Abstract
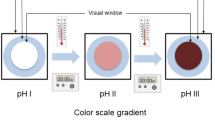
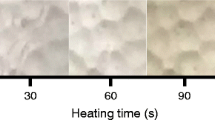
Time-temperature indicators (TTIs) are convenient intuitive devices that are widely used to predict food quality. The aim of this study is to develop a new simple device which can be attached to food packages as a quality indicator for turbot sashimi. In this study, a solid TTI based on the reaction between tyrosinase and tyrosine was developed. The Arrhenius behavior of this enzymatic TTI was studied. The kinetics of the tyrosinase-based TTI was investigated in the form of color change from colorless to dark black induced by the enzymatic reaction. The mathematical formula for the color alterations as a function of time and temperature was established. The longest indication time for the developed TTI was 50 hours at 4°C. The activation energy of the tyrosinase-based TTI was 0.409 kJ mol−1. The suitability of the tyrosinase-based TTI was validated for turbot sashimi using total plate count. The feasibility of using this TTI as a quality indicator for turbot sashimi was assessed based on the activation energy and indication time. Therefore, the tyrosinasebased TTI system developed in this study could be used as an effective tool for monitoring the quality changes of turbot sashimi during the distribution and storage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, J. B., and Langley, F. M., 1998. Nitrophenyl glucoside hydrolysis as a potential time-temperature integrator reaction. Food Chemistry, 62 (1): 65–68, DOI: 10.1016/S0308-8146(97) 00143-X.
Chen, Q. X., and Kubo, I., 2002. Kinetics of mushroom tyrosinase inhibition by quercetin. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50 (14): 4108–4112, DOI: 10.1021/jf011378z.
Chen, Q. X., Song, K. K., Wang, Q., and Huang, H., 2003. Inhibitory effects on mushroom tyrosinase by some alkylbenzaldehydes. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 18 (6): 491–496, DOI: 10.1080/147563603100016 13094.
Ellouze, M., and Augustin, J. C., 2010. Applicability of biological time temperature integrators as quality and safety indicators for meat products. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 138 (1): 119–129, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro. 2009.12.012.
Fu, B., Taoukis, P. S., and Labuza, T. P., 1991. Predictive microbiology for monitoring spoilage of dairy products with time-temperature integrators. Journal of Food Science, 56 (5): 1209–1215, DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1991.tb04736.x.
Giannakourou, M. C., and Taoukis, P. S., 2003. Application of a TTI-based distribution management system for quality optimization of frozen vegetables at the consumer end. Journal of Food Science–Chicago, 68 (1): 201–209, DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2003.tb14140.x.
Giannakourou, M. C., Koutsoumanis, K., Nychas, G. J. E., and Taoukis, P. S., 2005. Field evaluation of the application of time temperature integrators for monitoring fish quality in the chill chain. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 102 (3): 323–336, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.11.037.
Guiavarc’h, Y., Van-Loey, A., Zuber, F., and Hendrickx, M., 2004a. Development characterization and use of a high-performance enzymatic Time-Temperature Integrator for the control of sterilization process’ impacts. Biotechnology and bioengineering, 88 (1): 15–25, DOI: 10.1002/bit.20183.
Guiavarc’h, Y., Van-Loey, A., Zuber, F., and Hendrickx, M., 2004b. Bacillus licheniformis α-amylase immobilized on glass beads and equilibrated at low moisture content: potentials as a Time-Temperature Integrator for sterilisation processes. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 5 (3): 317–325, DOI: 10.1016/j.ifset.2004.03.004.
In’t-Veld, J. H. H., 1996. Microbial and biochemical spoilage of foods: An overview. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 33 (1): 1–18, DOI: 10.1016/0168-1605(96)01139-7.
Kang, Y. J., Kang, J. W., Choi, J. H., Park, S. Y., Rahman, A. M., Jung, S. W., and Lee, S. J., 2014. A feasibility study of application of laccase-based time-temperature indicator to kimchi quality control on fermentation process. Journal of The Korean Society for Applied Biological Chemistry, 57 (6): 819–825, DOI: 10.1007/s13765-014-4178-x.
Kim, E., Choi, D. Y., Kim, H. C., Kim, K., and Lee, S. J., 2013. Calibrations between the variables of variables of microbial TTI response and ground pork qualities. Meat Science, 95 (2): 362–367, DOI: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2013.04.050.
Kim, J. U., Ghafoor, K., Ahn, J., Shin, S., Lee, S. H., Shahbaz, H. M., Shin, H. H., Kim, S., and Park, J., 2016. Kinetic modeling and characterization of a diffusion-based time-temperature indicator (TTI) for monitoring microbial quality of non-pasteurized angelica juice. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 67: 143–150, DOI: 10.1016/j.lwt.2015.11.034.
Kim, K., Kim, E., and Lee, S. J., 2012. New enzymatic timetemperature integrator (TTI) that uses laccase. Journal of Food Engineering, 113 (1): 118–123, DOI: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2012. 05.009.
Koutsoumanis, K., Taoukis, P. S., and Nychas, G. J. E., 2005. Development of a safety monitoring and assurance system for chilled food products. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 100 (1): 253–260, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.10. 024.
Kuswandi, B., Restyana, A., Abdullah, A., Heng, L. Y., and Ahmad, M., 2012. A novel colorimetric food package label for fish spoilage based on polyaniline film. Food Control, 25 (1): 184–189, DOI: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.10.008.
Labuza, T. P., and Taoukis, P. S., 1990. The relationship between processing and shelf life. In: Foods for the 90’s. Birch, G. G., et al., eds., Elsevier Applied Science, London, UK,73–106.
