Abstract
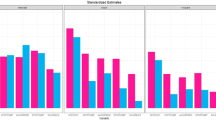
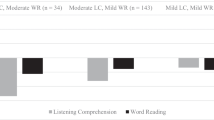
Few studies have systematically investigated the reading skill profiles of English learners (ELs) in late elementary school, a critical developmental period for language and literacy and the most common grades for initial identification with specific learning disabilities (O’Connor et al., Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 28(3), 98–112, 2013). We investigated the reading skill profiles of 331 ELs in 3rd and 4th grades, including ELs with and without risk for dyslexia due to significant deficits in word and pseudo-word reading accuracy and fluency. We utilized latent profile analysis and factor mixture modeling to investigate (1) the nature and distribution of reading skill profiles; (2) whether these profiles were associated with differences in reading comprehension growth across one academic year; and (3) the stability of reading profiles across an academic year. We selected a two-class solution (reading disabled and typically developing) based on model fit indices, theoretical considerations, pattern of results across profile-solutions and time-points, and parameterizations, making the approach stronger and more generalizable. These classes demonstrated clear, consistent differences in performance across reading component skills, with the RD class scoring consistently below the TD class across code-based and meaning-based domains of reading. Across the year, the TD class demonstrated significantly higher patterns of growth in reading comprehension (χ2 (1) = 206.21, p < 0.001). Class membership was largely stable (97% of participants maintain class membership). These results suggest that ELs with risk for dyslexia demonstrate multiple component skill deficits that may require long-term, comprehensive, intensive interventions to remediate.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asparouhov, T., & Muthén, B. (2014). Auxiliary variables in mixture modeling: Using the BCH method in Mplus to estimate a distal outcome model and an arbitrary secondary model. Mplus Web Notes, 21(2), 1–22.
August, D., Shanahan, T., & Escamilla, K. (2009). English language learners: Developing literacy in second language learners—report of the National Literacy Panel on Language-Minority Children and Youth. Journal of Literacy Research, 41(4), 432–452.
Bakk, Z., & Vermunt, J. K. (2016). Robustness of stepwise latent class modeling with continuous distal outcomes. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 23(1), 20–31.
Betts, J., Bolt, S., Decker, D., Muyskens, P., & Marston, D. (2009). Examining the role of time and language type in reading development for English language learners. Journal of School Psychology, 47(3), 143–166.
Bialystok, E. (2007). Acquisition of literacy in bilingual children: A framework for research. Language Learning, 57, 45–77.
Bolck, A., Croon, M., & Hagenaars, J. (2004). Estimating latent structure models with categorical variables: One-step versus three-step estimators. Political analysis, 3–27.
Brasseur-Hock, I. F., Hock, M. F., Kieffer, M. J., Biancarosa, G., & Deshler, D. D. (2011). Adolescent struggling readers in urban schools: Results of a latent class analysis. Learning and Individual Differences, 21(4), 438–452.
Buly, M. R., & Valencia, S. W. (2002). Below the bar: Profiles of students who fail state reading assessments. Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 24(3), 219–239.
Burr, E., Haas, E., & Ferriere, K. (2015). Identifying and supporting english learner students with learning disabilities: Key issues in the literature and state practice. REL 2015–086. Regional Educational Laboratory West.
Capin, P., Cho, E., Miciak, J., Roberts, G., & Vaughn, S. (2021). Examining the reading and cognitive profiles of students with significant reading comprehension difficulties. Learning Disability Quarterly, 44(3), 183–196.
Catts, H. W., Adlof, S. M., & Weismer, S. E. (2006). Language deficits in poor comprehenders: A case for the simple view of reading.
Chall, J. S., & Jacobs, V. A. (1983). Writing and reading in the elementary grades: Developmental trends among low SES children. Language Arts, 60(5), 617–626.
Cirino, P. T., Romain, M. A., Barth, A. E., Tolar, T. D., Fletcher, J. M., & Vaughn, S. (2013). Reading skill components and impairments in middle school struggling readers. Reading and Writing, 26(7), 1059–1086.
Cho, E., Capin, P., Roberts, G., Roberts, G. J., & Vaughn, S. (2019). Examining sources and mechanisms of reading comprehension difficulties: Comparing English learners and non-English learners within the simple view of reading. Journal of Educational Psychology, 111(6), 982.
Cho, E., Roberts, G. J., Capin, P., Roberts, G., Miciak, J., & Vaughn, S. (2015). Cognitive attributes, attention, and self-efficacy of adequate and inadequate responders in a fourth grade reading intervention. Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 30(4), 159–170.
Clark, S. L., Muthén, B., Kaprio, J., D’Onofrio, B. M., Viken, R., & Rose, R. J. (2013). Models and strategies for factor mixture analysis: An example concerning the structure underlying psychological disorders. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 20(4), 681–703.
