Abstract
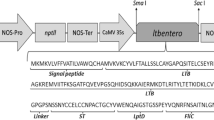
Chloroplast genetic engineering offers an opportunity for high level expression and cost-effective recombinant protein production. Escherichia coli O157:H7 is one of the most important zoonotic pathogens causing hemorrhagic colitis (HC) and the life-threatening hemolytic-uremic syndrome in humans worldwide. The occurrence of zoonotic E. coli O157:H7 outbreaks in recent years has led to increased efforts in the development of safe and cost-effective immunogenic antigens against E. coli O157:H7. EspA and Tir/Intimin proteins are the important virulence factors which are encoded by the LEE locus of enterohemorrhagic E. coli. In this study, we hypothesized that the high level expression of the chimeric form of these effectors in chloroplasts and using tobacco transplastomic plants as an oral delivery system for the development of an edible-base vaccine would induce an immune response for the prevention of E. coli 0157:H7 attachment and colonization in animal model mice. The prokaryotic codon-optimized EIT protein was expressed in plastid genome via chloroplast transformation. Putative transplastomic plants were analyzed by PCR, and Southern blot analysis confirming chloroplast integration and homoplasmy in the T1 progeny. Immunoblotting and ELISA assays demonstrated that the EIT protein was expressed in chloroplasts and accumulated up to 1.4 % of total soluble protein in leaf tissue. In mice orally immunized with transplastomic tobacco plant leaves, high immunological responses (IgG and IgA specific antibodies) were detected in serum and feces. Finally, the challenging assay with E. coli O157:H7 in immunized mice showed reduced bacterial shedding.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amani J, Mousavi SL, Rafat S, Salmanian AH (2009) In silico analysis of chimeric espA, eae and tir fragment of Escherichia coli O157:H7 for oral immunogenic applications. Theor Biol Med Model 6:28
Amani J, Salmanian AH, Rafati S, Mousavi SL (2010) Immunogenic properties of chimeric protein from espA, eae and tir genes of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Vaccine 28:6923–6929
Arlen PA, Singleton M, Adamovicz JJ, Ding Y, Davoodi-Semiromi A, Daniell H (2008) Effective plague vaccination via oral delivery of plant cells expressing F1-V antigens in chloroplasts. Infect Immun 76:3640–3650
Babiuk S, Asper DJ, Rogan D, Mutwiri GK, Potter AA (2008) Subcutaneous and intranasal immunization with type III secreted proteins can prevent colonization and shedding of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in mice. Microb Pathog 45:7–11
Chebolu S, Daniell H (2009) Chloroplast-derived vaccine antigens and biopharmaceuticals: expression, folding, assembly and functionality. Curr Microbiol Immunol 332:33–54
Daniell H (1997) Transformation and foreign gene expression in plants by microprojectile bombardment. Methods Mol Biol 62:463–489
Daniell H, Lee SB, Panchal T, Wiebe P (2001) Expression of native cholera toxin B sub-unit gene and assembly as functional oligomers in transgenic tobacco chloroplasts. J Mol Biol 311:1001–1009
Daniell H, Watson J, Koya V, Leppla SH (2004) Expression of Bacillus anthracis protective antigen in transgenic chloroplasts of tobacco, a non-food/feed crop. Vaccine 22:4374–4384
Daniell H, Ruiz D, Dhingra A (2005) Chloroplast genetic engineering to improve agronomic traits. Methods Mol Biol 286:111–138
Davoodi-Semiromi A, Samson N, Daniell H (2009) The green vaccine: a global strategy to combat infectious and autoimmune diseases. Hum Vaccine 5(7):488–493
Dean-Nystrom EA, Gansheroff LJ, Mills M, Moon HW, O’Brien AD (2002) Vaccination of pregnant dams with intimin(O157) protects suckling piglets from Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection. Infect Immun 70:2414–2418
