Grusby MJ, Kaplan CD, et al.: IL-4 and IL-12 regulate proteoglycan-induced arthritis through Stat-dependent mechanisms. J Immunol 2002, 169:3345–3352.
Behera AK, Kumar M, Lockey RF, Mohapatra SS: Adenovirus-mediated interferon gamma gene therapy for allergic asthma: involvement of interleukin 12 and STAT4 signaling. Hum Gene Ther 2002, 13:1697–1709.
Hildner KM, Schirmacher P, Atreya I, et al.: Targeting of the transcription factor STAT4 by antisense phosphorothioate oligonucleotides suppresses collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol 2007, 178:3427–3436.
Nandakumar KS, Holmdahl R: Arthritis induced with cartilage-specific antibodies is IL-4-dependent. Eur J Immunol 2006, 36:1608–1618.
Klinman DM, Gursel I, Klaschik S, et al.: Therapeutic potential of oligonucleotides expressing immunosuppressive TTAGGG motifs. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2005, 1058:87–95.
Shirota H, Gursel M, Klinman DM: Suppressive oligodeoxynucleotides inhibit Th1 differentiation by blocking IFN-gamma-and IL-12-mediated signaling. J Immunol 2004, 173:5002–5007.
Thierfelder WE, van Deursen JM, Yamamoto K, et al.: Requirement for Stat4 in interleukin-12-mediated responses of natural killer and T cells. Nature 1996, 382:171–174.
Fukao T, Frucht DM, Yap G, et al.: Inducible expression of Stat4 in dendritic cells and macrophages and its critical role in innate and adaptive immune responses. J Immunol 2001, 166:4446–4455.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korman, B.D., Kastner, D.L., Gregersen, P.K. et al. STAT4: Genetics, mechanisms, and implications for autoimmunity. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 8, 398–403 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-008-0077-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-008-0077-8