Clemens, N. H., Simmons, D., Simmons, L. E., Wang, H., & Kwok, O. M. (2017). The prevalence of reading fluency and vocabulary difficulties among adolescents struggling with reading comprehension. Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment, 35(8), 785–798.
Croon, M. (2002). Ordering the classes. Applied latent class analysis, 137–162.
Cummins, J. (2000). Immersion education for the millennium: What we have learned from 30 years of research on second language immersion. In M. R. Childs & R. M. Bostwick (Eds.) Learning through two languages: Research and practice. Second Katoh Gakuen International Symposium on Immersion and Bilingual Education. (pp. 34–47). Katoh Gakuen, Japan.
Donovan, S., & Cross, C. (Eds.). (2002). Minority students in special and gifted education. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Duke, N., & Carlisle, J. F. (2011). Comprehension Development. Handbook of Reading Research, 4, 199–228.
Elliott, J. G., & Grigorenko, E. L. (2014). The dyslexia debate (No. 14). Cambridge University Press.
Ferguson, S. L., Moore, G., & E. W., & Hull, D. M. (2020). Finding latent groups in observed data: A primer on latent profile analysis in Mplus for applied researchers. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 44(5), 458–468.
Francis, D. J., Rivera, M., Lesaux, N., Kieffer, M., & Rivera, H. (2006). Based Recommendations for Instruction and Academic Interventions. Practical Guidelines for the Education of English Language Learners. Book 1 of 3. Center on Instruction.
Geva, E., & YaghoubZadeh, Z. (2006). Reading efficiency in native English-speaking and English-as-a-second-language children: The role of oral proficiency and underlying cognitive-linguistic processes. Scientific Studies of Reading, 10(1), 31–57.
Gough, P. B., & Tunmer, W. E. (1986). Decoding, reading, and reading disability. Remedial and Special Education, 7(1), 6–10.
Gottardo, A., & Mueller, J. (2009). Are first-and second-language factors related in predicting second-language reading comprehension? A study of Spanish-speaking children acquiring English as a second language from first to second grade. Journal of Educational Psychology, 101(2), 330.
Hall, C., Steinle, P. K., & Vaughn, S. (2019). Reading instruction for English learners with learning disabilities: What do we already know, and what do we still need to learn? New Directions for Child and Adolescent Development, 2019(166), 145–189.
Henson, J. M., Reise, S. P., & Kim, K. H. (2007). Detecting mixtures from structural model differences using latent variable mixture modeling: A comparison of relative model fit statistics. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 14(2), 202–226.
Hoover, W. A., & Gough, P. B. (1990). The simple view of reading. Reading and Writing, 2(2), 127–160.
Hoover, J. J., Erickson, J. R., Patton, J. R., Sacco, D. M., & Tran, L. M. (2019). Examining IEPs of English learners with learning disabilities for cultural and linguistic responsiveness. Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 34(1), 14–22.
Jean, M., & Geva, E. (2009). The development of vocabulary in English as a second language children and its role in predicting word recognition ability. Applied Psycholinguistics, 30(1), 153–185.
Jeon, E. H., & Yamashita, J. (2014). L2 reading comprehension and its correlates: A meta-analysis. Language Learning, 64(1), 160–212.
Johnson, E. S., Jenkins, J. R., Petscher, Y., & Catts, H. W. (2009). How can we improve the accuracy of screening instruments? Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 24(4), 174–185.
Kaufman, A. S., & Kaufman, N. L. (2014). Technical & interpretive manual: Kaufman Test of Educational Achievement (3rd ed.). NCS Pearson.
Kieffer, M. J., & Lesaux, N. K. (2008). The role of derivational morphology in the reading comprehension of Spanish-speaking English language learners. Reading and Writing, 21(8), 783–804.
Klem, M., Melby-Lervåg, M., Hagtvet, B., Lyster, S. A. H., Gustafsson, J. E., & Hulme, C. (2015). Sentence repetition is a measure of children’s language skills rather than working memory limitations. Developmental Science, 18(1), 146–154.
Klingner, J. K., Artiles, A. J., & Barletta, L. M. (2006). English language learners who struggle with reading: Language acquisition or LD? Journal of Learning Disabilities, 39(2), 108–128.
Leite, W. L., & Cooper, L. A. (2010). Detecting social desirability bias using factor mixture models. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 45(2), 271–293.
Lesaux, N. K., & Kieffer, M. J. (2010). Exploring sources of reading comprehension difficulties among language minority learners and their classmates in early adolescence. American Educational Research Journal, 47(3), 596–632.
Lesaux, N. K., Lipka, O., & Siegel, L. S. (2006). Investigating cognitive and linguistic abilities that influence the reading comprehension skills of children from diverse linguistic backgrounds. Reading and Writing, 19(1), 99–131.
Lesaux, N. K., Crosson, A. C., Kieffer, M. J., & Pierce, M. (2010). Uneven profiles: Language minority learners’ word reading, vocabulary, and reading comprehension skills. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 31(6), 475–483.
