Abstract
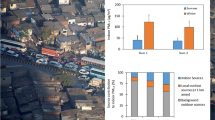
This study investigated the levels and determinant factors of indoor air pollutants including fine particles (PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and formaldehyde (HCHO) in 55 households exclusively for the elderly in Hong Kong during summer and winter (Jul.–Sep. 2016 and Nov. 2016–Mar. 2017). The average concentrations of PM2.5, NO2, and formaldehyde were 25.3 ± 15.0, 40.5 ± 16.0, and 26.1 ± 22.8 μg/m3 in summer and 34.2 ± 19.0, 43.5 ± 17.0, and 15.4 ± 4.5 μg/m3 in winter, respectively. There were ~ 50.3% of households exceeding the World Health Organization indoor air quality standard for PM2.5 throughout the study, with ~ 40.6 and ~61.0% of the households in summer and winter, respectively. The determinant factors for indoor PM2.5 and NO2 concentrations were identified as from incense burning and cooking. Cooking with suitable ventilation is an important factor to ease indoor pollutant concentrations. Both of PM2.5 and NO2 indoor concentrations showed good correlations with outdoor concentrations. Winter was observed with higher pollutant concentrations than summer except for formaldehyde concentrations. Major factors controlling indoor formaldehyde concentrations are temperature and humidity. The outcome will be useful for the development of future indoor air quality guidelines for Hong Kong.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apte K, Salvi S (2016) Household air pollution and its effects on health. F1000 research 5: F 1000 faculty Rev-2593. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.7552.1
Azuma K, Uchiyama I, Uchiyama S, Kunugita N (2016) Assessment of inhalation exposure to indoor air pollutants: screening for health risks of multiple pollutants in Japanese dwellings. Environ Res 145:39–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.11.015
Baxter LK, Clougherty JE, Paciorek CJ, Wright RJ, Levy JI (2007) Predicting residential indoor concentrations of nitrogen dioxide, fine particulate matter, and elemental carbon using questionnaire and geographic information system based data. Atmos Environ (1994) 41(31):6561–6571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.04.027
Chakrabarti B, Fine PM, Delfino R, Sioutas C (2004) Performance evaluation of the active-flow personal DataRAM PM2.5 mass monitor (Thermo Anderson pDR-1200) designed for continuous personal exposure measurements. Atmos Environ 38(20):3329–3340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.03.007
Chao CYH, Tung TCW, Burnett J (1998) Influence of different indoor activities on the indoor particulate levels in residential buildings. Indoor and Built Environ 7(2):110–121
Day DE, Malm WC (2001) Aerosol light scattering measurements as a function of relative humidity: a comparison between measurements made at three different sites. Atmos Environ 35(30):5169–5176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00320-X
GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators (2015) Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 385(9963):117–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2
Guo H, Kwok NH, Cheng HR, Lee SC, Hung WT, Li YS (2009) Formaldehyde and volatile organic compounds in Hong Kong homes: concentrations and impact factors. Indoor Air 19(3):206–217. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0668.2008.00580.x
Haghighat F, De Bellis L (1998) Material emission rates: literature review, and the impact of indoor air temperature and relative humidity. Build Environ 33:261–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-1323(97)00060-7
Hong Kong Census and Statistics Department (2016a) Census and Statistics Department geography and climate, Hong Kong in figures. The Hong Kong Government of Special Administrative Region (HKSAR)
Hong Kong Census and Statistics Department (2016b) Hong Kong annual digest of statistics, Census and Statistics Department, the Hong Kong Government of Special Administrative Region (HKSAR)
Hong Kong Census and Statistics Department (2016c) The profile of Hong Kong population analysed by district council district, 2015. Hong Kong monthly digest of statistics, July 2016. Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR)
Hong Kong EPD (2014) A report on the results from the Air Quality Monitoring Network (AQMN). Air Science Group, Environmental Protection Department, The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region
