Abstract
Background
For evaluating the severity of coronary heart disease (CHD), coronary arteriography may not be available everywhere due to technical limitations. MicroRNA-101a (miR-101a) associated with inflammation and cholesterol homeostasis. However, whether it related to presence and stratification of CHD is still unknown.
Aim
We aim to evaluate the value of miR-101a in stratifying CHD patients.
Methods
We enrolled 200 CHD patients and 100 controls, and 200 CHD patients were divided into two groups of low and high SYNTAX score (SYNTAX score ≤ 22 versus SYNTAX score ≥ 33). Intergroup comparisons of miR-101a level were compared among the controls and two groups of low and high SYNTAX score. Correlation between miR-101a and blood lipid profiles was analyzed. The logistic regression analysis were conducted to evaluate the risk factors of CHD.
Results
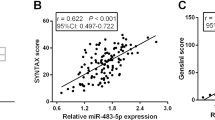
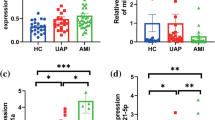
Relative level of miR-101a in the controls, SYNTAX score ≤ 22 and SYNTAX score ≥ 33 group were 4.61 (1.24–8.91), 3.28 (0.58–6.75) and 2.29 (1.04–3.62), respectively (p < 0.001). All lipid profiles significantly associated with miR-101a expression (all p < 0.001). The odds ratio (OR) of miR-101a in univariate analysis was 0.41 (95% CI, 0.33–0.52). After adjusting for the traditional risk factors, such as blood profiles and history of smoking, the odds ratio of miR-101a was 0.63 (95% CI, 0.47–0.43), which closely associated with CHD (p = 0.002).
Conclusions
Circulating miR-101a may be considered as a novel biomarker for evaluating the presence and severity of CHD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klingenberg R, Aghlmandi S, Räber L, Gencer B, Nanchen D, Heg D, Carballo S, Rodondi N, Mach F, Windecker S, Jüni P, von Eckardstein A, Matter CM, Lüscher TF (2018) Improved risk stratification of patients with acute coronary syndromes using a combination of hsTnT, NT-proBNP and hsCRP with the GRACE score. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care 7:129–138
Bularga A, Lee KK, Stewart S, Ferry AV, Chapman AR, Marshall L, Strachan FE, Cruickshank A, Maguire D, Berry C, Findlay I, Shah ASV, Newby DE, Mills NL, Anand A, On behalf of the High-STEACS Investigators (2019) High-sensitivity troponin and the application of risk stratification thresholds in patients with suspected acute coronary syndrome. Circulation 140:1557–1568
Kaur A, Mackin ST, Schlosser K, Wong FL, Elharram M, Delles C, Stewart DJ, Dayan N, Landry T, Pilote L (2020) Systematic review of microRNA biomarkers in acute coronary syndrome and stable coronary artery disease. Cardiovasc Res 116:1113–1124
Welten SM, Goossens EA, Quax PH, Nossent AY (2016) The multifactorial nature of microRNAs in vascular remodelling. Cardiovasc Res 110:6–22
Zhang N, Lei J, Lei H, Ruan X, Liu Q, Chen Y, Huang W (2015) MicroRNA-101 overexpression by IL-6 and TNF-α inhibits cholesterol efflux by suppressing ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 expression. Exp Cell Res 336:33–42
Pan Z, Sun X, Shan H, Wang N, Wang J, Ren J, Feng S, Xie L, Lu C, Yuan Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Lu Y, Yang B (2012) MicroRNA-101 inhibited postinfarct cardiac fibrosis and improved left ventricular compliance via the FBJ osteosarcoma oncogene/transforming growth factor-β1 pathway. Circulation 126:840–850
Ikeda S, Kong SW, Lu J, Bisping E, Zhang H, Allen PD, Golub TR, Pieske B, Pu WT (2007) Altered microRNA expression in human heart disease. Physiol Genomics 31:367–373
van Rooij E, Sutherland LB, Thatcher JE, DiMaio JM, Naseem RH, Marshall WS et al (2008) Dysregulation of microRNAs after myocardial infarction reveals a role of miR-29 in cardiac fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:13027–13032
Frankel LB, Wen J, Lees M, Høyer-Hansen M, Farkas T, Krogh A, Jäättelä M, Lund AH (2011) microRNA-101 is a potent inhibitor of autophagy. EMBO J 30:4628–4641
Rayner KJ, Moore KJ (2014) MicroRNA control of high-density lipoprotein metabolism and function. Circ Res 114:183–192
Kim CH, Koo BK, Lee JM, Shin ES, Park J, Choi KH et al (2019) Influence of sex on relationship between total anatomical and physiologic disease burdens and their prognostic implications in patients with coronary artery disease. J Am Heart Assoc 8:e011002
Zhang Y, Li HH, Yang R, Yang BJ, Gao ZY (2017) Association between circulating microRNA-208a and severity of coronary heart disease. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 77:379–384
Zhou J, Yu L, Gao X, Hu J, Wang J, Dai Z, Wang JF, Zhang Z, Lu S, Huang X, Wang Z, Qiu S, Wang X, Yang G, Sun H, Tang Z, Wu Y, Zhu H, Fan J (2011) Plasma microRNA panel to diagnose hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 29:4781–4788
Rief M, Feger S, Martus P, Laule M, Dewey M, Schönenberger E (2015) Acceptance of combined coronary CT angiography and myocardial CT perfusion versus conventional coronary angiography in patients with coronary stents--intraindividual comparison. PLoS One 10:e0136737
Coffey S, Williams MJ, Phillips LV, Jones GT (2015) Circulating microRNA profiling needs further refinement before clinical use in patients with aortic stenosis. J Am Heart Assoc 4:e002150
Neth P, Nazari-Jahantigh M, Schober A, Weber C (2013) MicroRNAs in flow-dependent vascular remodelling. Cardiovasc Res 99:294–303
Ghanbari M, Franco OH, de Looper HW, Hofman A, Erkeland SJ, Dehghan A (2015) Genetic variations in microRNA-binding sites affect microRNA-mediated regulation of several genes associated with cardio-metabolic phenotypes. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 8:473–486
Niu J, Jin Z, Kim H, Kolattukudy PE (2015) MCP-1-induced protein attenuates post-infarct cardiac remodeling and dysfunction through mitigating NF-κB activation and suppressing inflammation-associated microRNA expression. Basic Res Cardiol 110:26
Cheng S, Zhou F, Xu Y, Liu X, Zhang Y, Gu M, Su Z, Zhao D, Zhang L, Jia Y (2019) Geniposide regulates the miR-101/MKP-1/p38 pathway and alleviates atherosclerosis inflammatory injury in ApoE−/− mice. Immunobiology 224:296–306
Li X, Zhang S, Wa M, Liu Z, Hu S (2019) MicroRNA-101 protects against cardiac remodeling following myocardial infarction via downregulation of runt-related transcription factor 1. J Am Heart Assoc 8:e013112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Tu, YF., Liu, HM. et al. Diagnostic utility of circulating plasma microRNA-101a in severity of coronary heart disease. Ir J Med Sci 190, 1391–1396 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-021-02512-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-021-02512-7