Labuza, T. P., 1982. Shelf-Life Dating of Foods. Food & Nutrition Press, Westport, Connecticut, USA, 66-120pp.
Manske, W. J., 1984. Critical temperature indicator. U.S. Patent No. 4457252. 3 Jul.
Nuin, M., Alfaro, B., Cruz, Z., Argarate, N., George, S., Le Marc, Y., and Pin, C., 2008. Modelling spoilage of fresh turbot and evaluation of a time-temperature integrator (TTI) label under fluctu ating emperature. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 127 (3): 193–199, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2008. 04.010.
Pereira, V. A., de-Arruda, I. N. Q., and Stefani, R., 2015. Active chitosan/PVA films with anthocyanins from Brassica oleraceae (red cabbage) as Time-Temperature Indicators for application in intelligent food packaging. Food Hydrocolloid, 43: 180–188, DOI: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.05.014.
Qian, J., Zheng, G. L., and Feng, Q., 2013. Glucoamylase timetemperature indicators based on fat oxidation of chilled pork. Food Science, 18: 070.
Reichert, H., Simmendinger, P., and Thomas, B., 2010. Comprising an immobilized enzyme and a substrate of the enzyme, the substrate being a pigment precursor; the reaction product of the enzyme catalyzed reaction, can be detected by monitoring a physical characteristic of the substrate and/or the product which is linked to its concentration; labels; inks. U.S. Patent No. 7736866. 15 Jun.
Rokka, M., Eerola, S., Smolander, M., Alakomi, H. L., and Ahvenainen, R., 2004. Monitoring of the quality of modified atmosphere packaged broiler chicken cuts stored in different temperature conditions: B. Biogenic amines as quality-in-dicating metabolites. Food Control, 15 (8): 601–607, DOI: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2003.10.002.
Schoen, H. M., and Byrne, C. H., 1972. Defrost indicators. Food Technology, 26 (10): 46.
Smolander, M., Alakomi, H. L., Ritvanen, T., Vainionpää, J., and Ahvenainen, R., 2004. Monitoring of the quality of modified atmosphere packaged broiler chicken cuts stored in different temperature conditions. A. Time-temperature indicators as quality-indicating tools. Food Control, 15 (3): 217–229, DOI: 10.1016/S0956-7135(03)00061-6.
Sun, Y., Cai, H. W., Zheng, L. M., Ren, F. Z., Zhang, L. D., and Zhang, H. T., 2008. Development and characterization of a new amylase type time-temperature indicator. Food Control, 19 (3): 315–319, DOI: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2007.04.012.
Szwarc, M., and Williams, D., 1952. Relation between activation energy and frequency factor. Nature, 170: 290, DOI: 10.1038/170290a0.
Taoukis, P. S., and Labuza, T. P., 1989. Applicability of timetemperature indicators as shelf life monitors of food products. Journal of Food Science, 54 (4): 783–788, DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1989.tb07882.x.
Taoukis, P. S., and Labuza, T. P., 2003. Time-temperature indicators (TTIs). In: Novel Food Packaging Techniques. Ahvenainen, R., eds., Woodhead Publishing Limited and CRC Press LLC, Washington, DC,103–126.
Taoukis, P. S., Fu, B., and Labuza, T. P., 1991. Time-temperature indicators. Food Technology (USA), 45: 70–81.
Taoukis, P. S., 2001. Modeling the use of time-temperature indicators in distribution and stock rotrotation. In: Food Process Modeling. Tijkskens, L. M. M., et al., eds., CRC Press, Washington, DC,402–432.
Tsironi, T., Gogou, E., Velliou, E., and Taoukis, P. S., 2008. Application and validation of the TTI based chill chain management system SMAS (Safety Monitoring and Assurance System) on shelf life optimization of vacuum packed chilled tuna. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 128 (1): 108–115, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2008.07.025.
Vaikousi, H., Biliaderis, C. G., and Koutsoumanis, K. P., 2009. Applicability of a microbial time temperature indicator (TTI) for monitoring spoilage of modified atmosphere packed minced meat. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 133 (3): 272–278, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2009.05.030.
Wan, X., and Knoll, M., 2016. A new type of TTI based on an electrochemical pseudo transistor. Journal of Food Engineering, 168: 79–83, DOI: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2015.07.030.
Wanihsuksombat, C., Hongtrakul, V., and Suppakul, P., 2010. Development and characterization of a prototype of a lactic acid-based time-temperature indicator for monitoring food product quality. Journal of Food Engineering, 100 (3): 427–434, DOI: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2010.04.027.
Wu, D., Pan, J. Z., Chen, J. C., Ye, X. Q., and Liu, D. H., 2014. Dynamics research of time-temperature indicating system based on alkaline lipase. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 469: 422–427, DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.469.422.
Wu, D., Wang, Y., Chen, J., Ye, X., Wu, Q., Liu, D., and Ding, T., 2013. Preliminary study on time-temperature indicator (TTI) system based on urease. Food Control, 34 (1): 230–234, DOI: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.04.041.
Acknowledgements
The study is supported by the Science and Technology Major Projects of Shandong Province (No. 2015ZDZX05 003) and the National Science & Technology Pillar Program (No. 2015BAD16B0902).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, F., Ge, L., Li, Z. et al. Development and application of a tyrosinase-based time-temperature indicator (TTI) for determining the quality of turbot sashimi. J. Ocean Univ. China 16, 847–854 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-017-3220-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-017-3220-0