Hong Kong EPD (2015) A report on the results from the Air Quality Monitoring Network (AQMN), 2015. Air Science Group, Environmental Protection Department, The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region
Hong Kong Housing Society (2016) The types of housing. Hong Kong Housing Society Web https://www.hkhs.com/pdf/liberal/Book1_Part1_02.pdf. Accessed 10 May 2017
Hong Kong Observatory (2017) Hong Kong Observatory Web. http://www.weather.gov. hk/cis/climahk_e.htm. Accessed 15 May
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans (2006) Formaldehyde, 2-butoxyethanol and 1-tertbutoxypropan-2-ol. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum 88:1–478
Jones NC, Thornton CA, Mark D, Harrison RM (2000) Indoor/outdoor relationships of particulate matter in domestic homes with roadside, urban and rural locations. Atmos Environ 34(16):2603–2612. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(99)00489-6
Karakas B, Lakestani S, Guler C, Guciz Dogan B, Acar Vaizoglu S, Taner A et al (2013) Indoor and outdoor concentration of particulate matter at domestic homes. Int J Environ Chem Ecol Geol Geophys Eng 7(6):281–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(99)00489-6
Karottki DG, Spilak M, Frederiksen M, Gunnarsen L, Brauner EV, Kolarik B, Andersen ZJ, Sigsgaard T, Barregard L, Strandberg B, Sallsten G, Møller P, Loft S (2013) An indoor air filtration study in homes of elderly: cardiovascular and respiratory effects of exposure to particulate matter. Environ Health 12:116–125. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069X-12-116
Kelly TJ, Smith DL, Satola J (1999) Emission rates of formaldehyde from materials and consumer products found in California homes. Environ Sci Technol 33:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1021/es980592+
Kimbrough S, Baldauf RW, Hagler GSW, Shores RC, Mitchell W, Whitaker DA, Croghan CW, Vallero DA (2013) Long-term continuous measurement of near-road air pollution in Las Vegas: seasonal variability in traffic emissions impact on local air quality. Air Qual Atmos Health 6(1):295–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-012-0171-xLee
Kotzias D, Koistinen K, Kephalopoulos S et al. (2005) The INDEX project. Critical appraisal of the setting and implementation of indoor exposure limits in the EU. The European Commission’s science and knowledge service Web https://ec.europa.eu/ jrc/en/publication/eur-scientific-and-technical-research-reports/index-project-critical-appraisal-setting-and-implementation-indoor-exposure-limits-eu. Accessed 15 May 2017
Lai HK, Bayer-Oglesby L, Colvile R, Götschi T, Jantunen MJ, Künzli N, Kulinskaya E, Schweizer C, Nieuwenhuijsen MJ (2006) Determinants of indoor air concentrations of PM2.5, black smoke and NO2 in six European cities (EXPOLIS study). Atmos Environ 40(7):1299–1313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.10.030
Langer S, Ramalho O, Derbez M, Ribéron J, Kirchner S, Mandin C (2016) Indoor environmental quality in French dwellings and building characteristics. Atmos Environ 128:82–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.12.060
Lanki T, Ahokas A, Alm S, Janssen NA, Hoek G, De Hartog JJ et al (2007) Determinants of personal and indoor PM2.5 and absorbance among elderly subjects with coronary heart disease. J Exp Sci Environ Epidemiol 17(2):124–133
Lee SC, Li WM, Ao CH (2002) Investigation of indoor air quality at residential homes. Atmos Environ 36(2):225–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00435-6
Meier R, Schindler C, Eeftens M, Aguilera I, Ducret-Stich RE, Ineichen A, Davey M, Phuleria HC, Probst-Hensch N, Tsai MY, Künzli N (2015) Modeling indoor air pollution of outdoor origin in homes of SAPALDIA subjects in Switzerland. Environ Int 82:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2015.05.013
Meng QY, Spector D, Colome S, Turpin B (2009) Determinants of indoor and personal exposure to PM2.5 of indoor and outdoor origin during the RIOPA Study. Atmos Environ (1994) 43(36):5750–5758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.07.066
Mullen NA, Russell ML, Lunden MM, Singer BC (2013) Investigation of formaldehyde and acetaldehyde sampling rate and ozone interference for passive deployment of Waters Sep-Pak XPoSure samplers. Atmos Environ 80:184–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.07.074
