Abstract
Purpose
This review was aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of virtual reality simulation as a teaching / learning strategy on the acquisition of clinical skills and performance, self-confidence, satisfaction and anxiety level in nursing education.
Methodology
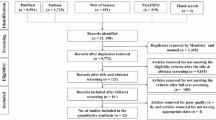
The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews guidelines, using the PICO model that is based on an evidence-based practice process was matched. A total of twenty-three studies included six themes: performance skills (n = 13), self-confidence (n = 8), satisfaction (n = 10), anxiety level (n = 3), self-efficacy (n = 4), and knowledge (n = 15). Experimental randomised control trials and quasi-experimental studies from 2009 to 2019, conducted in English, were included. Nursing students (n = 1797; BSN, ADN, MSc, LPN) participated.
Results and conclusion
This review was indicated that virtual reality simulation provides learning strategy to acquire clinical skills, improve knowledge acquisition, increase self-confidence, self-efficacy, and satisfaction level, and decrease anxiety levels among nursing students.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Foronda CL, Hudson KW, Budhathoki C (2017) Use of virtual simulation to impact nursing students’ cognitive and affective knowledge of evidence-based practice. Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing 14(2):168–170. https://doi.org/10.1111/wvn.12207
Yilmaz DU, Tuncalı SH, Yilmaz Y (2020) Nursing education in the era of virtual reality. In: Virtual and augmented reality in education, art, and museums. IGI Global, pp 47–70.
Ferguson TD, Howell TL, Parsons LC (2014) The birth experience: learning through clinical simulation. International Journal of Childbirth Education 29(3).
Dubovi I, Levy ST, Dagan E (2017) Now I know how! The learning process of medication administration among nursing students with non-immersive desktop virtual reality simulation. Comput Educ 113:16–27
Cant RP, Cooper SJ (2014) Simulation in the Internet age: the place of Web-based simulation in nursing education. An integrative review Nurse Education Today 34(12):1435–1442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2014.08.001
Hege I, Kononowicz AA, Adler M (2017) A clinical reasoning tool for virtual patients: design-based research study. JMIR medical education 3(2):e21.
Jeffries P (2013) Simulation in nursing education: from conceptualization to evaluation. 2nd ed. edn., New York: National League for Nursing.
Cant RP, Cooper SJ (2017) Use of simulation-based learning in undergraduate nurse education: an umbrella systematic review. Nurse Educ Today 49:63–71
NLN (2013) National League for Nursing & Society for Simulation in Healthcare. White paper to advance interprofessional education and practice through simulation.
Isik B, Jallad ST (2019) Future of nursing education: changing values, educational paradigm and learner-educator profiles and roles. New Trends and Issues Proceedings on Humanities and Social Sciences 6(1):165–174
Lioce L, Lopreiato J, Downing D et al (2020) Healthcare simulation dictionary. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA,
Işık B, Kaya H (2014) The effect of simulation software on learning of psychomotor skills and anxiety level in nursing education. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 116:3864–3868
Farra S, Miller E, Timm N, Schafer J (2013) Improved training for disasters using 3-D virtual reality simulation. West J Nurs Res 35(5):655–671
Boland A, Cherry G, Dickson R (2017) Doing a systematic review: a student’s guide. Sage
Higgins J (2011) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Version 5.1. 0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration. www cochrane-handbook org
Rossler KL, Sankaranarayanan G, Duvall A (2019) Acquisition of fire safety knowledge and skills with virtual reality simulation. Nurse Educ 44(2):88–92. https://doi.org/10.1097/NNE.0000000000000551
Farra SL, Smith S, Gillespie GL et al (2015) Decontamination training: With and without virtual reality simulation. Adv Emerg Nurs J 37(2):125–133. https://doi.org/10.1097/TME.0000000000000059
LeFlore JL, Anderson M, Zielke MA et al (2012) Can a virtual patient trainer teach student nurses how to save lives—teaching nursing students about pediatric respiratory diseases. Simulation in Healthcare 7(1):10–17
Smith SJ, Farra S, Ulrich DL et al (2016) Learning and retention using virtual reality in a decontamination simulation. Nurs Educ Perspect 37(4):210–214. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.NEP.0000000000000035
Ausburn LJ, Ausburn FB, Kroutter P (2010) An exploration of desktop virtual reality and visual processing skills in a technical training environment. J Educ Technol 6(4):43–54
Bryant R, Miller CL, Henderson D (2015) Virtual clinical simulations in an online advanced health appraisal course. Clin Simul Nurs 11(10):437–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecns.2015.08.002
