Abstract
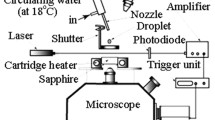
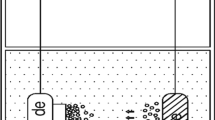
Enhanced boiling experiments of two different enhanced structures were carried out in a thermosyphon loop evaporator chamber. One was micro-columns array structure (MCAS), which was fabricated on copper plate surface with interaction high speed wire electrode discharge machining (HS-WEDM). The other was the ramification of MCAS, named micro-column-array and sintered-copper compound structure (MSCS), which was fabricated with sintered method on micro-column array structure. Considering the wall superheat and critical heat flux (CHF), comparisons were made between them. The results show that both MCAS and MSCS can enhance the boiling heat transfer. It is also found that the enhanced boiling heat transfer ability of MSCS is changed obviously while the porosity of the sintered copper layer is changed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
VASILIEV L L. Micro and miniature heat pipes-electronic component coolers [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2008, 28: 266–273.
CHEN Ping, TANG Yong, LIU Xiao-kang, LIU Xiao-qing. Formation of integral fins function-surface by extrusion-ploughing process [J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2006, 16(5): 1029–1034.
HONDA H, WEI J J. Enhanced boiling heat transfer from electronic components by use of surface microstructures [J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2004, 28: 159–169.
QIU Yun-ren, CHEN Wei-ping, SI Qin. Enhancement of flow boiling heat transfer with surfactant [J]. Journal of Central China University of Technology, 2000, 7(4): 219–222.
NAKAYAMA W, DAIKOKU T, KUWAHARA H, NAKAJIMA T. Dynamic model of enhanced boiling heat transfer on porous surfaces part I: Experimental investigation [J]. J Heat Transfer Trans ASME, 1980, 102(3): 445–450.
MURTHY S S, JOSHI Y K, NAKAYAMA W, JOHNSON W B. Thermal performance of a compact two-phase spreaders with microfabricated boiling enhancement structures [J]. Journal of Enhanced Heat Transfer, 1999, 6: 279–288.
GHIU C D, JOSHI Y K. Visualization study of pool boiling from thin confined enhanced structures [J]. International Journal Heat Mass Transfer, 2005, 48: 4287–4299.
TANG Yong, PAN Min-qiang, LU Long-sheng, LIU Xiao-qing, Performances of electrically heated microgroove vaporizers [J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2007, 17(5): 981–986.
BRANDNER J J, ANURJEW E, BOHN L, HANSJOSTEN E, HENNING T, SCHYGULLA U, WENKA A, SCHUBERT K. Concepts and realization of microstructure heat exchangers for enhanced heat transfer [J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2006, 30: 801–809.
XUAN Yi-min, HONG Yu-ping, LI Qiang. Investigation on transient behaviors of flat plate heat pipes [J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2004, 28: 249–255.
SCOTT G L, MASSOUD K. Pool boiling CHF enhancement by modulated porous layer coating theory and experiment [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2001, 44: 4287–4311.
GHIU C D, JOSHI Y K. Visualization study of pool boiling from thin confined enhanced structures [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2005, 48: 4287–4299.
VEMURI S, KIM K J. Pool boiling of saturated FC-72 on nano-porous surface [J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2005, 32: 27–31.
CHIU L H, WU C H, LEE P Y. Comparison between oxide-reduced and water-atomized copper powders used in making sintered wicks of heat pipe [J]. China Particuology, 2007, 5: 220–224.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(50605023; 50436010) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Y., Lu, Ls., Yuan, D. et al. Micro-column enhanced boiling structure and its ramification. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 15 (Suppl 2), 222–227 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-008-0461-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-008-0461-5