Abstract
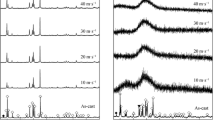
In this work, a comprehensive comparison regarding the impacts of M (M=Cu, Co, Mn) substitution for Ni on the structures and the hydrogen storage kinetics of the nanocrystalline and amorphous Mg20Ni10−x M x (M=Cu, Co, Mn; x=0–4) alloys prepared by melt spinning has been carried out. The analysis of XRD and TEM reveals that the as-spun (M=None, Cu) alloys display an entire nanocrystalline structure, whereas the as-spun (M=Co, Mn) alloys hold a mixed structure of nanocrystalline and amorphous structure when M content x=4, indicating that the substitution of M (M=Co, Mn) for Ni facilitates the glass formation in the Mg2Ni-type alloy. Besides, all the as-spun alloys have a major phase of Mg2Ni but M (M=Co, Mn) substitution brings on the formation of some secondary phases, MgCo2 and Mg phases for M=Co as well as MnNi and Mg phases for M=Mn. Based upon the measurements of the automatic Sieverts apparatus and the automatic galvanostatic system, the impacts engendered by M (M=Cu, Co, Mn) substitution on the gaseous and electrochemical hydrogen storage kinetics of the alloys appear to be evident. The gaseous hydriding kinetics of the alloys first rises and then declines with the growing of M (M=Cu, Co, Mn) content. Particularly, the M (M= Mn) substitution results in a sharp drop in the hydriding kinetics when x=4. The M (M=Cu, Co, Mn) substitution ameliorates the dehydriding kinetics dramatically in the order (M=Co)>(M=Mn)>(M=Cu). The electrochemical kinetics of the alloys visibly grows with M content rising for (M=Cu, Co), while it first increases and then declines for (M=Mn).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
JAIN I P, LAL C, JAIN A. Hydrogen storage in Mg: A most promising material [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 35(10): 5133–5144.
SAKINTUNA B, LAMATI-DARKRIM F, HIRSCHER M. Metal hydride materials for solid hydrogen storage: A review [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32(9): 1121–1140.
EBRAHIMI-PURKANI A, KASHANI-BOZORG S F. Nanocrystalline Mg2Ni-based powders produced by high-energy ball milling and subsequent annealing [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 456(1/2): 211–215.
CHANDRA D, SHARMA A, CHELLAPPA R, CATHEY W N, LYNCH F E, BOWMAN Jr R C, WERMER J R, PAGLIERI S N. Hydriding and structural characteristics of thermally cycled and cold-worked V-0.5 at.%C alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 452(2): 312–324.
SCHLAPBACH L, ZÜTTEL A. Hydrogen-storage materials for mobile applications [J]. Nature, 2001, 414: 353–358.
LASS E A. Hydrogen storage measurements in novel Mg-based nanostructured alloys produced via rapid solidification and devitrification [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(17): 10787–10796.
JEON K J, MOON H R, RUMINSKI A M, JIANG B, KISIELOWSKI C, BARDHAN R, URBAN J J. Air-stable magnesium nanocomposites provide rapid and high-capacity hydrogen storage without using heavy-metal catalysts [J]. Nature Materials, 2011, 10(4): 286–290.
KHRUSSANOVA M, MANDZHUKOVA T, GRIGOROVA E, KHRISTOV M, PESHEV P. Hydriding properties of the nanocomposite 85 wt.%Mg-15 wt.% Mg2Ni0.8Co0.2 obtained by ball milling [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42(10): 3338–3342.
XIE L, SHAO H Y, WANG Y T, LI Y, LI X G. Synthesis and hydrogen storing properties of nanostructured ternary Mg-Ni-Co compounds [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32(12): 1949–1953.
IWAKURA C, INOUE H, NOHARA S, SHIN-YA R, KUROSAKA S, MIYANOHARA K. Effects of surface and bulk modifications on electrochemical and physicochemical characteristics of MgNi alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2002, 330–332: 636–339.
ZHANG Y H, HAN X Y, LI B W, REN H P, DONG X P, WANG X L. Electrochemical characteristics of Mg2−x ZrxNi (x=0–0.6) electrode alloys prepared by mechanical alloying [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 450(1/2): 208–214.
ANIK M. Improvements of the electrochemical hydrogen storage performance of Mg2Ni by the partial replacements of Mg by Al, Ti and Zr [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 486(1/2): 109–114.
FROES F H, SURYANARAYANA C, RUSSELL K, LI C G. Synthesis of intermetallics by mechanical alloying [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 1995, 192–193: 612–623.