Padilha JM, Machado PP, Ribeiro A et al (2019) Clinical virtual simulation in nursing education: randomized controlled trial. J Med Internet Res 21(3):e11529. https://doi.org/10.2196/11529
Smith SJ, Farra SL, Ulrich DL et al (2018) Effectiveness of two varying levels of virtual reality simulation. Nursing education perspectives 39(6):E10-E15. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.NEP.0000000000000369
Verkuyl M, Atack L, McCulloch T et al (2018) Comparison of debriefing methods after a virtual simulation: an experiment. Clin Simul Nurs 19:1–7
Verkuyl M, Hughes M, Tsui J et al (2017) Virtual gaming simulation in nursing education: A focus group study. J Nurs Educ 56(5):274–280. https://doi.org/10.3928/01484834-20170421-04
Vidal VL, Ohaeri BM, John P, Helen D (2013) Virtual reality and the traditional method for phlebotomy training among college of nursing students in Kuwait: implications for nursing education and practice. J Infus Nurs 36(5):349–355. https://doi.org/10.1097/NAN.0b013e318243172f
Ismailoglu EG, Zaybak A (2018) Comparison of the effectiveness of a virtual simulator with a plastic arm model in teaching intravenous catheter insertion skills. CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing 36(2):98–105
Reinhardt AC, Mullins IL, De Blieck C, Schultz P (2012) IV insertion simulation: confidence, skill, and performance. Clin Simul Nurs 8(5):e157–e167
Bayram SB, Caliskan N (2019) Effect of a game-based virtual reality phone application on tracheostomy care education for nursing students: A randomized controlled trial. Nurse Educ Today 79:25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2019.05.010
Jung E-Y, Park DK, Lee YH et al (2012) Evaluation of practical exercises using an intravenous simulator incorporating virtual reality and haptics device technologies. Nurse Educ Today 32(4):458–463
Luctkar-Flude M, Pulling C, Larocque M (2012) Ending infusion confusion: evaluating a virtual intravenous pump educational module. Clin Simul Nurs 8(2):e39–e48
Smith PC, Hamilton BK (2015) The effects of virtual reality simulation as a teaching strategy for skills preparation in nursing students. Clin Simul Nurs 11(1):52–58
Wright RR, Tinnon EA, Newton RH (2018) Evaluation of vSim for nursing in an adult health nursing course: a multisite pilot study. CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing 36(2):84–89
Cobbett S, Snelgrove-Clarke E (2016) Virtual versus face-to-face clinical simulation in relation to student knowledge, anxiety, and self-confidence in maternal-newborn nursing: a randomized controlled trial. Nurse Educ Today 45:179–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2016.08.004
Kardong-Edgren S, Breitkreuz K, Werb M et al (2019) Evaluating the usability of a second-generation virtual reality game for refreshing sterile urinary catheterization skills. Nurse Educ 44(3):137–141
William A, Vidal VL, John P (2016) Traditional instruction versus virtual reality simulation: a comparative study of phlebotomy training among nursing students in Kuwait. J Educ Pract 7(9):18–25. https://doi.org/10.1097/NAN.0b013e318243172f
Bandura A (1986) Fearful expectations and avoidant actions as coeffects of perceived self-inefficacy.
Farra S, Miller ET (2013) Integrative review: virtual disaster training. J Nurs Educ Pract 3(3):93. https://doi.org/10.5430/jnep.v3n3p93
Kolb DA (2014) Experiential learning: experience as the source of learning and development. FT press,
Squire K (2006) From content to context: videogames as designed experience. Educ Res 35(8):19–29. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X035008019
Poore JA, Cullen DL, Schaar GL (2014) Simulation-based interprofessional education guided by Kolb’s experiential learning theory. Clin Simul Nurs 10(5):e241–e247
Succar T, Zebington G, Billson F et al (2013) The impact of the Virtual Ophthalmology Clinic on medical students’ learning: a randomised controlled trial. Eye 27(10):1151–1157
Foronda CL, Fernandez-Burgos M, Nadeau C et al (2020) Virtual simulation in nursing education: a systematic review spanning 1996 to 2018. Simulation in Healthcare 15(1):46–54
Curtin LB, Finn LA, Czosnowski QA et al (2011) Computer-based simulation training to improve learning outcomes in mannequin-based simulation exercises. Am J Pharm Educ 75(6)
Chen FQ, Leng YF, Ge JF et al (2020) Effectiveness of virtual reality in nursing education: meta-analysis. J Med Internet Res 22(9):e18290
Nielsen B, Harder N (2013) Causes of student anxiety during simulation: what the literature says. Clin Simul Nurs 9(11):e507–e512
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jallad, S.T., Işık, B. The effectiveness of virtual reality simulation as learning strategy in the acquisition of medical skills in nursing education: a systematic review. Ir J Med Sci 191, 1407–1426 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-021-02695-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-021-02695-z