Dziva F, Vlisidou I, Crepin VF, Wallis TS, Frankel G, Stevens MP (2007) Vaccination of calves with EspA, a key colonization factor of Escherichia coli O157:H7, induces antigen-specific humoral responses but does not confer protection against intestinal colonization. Vet Microbiol 123:254–261
Fischer R, Stoger E, Schillberg S, Christou P, Twyman RM (2004) Plant based production of biopharmaceuticals. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:152–158
Frankel G, Phillips AD, Rosenshine I, Dougan G, Kaper JB, Knutton S (1998) Enteropathogenic and enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli: more subversive elements. Mol Microbiol 30:911–921
Giddings G, Allison G, Brooks D, Carter A (2000) Transgenic plants as factories for biopharmaceuticals. Nat Biotechnol 18:1151–1155
Grauke LJ, Kudva IT, Yoon JW, Hunt CW, Williams CJ, Hovde CJ (2002) Gastrointestinal tract location of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in ruminants. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:2269–2277
Judge NA, Mason HS, O’Brien AD (2004) Plant cell-based intimin vaccine given orally to mice primed with intimin reduces time of Escherichia coli O157:H7 shedding in feces. Infect Immun 72:168–175
Kudva IT, Jelacic S, Tarr PI, Youderian P, Hovde CJ (1999) Biocontrol of O157 with O157-specific bacteriophages. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3767–3773
Kuhne SA, Hawes WS, La Ragione RM, Woodwaed MJ, Whitelam GC, Gough KC (2004) Isolation of recombinant antibodies against EspA and intimin of Escherichia coli 0157:H7. J Clin Microbiol 42:2966–2976
Lee SB, Kwon HB, Kwon SJ, Park SC, Jeong MJ, Han SE, Byun MO, Daniell H (2003) Accumulation of trehalose within transgenic chloroplasts confers drought tolerance. Mol Breed 11:1–13
Lim JY, Sheng H, Keun SS, Park YH, Hovde CJ (2007) Characterization of an Escherichia coli O157:H7 plasmid O157 deletion mutant and its survival and persistence in cattle. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2037–2047
Limaye A, Koya V, Samsam M, Daniell H (2006) Receptor-mediated oral delivery of a bioencapsulated green fluorescent protein expressed in transgenic chloroplasts into the mouse circulatory system. FASEB J 20:959–961
Ma JK, Chikwamba R, Sparrow P, Fischer R, Mahoney R, Twyman RM (2005) Plant-derived pharmaceuticals—the road forward. Trends Plant Sci 10:580–585
Madisis P, Osathanunkul M, Georgopoulou U, Gisby MF, Mudd EA, Nianiou I, Tsitoura P, Mavromara P, Tsaftaris A, day A (2010) A hepatitis C virus core polypeptide expressed in chloroplasts detects anti-core antibodies in infected human sera. J Biotechnol 145:377–386
Maliga P (2002) Engineering the plastid genome of higher plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:164–172
Maliga P (2003) Progress towards commercialization of plastid transformation technology. Trends Biotechnol 21:20–28
Maliga P (2004) Plastid transformation in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:289–313
McNeilly TN, Mitchell MC, Rosser T, McAteer S, Low JC, Smith DGE, Huntley JF, Mahajan A, Gally DL (2010) Immunization of cattle with a combination of purified intimin-531, EspA and Tir significantly reduces shedding of Escherichia coli O157:H7 following oral challenge. Vaccine 28:1422–1428
Molina A, Hervas-Stubbs S, Daniell H, Mingo-Castel AM, Veramendi J (2004) High yield expression of a viral peptide animal vaccine in transgenic tobacco chloroplasts. Plant Biotechnol 2:141–153
Moxley RA (2004) Escherichia coli 0157:H7: an update on intestinal colonization and virulence mechanisms. Anim Health Res Rev 511:15–33
Mundy R, Schuller S, Girard F, Fairbrother JM, Phillips AD, Frankel G (2007) Functional studies of intimin in vivo and ex vivo: implications for host specificity and tissue tropism. Microbiology 153:959–967
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–479