Li, M., Kirby, J. R., Geva, E., Koh, P. W., & Zhang, H. (2021). Profiles of Poor Decoders, Poor Comprehenders, and Typically Developing Readers in Adolescents Learning English as a Second Language. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 00222194211023200.
Lubke, G. H., & Muthén, B. (2005). Investigating population heterogeneity with factor mixture models. Psychological Methods, 10(1), 21.
MacGinitie, W. H. (2000). Gates-MacGinitie Reading Tests. Itasca. IL: Riverside.
Mancilla-Martinez, J., & Lesaux, N. K. (2010). Predictors of reading comprehension for struggling readers: The case of Spanish-speaking language minority learners. Journal of Educational Psychology, 102(3), 701.
Masyn, K. E., Henderson, C. E., & Greenbaum, P. E. (2010). Exploring the latent structures of psychological constructs in social development using the dimensional–categorical spectrum. Social Development, 19(3), 470–493.
Meyer, J. P., & Morin, A. J. (2016). A person-centered approach to commitment research: Theory, research, and methodology. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 37(4), 584–612.
Miciak, J., & Fletcher, J. M. (2020). The critical role of instructional response for identifying dyslexia and other learning disabilities. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 53(5), 343–353.
Miciak, J., Stuebing, K. K., Vaughn, S., Roberts, G., Barth, A. E., & Fletcher, J. M. (2014). Cognitive attributes of adequate and inadequate responders to reading intervention in middle school. School Psychology Review, 43(4), 407–427.
Morin, A. J., & Marsh, H. W. (2015). Disentangling shape from level effects in person-centered analyses: An illustration based on university teachers’ multidimensional profiles of effectiveness. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 22(1), 39–59.
Morin, A., & Litalien, D. (2019). Mixture modeling for lifespan developmental research. In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Psychology. Oxford University Press.
Morin, A. J., Boudrias, J. S., Marsh, H. W., Madore, I., & Desrumaux, P. (2016). Further reflections on disentangling shape and level effects in person-centered analyses: An illustration exploring the dimensionality of psychological health. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 23(3), 438–454.
Morgan, P. L., Farkas, G., Hillemeier, M. M., Mattison, R., Maczuga, S., Li, H., & Cook, M. (2015). Minorities are disproportionately underrepresented in special education: Longitudinal evidence across five disability conditions. Educational Researcher, 44(5), 278–292.
Muthén, L.K., & Muthén B.O. (2017). Mplus user’s guide, 8th ed., Muthén & Muthén.
Nylund, K. L., Asparouhov, T., & Muthén, B. O. (2007). Deciding on the number of classes in latent class analysis and growth mixture modeling: A Monte Carlo simulation study. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 14(4), 535–569.
O’Connor, R. E., Bocian, K. M., Beach, K. D., Sanchez, V., & Flynn, L. J. (2013). Special education in a 4-year response to intervention (RtI) environment: Characteristics of students with learning disability and grade of identification. Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 28(3), 98–112.
O’Connor, M., Geva, E., & Koh, P. W. (2019). Examining reading comprehension profiles of grade 5 monolinguals and English language learners through the lexical quality hypothesis lens. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 52(3), 232–246.
Samson, J. F., & Lesaux, N. K. (2009). Language-minority learners in special education: Rates and predictors of identification for services. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 42(2), 148–162.
Samson, J. F., & Lesaux, N. (2015). Disadvantaged language minority students and their teachers: A national picture. Teachers College Record, 117(2), 1–26.
Shaywitz, S. E. (2003). Overcoming dyslexia: A new and complete science-based program for reading problems at any level. Vintage.
Swanson, H. L., Arizmendi, G. D., & Li, J. T. (2020). The stability of learning disabilities among emergent bilingual children: A latent transition analysis. Journal of Educational Psychology, 113(6), 1244–1268. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000645.
Vellutino, F. R., Scanlon, D. M., & Reid Lyon, G. (2000). Differentiating between difficult-to-remediate and readily remediated poor readers: More evidence against the IQ-achievement discrepancy definition of reading disability. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 33(3), 223–238.
Vermunt, J. K. (2010). Latent class modeling with covariates: Two improved three-step approaches. Political analysis, 450–469.
Woodcock, R., McGrew, K., Mather, N., & Schrank, F. (2007). Woodcock-Johnson III NU tests of achievement.
Funding
This research was supported by grant R324B170012 from the National Center for Special Education Research in the Institute of Education sciences and grants P50 HD052117 and R01HD096262 from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center for Special Education Research, the Institute of Education Sciences, the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, or the National Institutes of Health,
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miciak, J., Ahmed, Y., Capin, P. et al. The reading profiles of late elementary English learners with and without risk for dyslexia. Ann. of Dyslexia 72, 276–300 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-022-00254-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-022-00254-4