Abstract
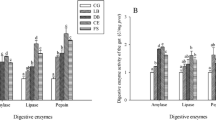
The influence of Bacillus probiotics on the digestive enzyme activity and the growth of Litopenaeus vannamei were determined in this study. The shrimp was treated with five percentages (1.5, 3.0, 4.5, 6.0 and 7.5) of probiotics (Bacillus spp.) supplemented to the feed and cultured for 45d. The growth measured as the weight gain at the end of culturing was significantly (P<0.05) higher in probiotic-treated shrimps than that of the control (without receiving probiotics). Activities of protease and amylase, two digestive enzymes of the midgut gland and the intestine were significantly (P<0.05) higher in probiotic-treated shrimp than in the control.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balcazar, J. L., I. De Blas, D. C. Ruiz-Zarzuela, D. Vendrell, and J. L. Muzquiz, 2006. The role of the probiotics in aquaculture. Veter. Microbiol., 114: 173–186.
Brito, R., M. G. Chimal, G. Gaxiola, and C. Rojas, 2000. Growth metabolic rate, and digestive enzyme activity in the white shrimp Litopenaeus setiferus early postlarvae fed diferent diets. J. Exp. Mar. Biol.. Ecol., 255: 21–36.
FAO (Food and Aquaculture Organization of the United Nation), 2003. Overview on fish production, utilization, consumption and trade based 2001 date. FAO Fisheries Information. Date and Stadistics Unit.
FAO/ WHO., 2001. Report of a joint FAO/WHO expert consultation on evaluation of health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk live lactic acid bacteria. Cordova, Argentina.
Gatesoupe, F. J., 1999. The use of probiotics in aquaculture. Aquaculture, 180: 147–165.
Lemos, D., and A. Rodriguez, 1998. Nutritional effects on body composition, energy content and trypsin activity of Penaeus japonicus during early postlarval development. Aquaculture, 160, 103–116.
Lemos, D., J. M. Ezquerra, and F. L. Garcia-Carreño, 2000. Protein digestion in penaeid shrimp: digestive proteinases, proteinase inhibitors and feed digestibility. Aquaculture, 186: 89–105.
Le Moullac, G., G. B. Klein, D. Sellos, and A. Van Wormhoudt, 1996. Adaptation of trypsin, chymotrypsin and α-amylase to casein level and protein source in Penaeus vannamei (Crustacea, Decapoda). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 208: 107–125.
Le-Vay, L., A. Rodriguez, M. S. Kamarudin, and D. A. Jones, 1993. Influence of live and artificial diets on tissue composition and trypsin activity in Penaeus japonicus larvae. Aquaculture, 118: 287–297.
McIntosh, D., T. M. Samocha, E. R. Jones, A. L. Lawrence, D. A. Mckee, S. Horowitz, and A. Horowitz, 2000. The effect of a commercial bacterial supplement on the high-density culturing of Litopenaeus vannamei with a low protein diet in an outdoor tank system and no water exchange. Aquac. Eng., 21: 215–227.
Moriarty, D. J. W., 1998. Control of luminous Vibrio species in penaid aquaculture ponds. Aquaculture, 164: 351–358.
Moriarty, D. J. W., 1996. Microbial Biotechnology: a key ingredient for sustainable aquaculture. Infofish Int., 4: 29–33.
Nakamura, K., 1987. Classification of diverticular cells of the midgut gland in the praw Penaeus japonicus. Mem. Fac. Fish. Kagoshima Univ., 36: 207–213.
Ochoa-Solano, L. J., and J. Olmos-Soto, 2006. The functional property of Bacillus for shrimps feeds. Food Microbiol., 23: 519–525.
Rengpipat, S., S. Runkpratanporn, S. Piyatiratitivorakul, and P. Menasaveta, 2000. Immunity enhancement on black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) by a probiont bacterium (Bacillus S11). Aquaculture, 1991: 271–288.
Rodriguez, A., L. G. Le Vay Mourente, and D. A. Jones, 1994. Biochemical composition and digestive enzyme activity in larvae and postlarvea of Penaeus japonicus during herbivorous and carnivorous feeding. Mar. Biol., 118: 45–51
Shariff, M., F. M. Yosoff, T. N. Vevaraja, and S. P. Srinivasa Rao, 2001. The effectiveness of a commercial microbial product in poorly prepared tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon (Fabricius), ponds. Aquac. Res., 32: 181–187.
Verschuere, L., G. Rombaut, P. Sorgeloos, and W. Verstraete, 2000. Probiotic bacteria as biological control agents in aquaculture. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev, 64: 655–671.
Vine, N. G., W. D. Leukes, and H. Kaiser, 2006. Probiotics in marine larviculture. FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 30: 404–427.
Ziaei-Nejad, S., 2004. The effect of Bacillus spp. bacteria as a probiotic on growth, survival and digestive enzyme activity of Indian white shrimps, Fenneropenaeus indicus, larvae and post-larvae. Msc thesis. Tehran University, 100pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gómez, R.G.D., Shen, M.A. Influence of probiotics on the growth and digestive enzyme activity of white Pacific shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). J. Ocean Univ. China 7, 215–218 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-008-0215-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-008-0215-x