Pope CA, Dockery DW, Schwartz J (1995) Review of epidemiological evidence of health effects of particulate air pollution. Inhal Toxicol 7(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.3109/08958379509014267
Raw GJ, Coward SKD, Brown VM, Crump DR (2004) Exposure to air pollutants in English homes. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 14(S1):S85–S94. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jea.7500363
Rohra H, Taneja A (2016) Indoor air quality scenario in India—an outline of household fuel combustion. Atmos Environ 129:243–255
Salthammer T, Mentese S, Marutzky R (2010) Formaldehyde in the indoor environment. Chem Rev 110:2536–2572. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr800399g
Shi Y, Lau KK, Ng E (2016) Developing street-level PM2.5 and PM10 land use regression models in high-density Hong Kong with urban morphological factors. Environ Sci Technol 50(15):8178–8187. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b01807
Shinohara N, Kumagai K, Yamamoto N, Yanagisawa Y, Fujii M, Yamasaki A (2004) Field validation of an active sampling cartridge as a passive sampler for long-term carbonyl monitoring. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 54(4):419–424
Steinemann A (2016) Fragranced consumer products: exposures and effects from emissions. Air Qual Atmos Health 9(8):861–888. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-016-0442-z
Tunsaringkarn T, Prueksasit T, Morknoy D, Sawatsing R, Chinveschakitvanich V, Rungsiyothin A, Zapaung K (2015) Indoor air assessment, health risks, and their relationship among elderly residents in urban warrens of Bangkok, Thailand. Air Qual Atmos Health 8(6):603–615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-014-0302-7
US EPA (2017a) Particulate matter (PM) pollution. United States Environmental Protection Agency Web. https://www.epa.gov/pm-pollution. Accessed 10 May 2017
US EPA (2017b) Facts about formaldehyde. United States Environmental Protection Agency Web. https://www.epa.gov/formaldehyde/facts-about-formaldehyde#whatisformaldehyde. Accessed 10 May 2017
US EPA(2017c) Nitrogen dioxide’s impact on indoor air quality. United States Environmental Protection Agency Web. https://www.epa.gov/indoor-air-quality-iaq/nitrogen-dioxides-impact-indoor-air-quality. Accessed 10 May 2017
US EPA report (AP-42) (1995) Emission factor documentation for AP-42 Section 9.13.2, coffee roasting final report. United States Environmental Protection Agency web https://www3.epa.gov/ttnchie1/ap42/ch09/final/c9s13-2.pdf. Accessed 10 May 2017
Wallace L (1996) Indoor particles: a review. J Air Waste Manag Assoc (1995) 46(2):98–126
Wallace LA, Wheeler AJ, Kearney J, Van Ryswyk K, You H, Kulka RH et al (2011) Validation of continuous particle monitors for personal, indoor, and outdoor exposures. J Exp Sci Environ Epidemiol 21(1):49–64. https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2010.15
Wang YXJ, Griffith JF, Zeng XJ, Deng M, Kwok AWL, Leung JCS et al (2013) Prevalence and gender difference of lumbar disc space narrowing in elderly Chinese men and women: Mr. OS (Hong Kong) and Ms. OS (Hong Kong) studies. Arthritis Rheum 65(4):1004–1010. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.37857
World Health Organization (WHO), Regional Office for Europe (2009) WHO guidelines for indoor air quality: dampness and mould. WHO, Copenhagen
World Health Organization (WHO), Regional Office for Europe (2010) WHO guidelines for indoor air quality: selected pollutants. WHO, Copenhagen
World Health Organization (WHO), Regional Office for Europe (2006) Air quality guidelines. Global update 2005. Particulate matter, ozone, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide. WHO, Copenhagen
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all of the families, experts, and field/laboratory technicians who participated in this campaign.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the Research Grants Council of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of China (Project No. CUHK 412413).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 333 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, X., Wang, B., Dai, WT. et al. Indoor air pollutant exposure and determinant factors controlling household air quality for elderly people in Hong Kong. Air Qual Atmos Health 11, 695–704 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-018-0576-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-018-0576-2