SONG M Y, KWON S N, BAE J S, HONG S H. Hydrogen-storage properties of Mg-23.5Ni-(0 and 5)Cu prepared by melt spinning and crystallization heat treatment [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2008, 33(6): 1711–1718.
HUANG L J, LIANG G Y, SUN Z B, ZHOU Y F. Nanocrystallization and hydriding properties of amorphous melt-spun Mg65Cu25Nd10 alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 432(1/2): 172–176.
SPASSOV T, KÖSTER U. Thermal stability and hydriding properties of nanocrystalline melt-spun Mg63Ni30Y7 alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1998, 279(2): 279–286.
HUANG L J, LIANG G Y, SUN Z B, WU D C. Electrode properties of melt-spun Mg-Ni-Nd amorphous alloys [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 160(1): 684–687.
ZHANG Y H, LIU Z C, LI B W, MA Z H, GUO S H, WANG X L. Structure and electrochemical performances of Mg2Ni1−x Mnx (x= 0–0.4) electrode alloys prepared by melt spinning [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 56(1): 427–434.
SIMIČIĆ M V, ZDUJIĆ M, DIMITRIJEVIĆ R, NIKOLIĆ-BUJANOVIĆ L, POPOVIĆ N H. Hydrogen absorption and electrochemical properties of Mg2Ni-type alloys synthesized by mechanical alloying [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 158(1) 730–734.
ZHANG Y H, REN H P, MA Z H, LI X, ZHANG G F, ZHAO D L. Gaseous and electrochemical hydrogen storage kinetics of as-spun nanocrystalline Mg2Ni1−x Cux (x=0–0.4) alloys [J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2011, 25(4): 373–380.
CUI N, LUO J L. Electrochemical study of hydrogen diffusion behavior in Mg2Ni-type hydrogen storage alloy electrodes [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 1999, 24(1): 37–42.
KUMAR L H, VISWANATHAN B, MURTHY S S. Hydrogen absorption by Mg2Ni prepared by polyol reduction [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 461(1–2): 72–76.
ZHAO X Y, DING Y, MA L Q, WANGL Y, YANG M, SHEN X D. Electrochemical properties of MmNi3.8Co0.75Mn0.4Al0.2 hydrogen storage alloy modified with nanocrystalline nickel [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2008, 33(22): 6727–6733.
WU Y, HAN W, ZHOU S X, LOTOTSKY M V, SOLBERG J K, YARTYS V A. Microstructure and hydrogenation behavior of ball-milled and melt-spun Mg-10Ni-2Mm alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 466(1/2): 176–181.
LIANG G X, WANG E D, FANG S S. Hydrogen absorption and desorption characteristics of mechanically milled Mg-35 wt% FeTi1.2 powders [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1995, 223(1): 111–114.
WOO J H, LEE K S. Electrode characteristics of nanostructured Mg2Ni-type alloys prepared by mechanical alloying [J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 1999, 146(3): 819–823.
RATNAKUMAR B V, WITHAM C, BOWMAN R C, Jr, HIGHTOWER A, FULTZ B. Electrochemical studies on LaNi5−x Snx metal hydride alloys [J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 1996, 143(8): 2578–2584.
ZHENG G, POPOV B N, WHITE R E. Electrochemical determination of the diffusion coefficient of hydrogen through an LaNi4.25Al0.75 electrode in alkaline aqueous solution [J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 1995, 142(8): 2695–2698.
KLEPERIS J, WÓJCIK G, CZERWINSKI A, SKOWRONSKI J, KOPCZYK M, BELTOWSKA-BRZEZINSKA M. Electrochemical behavior of metal hydrides [J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2001, 5(4): 229–249.
NOBUHARA K, KASAI H, DINO W A, NAKANISHI H. H2 dissociative adsorption on Mg, Ti, Ni, Pd and La surfaces [J]. Surface Science, 2004, 566–568: 703–707.
KURIYAMA N, SAKAI T, MIYAMURA H, UEHARA I, ISHIKAWA H, IWASAKI T. Electrochemical impedance and deterioration behavior of metal hydride electrodes [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1993, 202: 183–197.
DRENCHEV B, SPASSOV T, RADEV D. Influence of alloying and microstructure on the electrochemical hydriding of TiNi-based ternary alloys [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2007, 38(4): 437–444.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(51161015, 51371094) supported by National Natural Science Foundations of China; Project(2011ZD10) supported by Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Yh., Yang, T., Zhai, Tt. et al. Influences of substituting Ni with M (M=Cu, Co, Mn) on gaseous and electrochemical hydrogen storage kinetics of Mg20Ni10 alloys. J. Cent. South Univ. 21, 1705–1713 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2113-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2113-2