Abstract
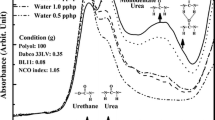
Flexible polyurethane (PU) foams with different loading mass fraction (0%–2.0%) of fumed silica were synthesized by free-rising foaming method. The addition of 1.4% fumed silica makes the cells diffuse more uniform in the PU foam and the temperature of degradation occurring with a maximum weight loss rate is about 7 °C higher than that of pure PU foam. Most significantly, the sound absorption peaks of the filled PU foams shift to the low frequency region (from 997 Hz to 711 Hz) with increasing fumed silica content (0%–2.0%). The average sound absorption coefficients of filled PU foams increase except the content of 0.35% fumed silica. The experimental results show that flexible PU foams filled with fumed silica have excellent sound absorption characteristics in low-frequency regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Bo, Zhou Hong, Huang Guangsu. A novel impedance matching material derived from polymer micro-particles[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42: 199–206.
Mendelsohn M A, Bolton R, Nvaish J. Sound absorbing and decoupling syntactic foam. US: 5422380[P]. 1995-06-06.
Cushman W B, Thomas G B. Acoustic attenuation and vibration damping materlals. US: 5400296[P]. 1995-03-21.
Cushman W B. Using additives to reduce sound transmission [J]. Modern Plastics, 1995, 72: 7226–8275.
Cushman W B, Fla P. Acoustic absorption or damping material with integral viscous damping. US: 5745434[P]. 1998-04-28.
Verdejo R, Stampfli R, Alvarez Lainez M, et al. Enhanced acoustic damping in flexible polyurethane foams filled with carbon nanotubes[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2009, 69: 1564–1569.
Pelrovic Z S, Javni I, Waddon A, et al. Structure and properties of polyurethane-silica nanocomposites[J]. J Appl Polym Sci, 2000, 76: 133–151.
Javni I, Zhang W, Karajkov V, et al. Effect of nano- and micro-silica fillers on polyurethane foam properties[J]. Journal of Cellular Plastics, 2002, 38: 229–237.
Lee S, Cha Y C, Hwang H J, et al. The effect of pH on the physicochemical properties of silica aerogels prepared by an ambient pressure drying method[J]. Materials Letters, 2007, 61: 3130–3133.
Zhang Xinmin, Xu Rongjing, Wu Zenggang, et al. The synthesis and characterization of polyurethane/clay nanocomposites[ J]. Polymer International, 2003, 52: 790–794.
Duquesne S, Le Bras M, Bourbigot S, et al. Thermal degradation of polyurethane and polyurethane/expandable graphite coatings[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2001, 74: 493–499.
Allard J F. Propagation of sound in porous media: Modelling sound absorbing materials [M]. London: Chapman and Hall, 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by National Science Fund for Talent Training in Basic Science ( J0830310) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (017)
Biography: LIU Ting, female, Master candidate, research direction: functional polymer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Mao, L., Liu, F. et al. Preparation, structure, and properties of flexible polyurethane foams filled with fumed silica. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 16, 29–32 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-011-0706-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-011-0706-2