Abstract
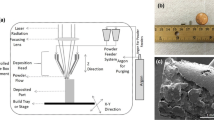
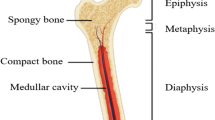
Interest is significant in patient-specific implants with the possibility of guided tissue regeneration, particularly for load-bearing implants. For such implants to succeed, novel design approaches and fabrication technologies that can achieve balanced mechanical and functional performance in the implants are necessary. This article is focused on porous load-bearing implants with tailored micro-as well as macrostructures using laser-engineered net shaping (LENS™), a solid freeform fabrication or rapid prototyping technique that can be used to manufacture patient-specific implants. This review provides an insight into LENS, some properties of porous metals, and the potential applications of this process to fabricate unitized structures which can eliminate longstanding challenges in load-bearing implants to increase their in-vivo lifetime, such as in a total hip prosthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.M. Pillar, J. Biomed. Mater. Res.-Appl. Biomater., 21(A1) (1987), pp. 1–33.
A.J.T. Clemow et al., J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 15 (1981), pp. 73–82.
I.H. Oh et al., Scripta Mater., 49 (2003), pp. 1197–1202.
R.M. Pillar, Int. J. Powder Metallurgy, 34(8) (1998), pp. 33–46.
C.E. Wen et al., Scripta Mater., 45 (2001), pp. 1147–1153.
K. Otsuka and C.M. Wayman, Shape Memory Materials (Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press, 1998).
J.C. Hey and A.P. Jardine, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 188 (1994), pp. 291–300.
W.U. Shuilin et al., Acta Mater., 55 (2007), pp. 3437–3451.
H.G. Willert, H. Bertram, and G.H. Buchhorn, Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res., 258 (1990), pp. 95–107.
Alloy Phase Diagrams: ASM Handbook, vol. 3 (Materials Park, OH: ASM International, 1992).
B. Vamsi Krishna, Susmita Bose, and Amit Bandyopadhyay, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 38A (2007) pp. 1096–1103.
B. Vamsi Krishna, Susmita Bose, and Amit Bandyopadhyay, International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology (on-line 29 February 2008), doi:10.1111/ j.1744-7402.2008.02202.x.
W. Liu and J.N. DuPont, Scripta Mater., 48 (2003), pp. 1337–1342.
W. Hofmeister et al., JOM, 53(9) (2001), pp. 30–34.
B. Vamsi Krishna, Susmita Bose, and Amit Bandyopadhyay, Acta Biomaterialia, 3 (2007), pp. 997–1006.
A. Simchi and H. Pohl, Mater. Sci. and Eng. A, 359 (2003), pp. 119–128.
Félix A. España et al., Journal of Materials Science—Materials in Medicine (submitted December 2007).
B. Vamsi Krishna, Susmita Bose, and Amit Bandyopadhyay, J. of Biomedical Research B: Applied Biomaterials (submitted April 2008).
Weichang Xue et al., Acta Biomaterialia, 3 (2007), pp. 1007–1018.
B. Vamsi Krishna et al., Acta Biomaterialia (2007), doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2007.10.005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vamsi Krishna, B., Xue, W., Bose, S. et al. Engineered porous metals for implants. JOM 60, 45–48 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-008-0059-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-008-0059-2