Nataro JP, Kaper JB (1998) Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev 11:142–201
Potter AA, Klashinsky S, Li Y, Frey E, Townsend H, Rogan D, Erickson G, Hinkley S, Klopfenstein T, Moxley RA, Smith DR, Finlay BB (2004) Decreased shedding of Escherichia coli O157:H7 by cattle following vaccination with type III secreted proteins. Vaccine 22:362–369
Reddy VS, Leellavathi S (2003) Chloroplast expression of His-tagged GUS-fusions: a general strategy to overproduce and purify foreign proteins using transplastomic plants as bioreactors. Mol Breed 11:49–58
Reddy VS, Leellavathi S, Selvapandiyan A, Raman R, Giovanni F, Shhukla V, Bhatnagar RR (2002) Analysis of chloroplast transformed tobacco plants with cry1Ia5 under rice psbA transcriptional elements reveal high level expression of Bt toxin without imposing yield penalty and stable inheritance of transplastome. Mol Breed 9:259–269
Ruiz ON, Daniell H (2005) Engineering cytoplasmic male sterility via the chloroplast genome by the expression of β-ketothiolase. Plant Physiol 138:1232–1246
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Schlundt J, Toyofuku H, Jansen J, Herbst SA (2004) Emerging food-borne zoonoses. Rev Sci Tech 23:513–533
Scotti N, Alagna F, Ferraiolo E, Formisano G, Sannino L, Buonaguro L, Stradis AD, Vitale A, Monti L, Grillo S, Buonaguro FM, Cardi T (2009) High-level expression of the HIV-1 Pr55gg polyprotein in transgenic tobacco chloroplast. Planta 229:1109–1122
Shao HB, He DM, Qian KX, Shen GF, Su ZL (2008) The expression of classical swine fever virus structural protein E2 gene in tobacco chloroplasts for applying chloroplasts as bioreactors. CR Biol 331:179–184
Shen H, Qian B, Chen W, Liu Z, Yang L, Zhang D, Liang W (2010) Immunogenicity of recombinant F4 (K88) fimbrial adhesin FaeG expressed in tobacco chloroplast. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 42:558–567
Soria-Guerra RE, Alpuche-Solis AG, Rosales-Mendoza S, Moreno-Fierros L, Bendik EM, Martinez-Gonzales L, Korban SS (2009) Expression of a multi-epitope DPT fusion protein in transplastomic tobacco plants retains both antigenicity and immunogenicity of all three components of the functional oligomer. Planta 229:1293–1302
Stevens MP, Diemen PM, Dziva F, Jones PW, Wallis TS (2002) Options for the control of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli in ruminants. Microbiology 148:3767–3778
Tkalcic S, Zhao T, Harmon BG, Doyle MP, Brown CA, Zhao P (2003) Fecal shedding of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli I weaned calves following treatment with probiotic Escherichia coli. J Food Prot 66:1184–1189
Tregoning JS, Nixon P, Kuroda H, Svab Z, Clare S, Bowe F (2003) Expression of tetanus toxin fragment C in tobacco chloroplast. Nucleic Acid Res 31(4):1174–1179
Yoon JW, Hovde CJ (2008) All blood, no stool: enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection. J Vet Sci 9:219–231
Yu J, Kaper JB (1992) Cloning and characterization of the eae gene of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Mol Microbiol 6:411–417
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof.V.S. Reddy (ICGEB, New Delhi, India) for generously providing the plasmid transformation vector pVSR326. We also thank Dr J. Amani for critical reading of this manuscript. This work was supported by funds from the National Institute of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (NIGEB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karimi, F., Mousavi, A., Salmanian, A.H. et al. Immunogenicity of EIT chimeric protein expressed in transplastomic tobacco plants towards development of an oral vaccine against Escherichia coli O157:H7. Plant Biotechnol Rep 7, 535–546 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-013-0296-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-013-0296-x